Alkanes – chemical properties
electron configuration and position of coal in the periodic table;
compounds called saturated hydrocarbons;
how to write molecular formula of an alkane with given number of carbon atoms;
how to create a generalized formula of homologous series of alkanes;
how to draw a structural and a semi‑structural formulae of alkanes.
to explain the impact of carbon chain length on the physical properties of alkanes, for example on the state of aggregation;
to plan experiments which will allow you to test properties of alkanes on the example of methane and ethane.
to observe and describe chemical properties (combustion reactions) of alkanes on the example of methane and ethane.
Chemical properties of alkanes
Formulate a research question and hypothesis before watching teacher conducts experiment “Testing of combustibility of gaseous hydrocarbons”. Write down your observations and conclusions. While watching pay attention to the chemical properties exhibited by methane.
Is methane a combustible gas?
Select one of the presented hypotheses, and then verify it.
Methane is a combustible gas. Methane is not a combustible gas.
gas burner,
beaker,
limestone water,
pliers.
Light up the gas burner, use the knob first to set the small and then large air access.
Hold a beaker moistened with limewater over a torch.
Bring the watch glass close to the outlet of the burner, limiting the air supply.
Observe changes.

The complete combustioncomplete combustion can be described with the following equation:
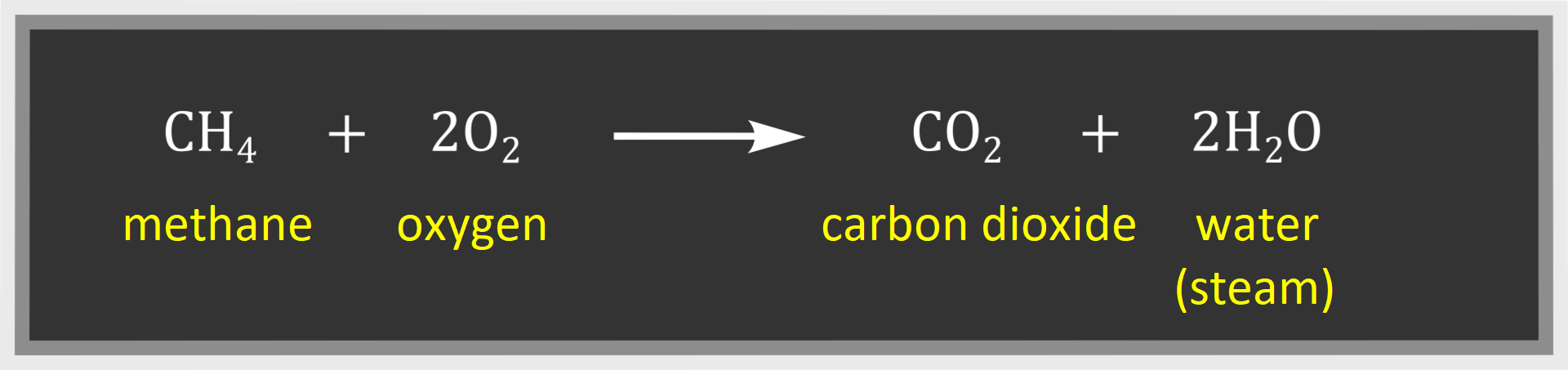
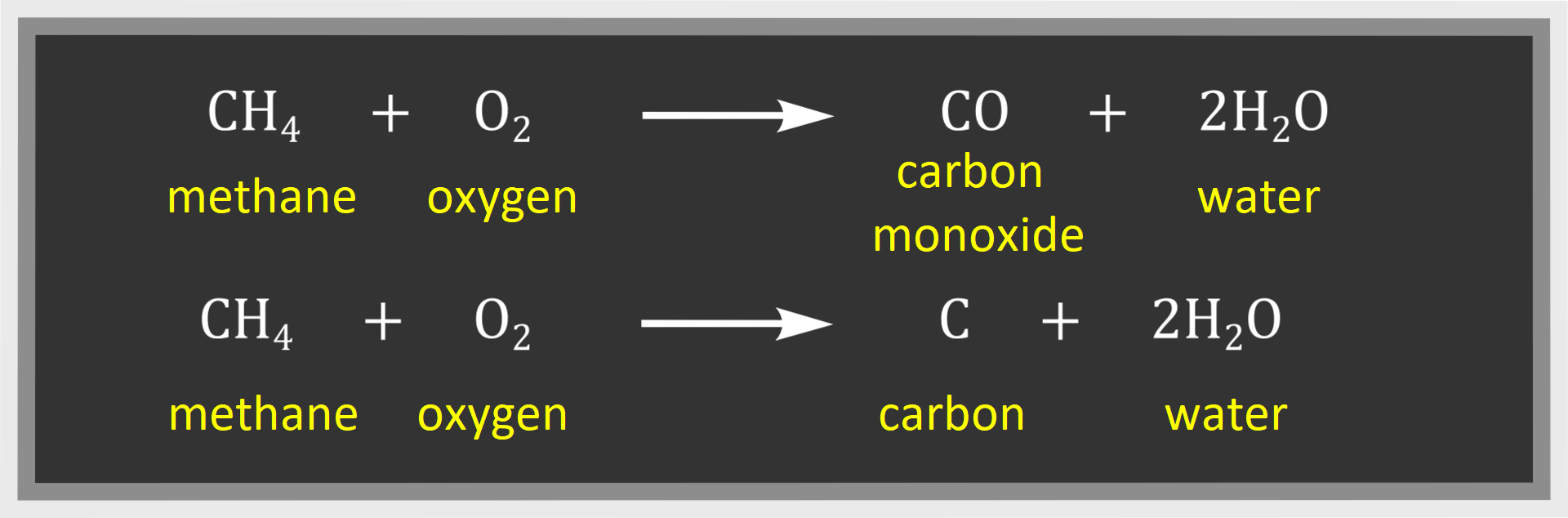
Incomplete combustionIncomplete combustion takes place with limited air access:

Film dostępny na portalu epodreczniki.pl
