Amines
what are structures and properties of selected groups of organic compounds, such as alcohols, carboxylic acids and esters;
what ammonia is;
what are physical and chemical properties of ammonia;
where this compound is used;
how this compound works on the human body and why we should be careful in contact with it.
what are amines;
describe the structure and properties of compounds containing nitrogen – on the example of methylamine (amine);
write down the methylamine and ethylamine formulas;
name application of amines.
Amines
The unpleasant smell of fish is caused by the presence of a compound containing nitrogen atoms in its molecules. This substance is methylaminemethylamine, belonging to the group of aminesamines.
AminesAmines can be treated as derivatives of ammonia, in which at least one hydrogen atom has been replaced with a hydrocarbon group.
Genera formula of amines:
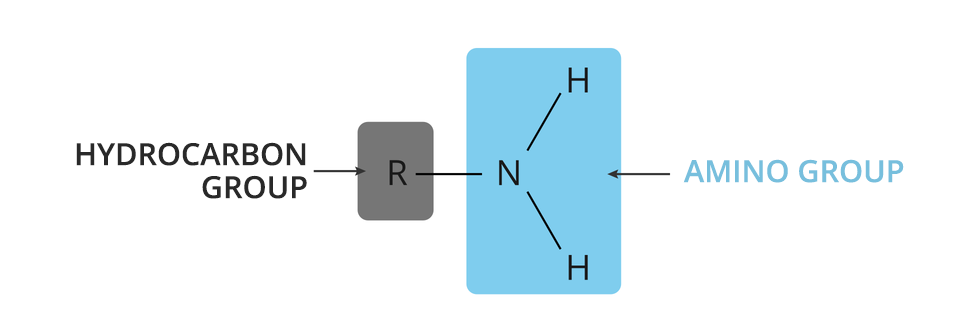
where:
– a hydrocarbon group,
– amino group (functional group).
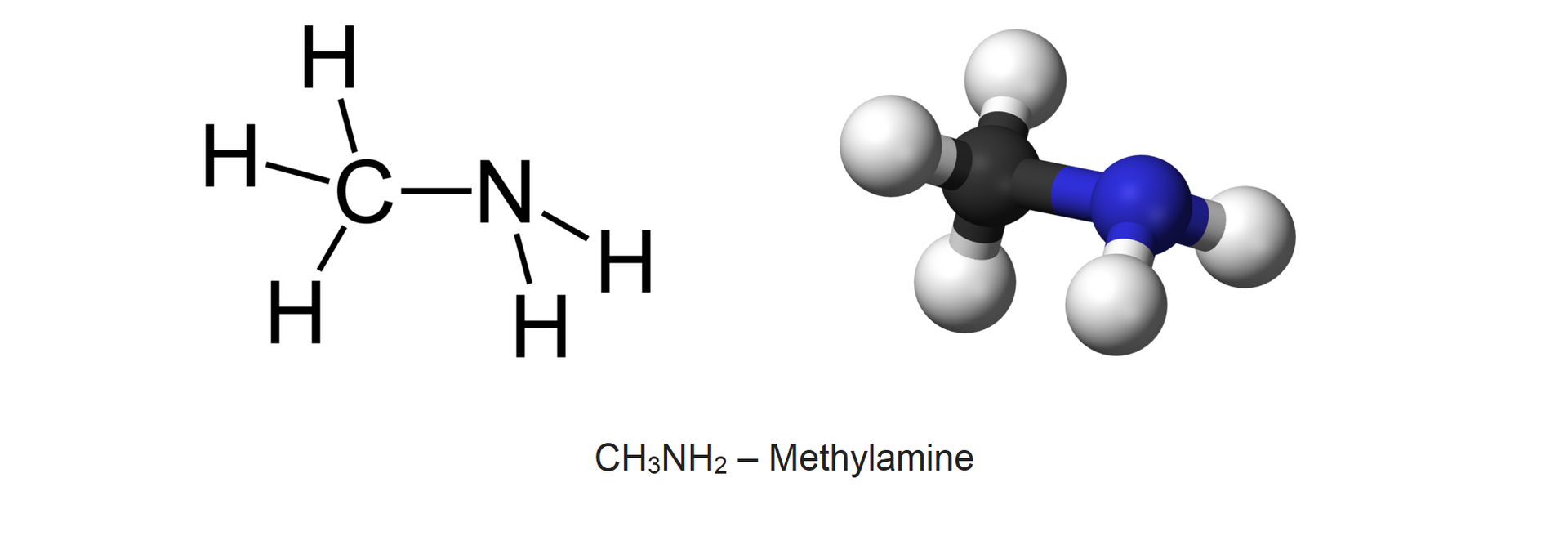
The amine compound is methylamine of the formula .