Nagranie przedstawia uzgadnianie równania reakcji spalania metanu: metan dodać dwie cząsteczki tlenu daje dwutlenek węgla dodać dwie cząsteczki wody, czyli c ha cztery dodać dwa o dwa strzałka w prawo c o dwa dodać dwa ha dwa o.
One of the products of incomplete combustion of methane is carbon monoxide. It is a colourless, odourless gas which attaches to haemoglobin about 300 times faster than oxygen in a human body.
This bond is more durable than oxygen and haemoglobin. Tissues are deprived of adequate oxygen supply, which in many cases leads to death. Immediate blood transfusion is the only thing that may help.

That is why detectors which constantly monitor air for presence of carbon monoxide are installed in rooms at risk of carbon monoxide emission. When certain values of carbon monoxide concentration are exceeded, an appropriate warning is started.
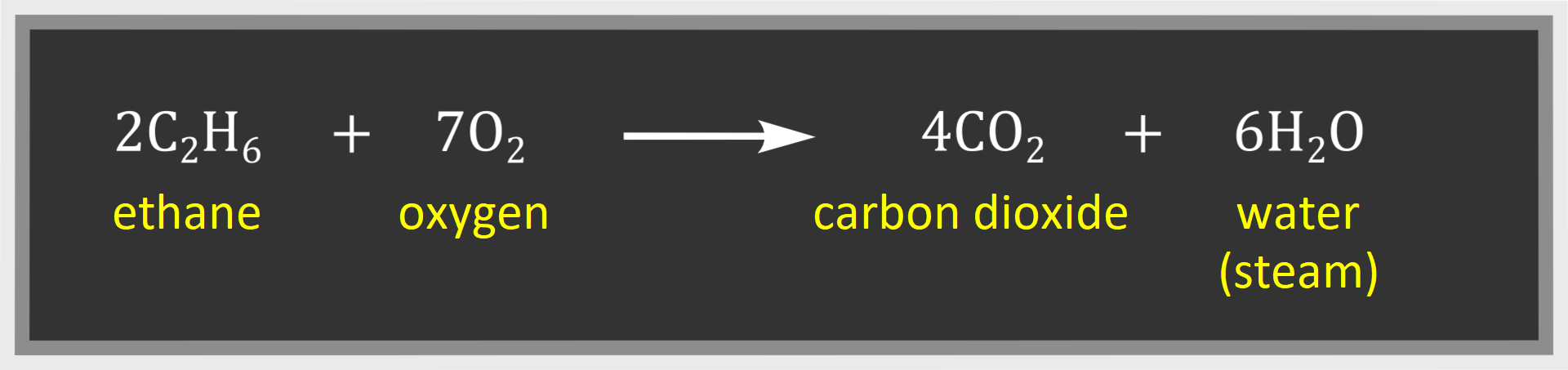
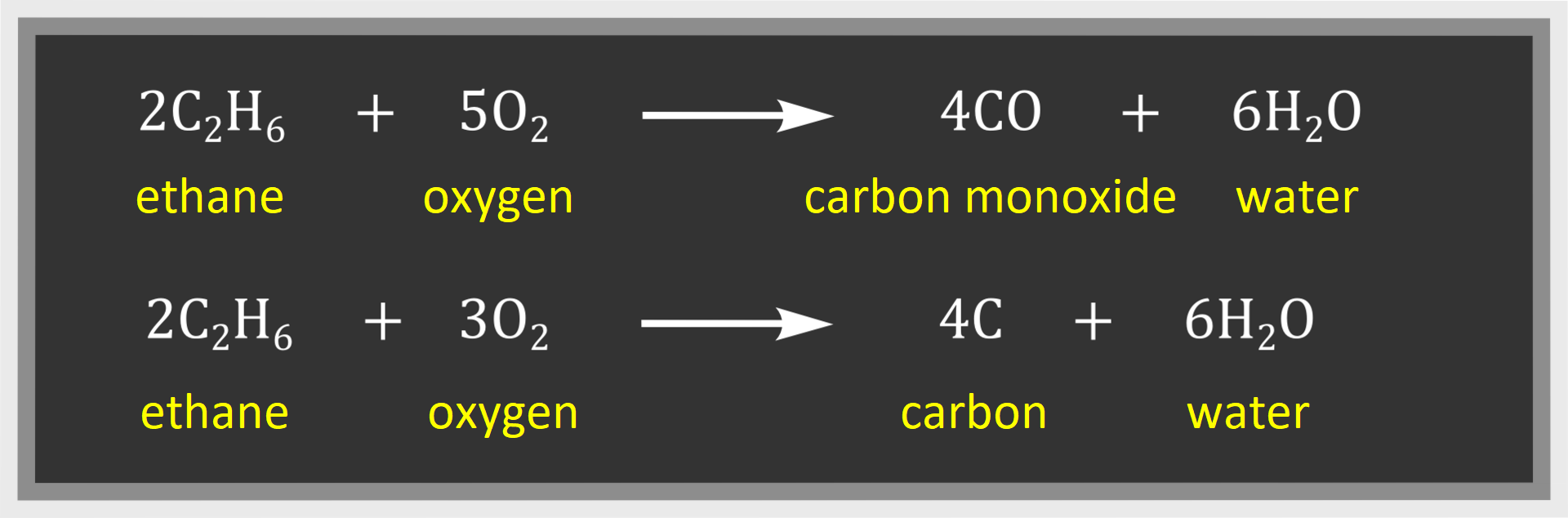
Carbon dioxide and water are the products of complete combustion of other alkanes – as in the case of methane. On the other hand, carbon monoxide and water or carbon and water are products of incomplete combustion.
Thus the following products of complete combustion of ethane may be distinguished:
Incomplete combustion takes place with limited air access:
A mixture of methane and air at a volume concentration of 4.5–15% exhibits explosive properties.

Formation of this mixture when methane passes into closed rooms is often a cause of dangerous explosions, both in residential buildings and mines. In a mixture containing more than 15% of methane, this gas burns with a flame. An explosive mixture will explode, for example, under the influence of fire or an electric spark. That is why if you suspect gas leakage, close its supply and open your windows. Do not fire anything and do not turn electrical appliances on.