Watch the „Creating a methylamine formula” animation. Remember how this formula is created.

Film dostępny na portalu epodreczniki.pl
Animacja tworzenia wzoru metyloaminy. Materiał pokazuje, źe zarówno od cząsteczki metanu jak i od cząsteczki amoniaku oderwany zostaje atom wodoru powstałe po odłączeniu atomów wodoru rodniki łącza się ze sobą tworząc aminę.
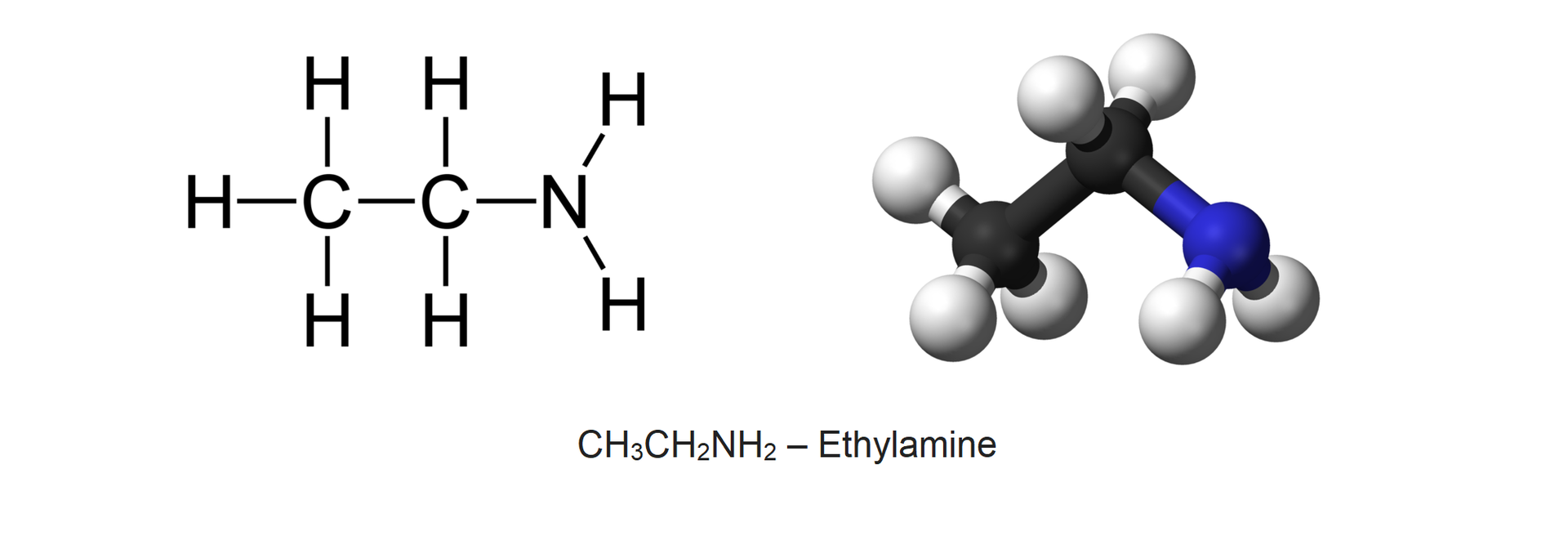
An example of an amine containing two carbon atoms is ethylamine of the formula . Ethylamine is a colourless liquid (at a temperature less than 16.6°C) with sharp, ammonia odour. It is a natural component of the urine.
With the increase in the number of carbon atoms in the molecules of amines, their properties change – the boiling point increases and the solubility in water decreases. Amines are mostly toxic compounds. These occur in small amounts in many plants. These are also secreted during the decomposition of fish. Amines are very important because these are used to receive medicines and also found application in the production of synthetic fibres and dyes.
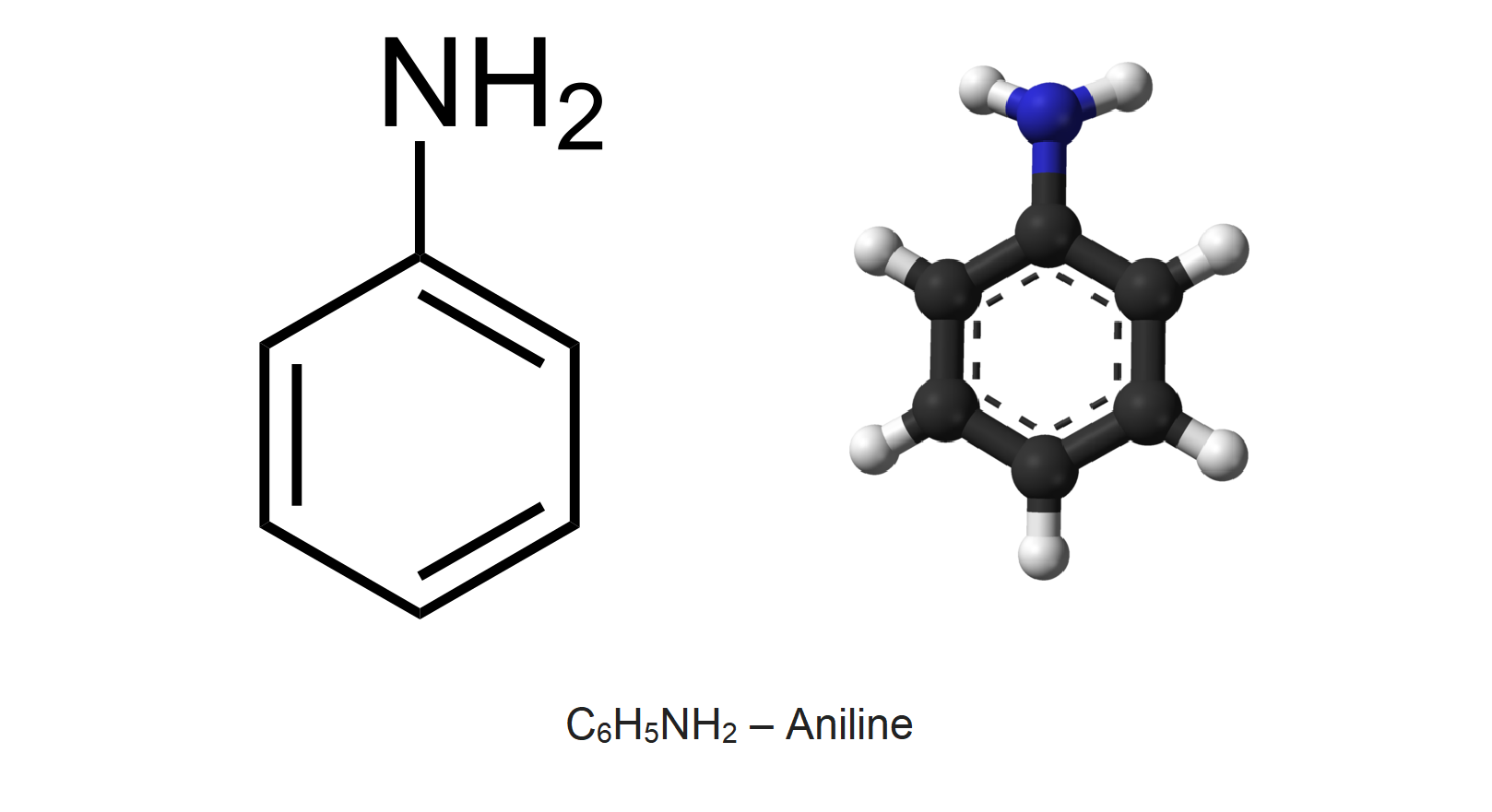
Aniline is the prototypical aromatic amine consisting of a phenyl group attached to an amino group. Its main use is in the manufacture of precursors to polyurethane and other industrial chemicals. Like most volatile amines, it has the odor of rotten fish. It ignites readily, burning with a smoky flame characteristic of aromatic compounds.
Degree of amine substitution is determined in the same way as the degree of carbon atoms. It is equal to the number of hydrogen atoms on the nitrogen atom replaced with carbon atoms. Amines are divided into primary (HIndeks dolny 22NR), secondary (HNRIndeks dolny 22), tertiary (NRIndeks dolny 33). It is also possible to have four organic substituents on the nitrogen. These species are not amines but are quaternary ammonium cations and have a charged nitrogen center. Quaternary ammonium salts exist with many kinds of anions. Amines with high molecular weights, usually tertiary and higher, are also called macromolecular amines.