Leave your home immediately and notify gas rescue services (phone: 992).
Formulate a research question and hypothesis before watching a video “Testing methane reactivity with bromine water”. After the screening, write down your observations and conclusions.

Film dostępny na portalu epodreczniki.pl
Nagranie filmowe eksperymentu. Badanie, czy metan reaguje z wodą bromową, testing methane activity with bromine water. Mamy dwie probówki: do jednej do jednej trzeciej objętości wlewamy wodę bromową koloru brązowego. W drugiej probówce jest metan. Tam również wlewamy wodę bromową. Zatykamy probówkę korkiem. Wstrząsamy. Woda bromowa nie zmienia koloru.
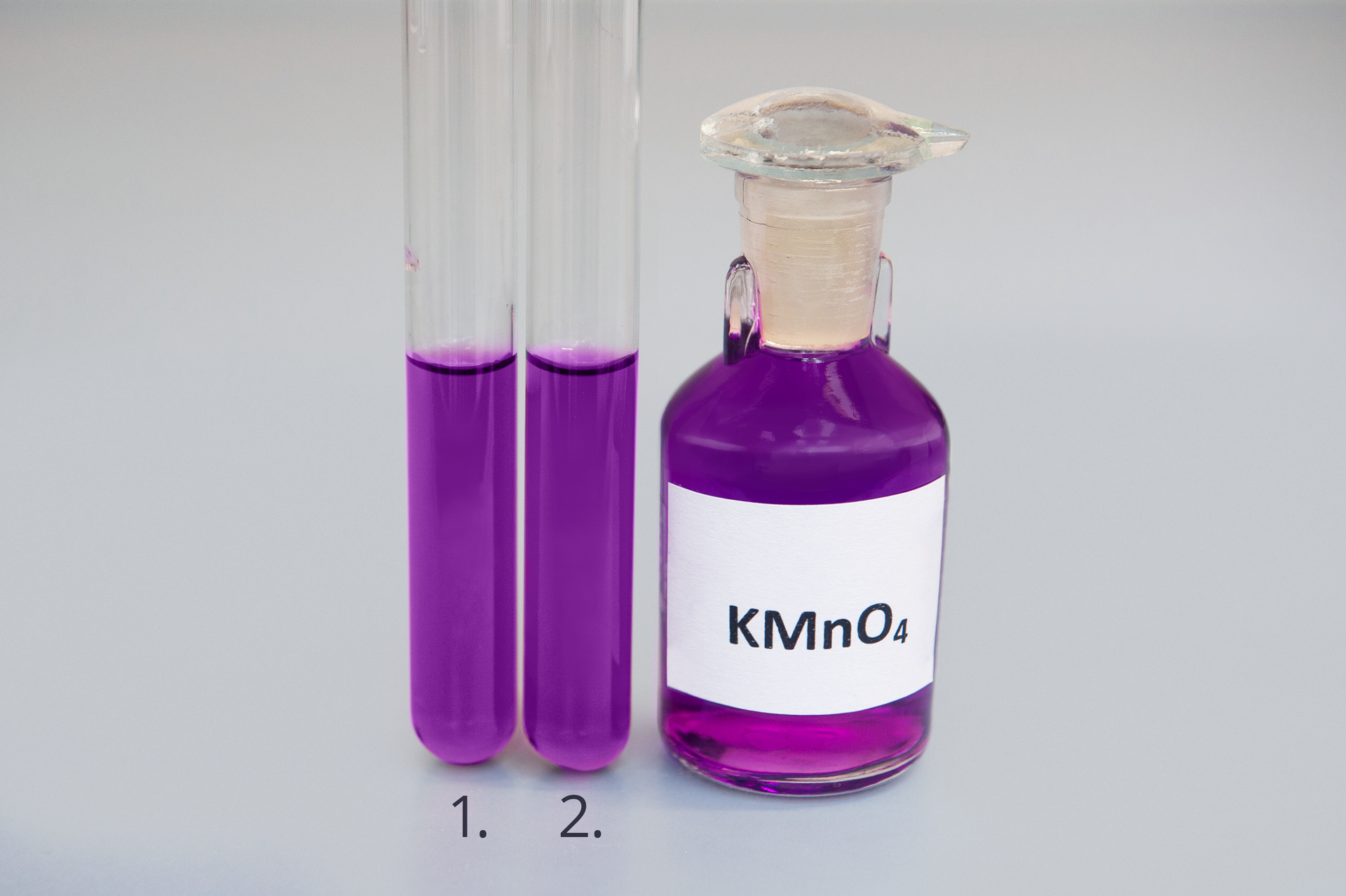
Formulate a research question and hypothesis before conducting experiment “Testing of the reactivity of propane and butane in presence of aqueous solution of potassium permanganate”. Write down your observations and conclusions.
Do propane and butane change the colour of the solution of potassium permanganate?
Select one of the presented hypotheses, and then verify it.
Propane and butane do not change the colour of the solution of potassium permanganate.
Propane and butane change the colour of the solution of potassium permanganate.
2 test tubes,
stopper,
diluted solution of potassium permanganate,
a mixture of propane and butane (for example lighter gas refill).
Fill the first test tube 1/3 with diluted solution of potassium permanganate.
Fill the second test tube with propane and butane mixture. Then pour the same quantity of potassium permanganate solution. Close the test tube with your gloved finger and mix well by shaking.