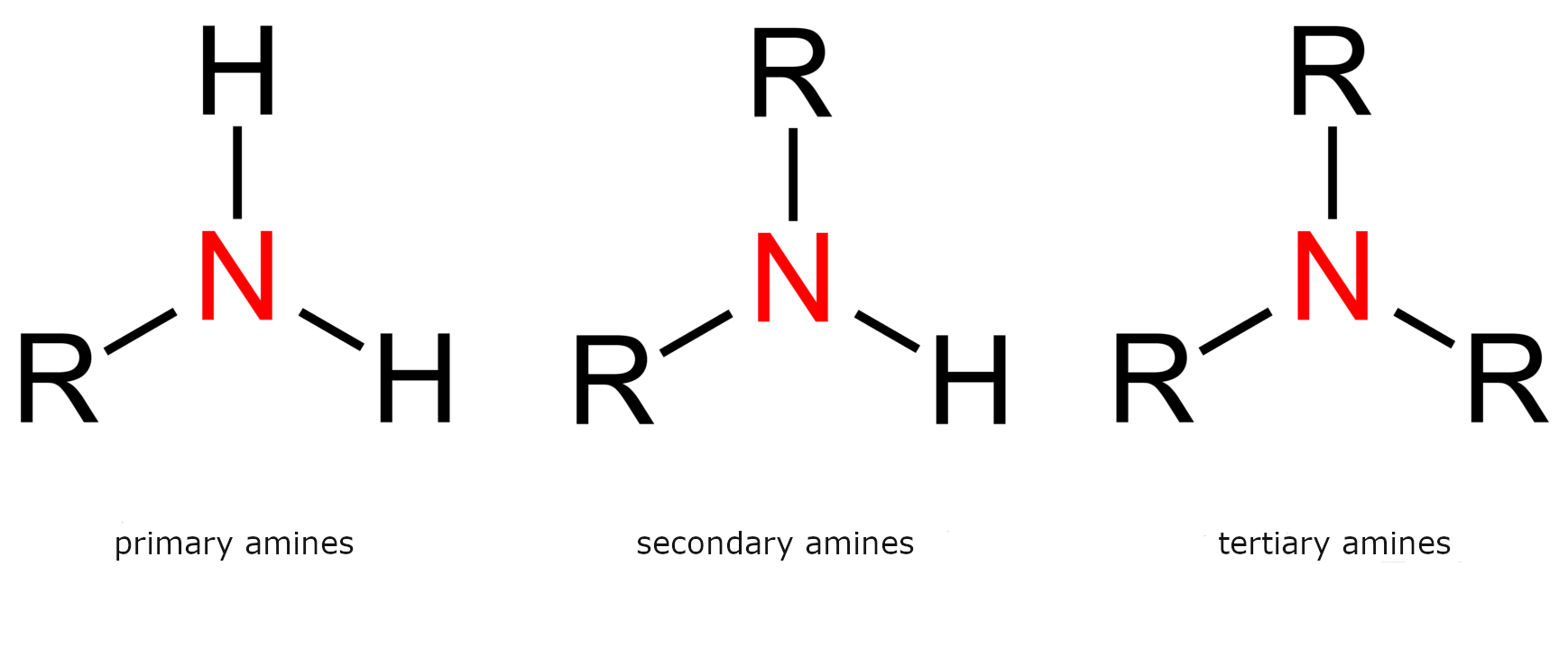
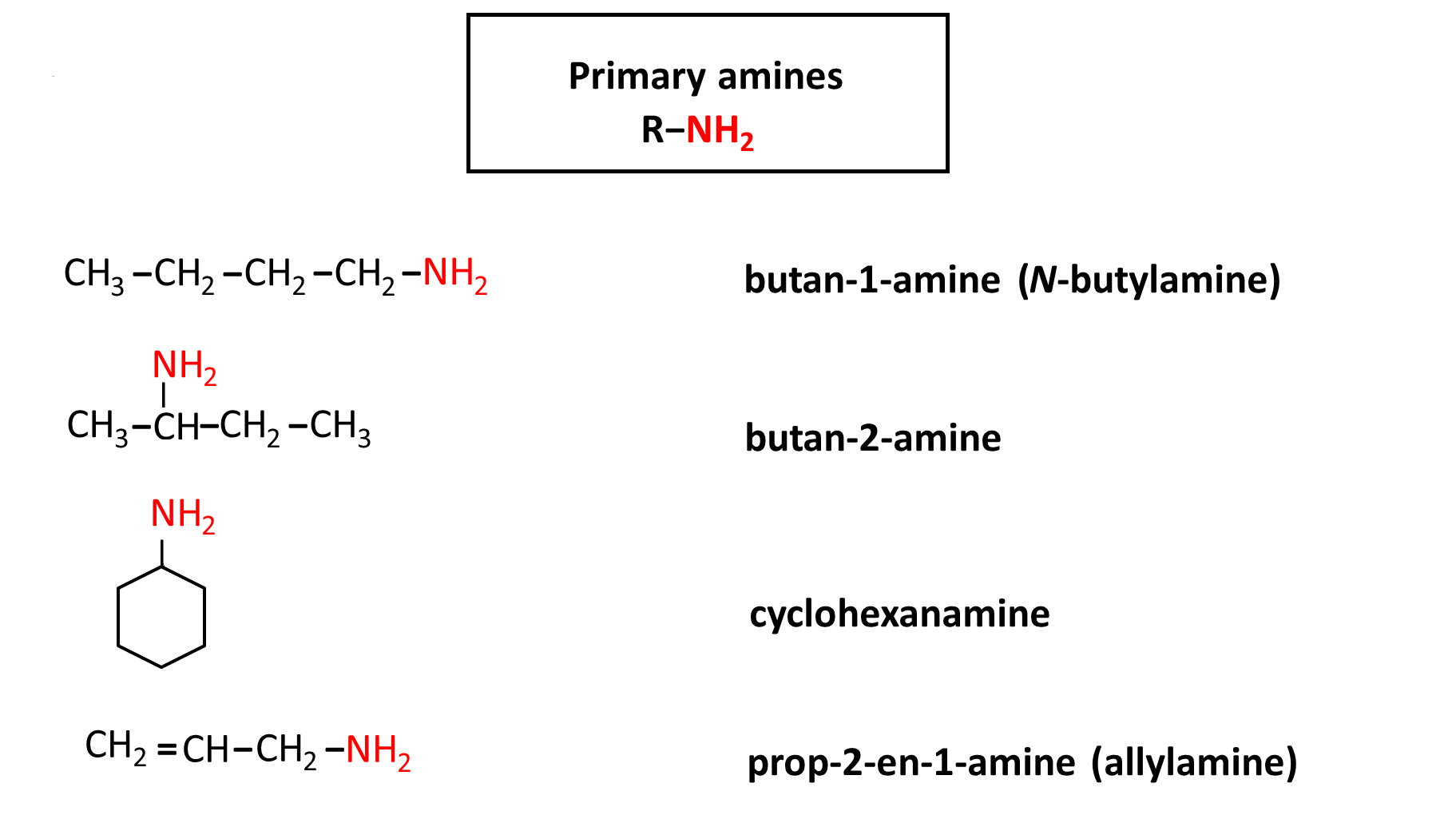
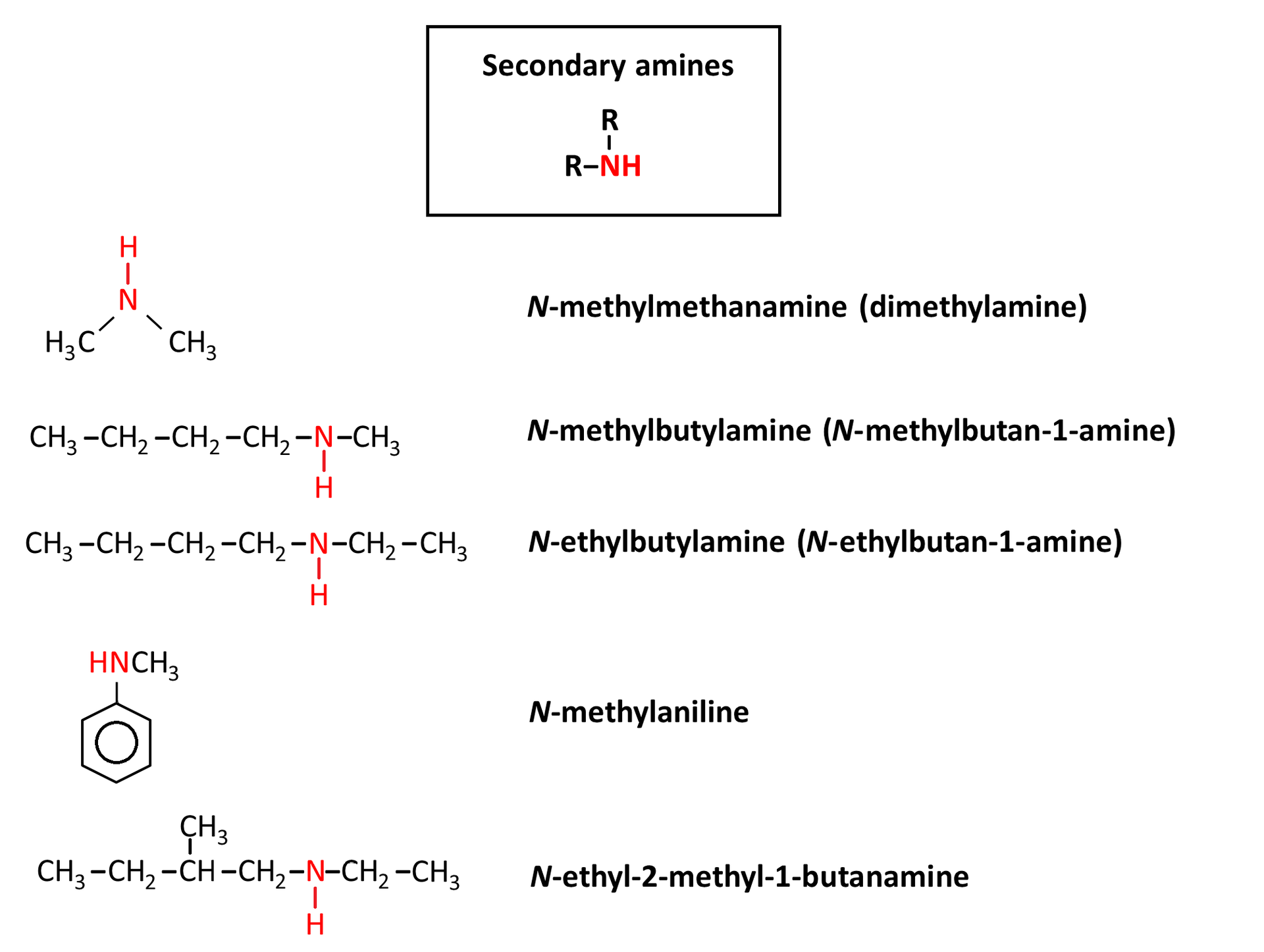
Rules of naming amines
The basic amine naming system is the use of the „amine” core and the names of the hydrocarbon substituents listed alphabetically in the prefix.
In the case of amines containing more amino groups, the name is derived from the parent hydrocarbon and after the linker „o”, the di‑tri‑etc. tip is added.
However, when an amine contains yet another functional group, the presence of an amino group is indicated by the prefix „amino” with the appropriate locant.
Sometimes in the names of secondary and tertiary amines, to avoid ambiguity, the names of the substituents associated with nitrogen are preceded by the inclined letter N.
For aromatic and heterocyclic amines, special names are used instead. See the examples below.
Select true statements.
- Methylamine is a gas with the smell of rotten fish.
- Aqueous solution of methylamine stains the universal paper in red because it is alkaline.
- The alkaline chemical properties of amines result from the presence of a free electron pair on the nitrogen atom.
- There are 6 binding electron pairs in the methylamine molecule.
Create a crossword for your classmate with at least six questions based on this lesson.
Summary
Amines and amino acids are organic compounds containing nitrogen atoms in their molecules.
The properties of amines change with increasing number of carbon atoms in the molecule.
Using the periodic table of elements, determine the properties of the atoms of elements constituting amines - give the numbers:
protons, neutrons, electrons,
valence electrons,
electron shells.
Keywords
Amines, organic compounds, methylamine, ethylamine
Glossary
aminy – do amin zaliczamy związki będące pochodnymi amoniaku, w których cząsteczkach co najmniej jeden atom wodoru zastąpiono grupą węglowodorową; wzór ogólny amin to, gdzieto grupa węglowodorowa, a to grupa aminowa
metyloamina – amina o wzorze; jest gazem o charakterystycznym, nieprzyjemnym zapachu