Observe what is happening.
Compare the contents of both test tubes.

Solve a logogriph and provide definition of your solution.
- The physical properties of saturated depend on length of a carbon chain.
- Capacity of an element or chemical compound to participate in chemical reactions.
- Because of it's harmfull properties at high concentration, people install detectors that monitor air for presence of carbon ...
- Type of combustion with unlimited oxygen access, the products of which are carbon dioxide and water.
| 1 | |||||||||||||
| 2 | |||||||||||||
| 3 | |||||||||||||
| 4 |
Summary
Physical properties of alkanes change if the length of carbon chain is increasing.
Alkanes are compounds that are slightly reactive; they undergo combustion reactions at room temperature.
Propane and butane do not react with potassium permanganate.
Keywords
alkanes, complete combustion, incomplete combustion, reactivity, carbon monoxide
Match the pairs: English words with Polish definition.
proces spalania węglowodorów przy nieograniczonym dostępie powietrza (tlenu); jego produktami są tlenek węgla(IV) i woda, proces spalania węglowodorów przy ograniczonym dostępie powietrza (tlenu); jego produktami są tlenek węgla(II) (czad) oraz woda lub węgiel (sadza) i woda
| complete combustion | |
| incomplete combustion |
Glossary
spalanie całkowite – proces spalania węglowodorów przy nieograniczonym dostępie powietrza (tlenu); jego produktami są tlenek węgla(IV) i woda
spalanie niecałkowite – proces spalania węglowodorów przy ograniczonym dostępie powietrza (tlenu); jego produktami są tlenek węgla(II) (czad) oraz woda lub węgiel (sadza) i woda