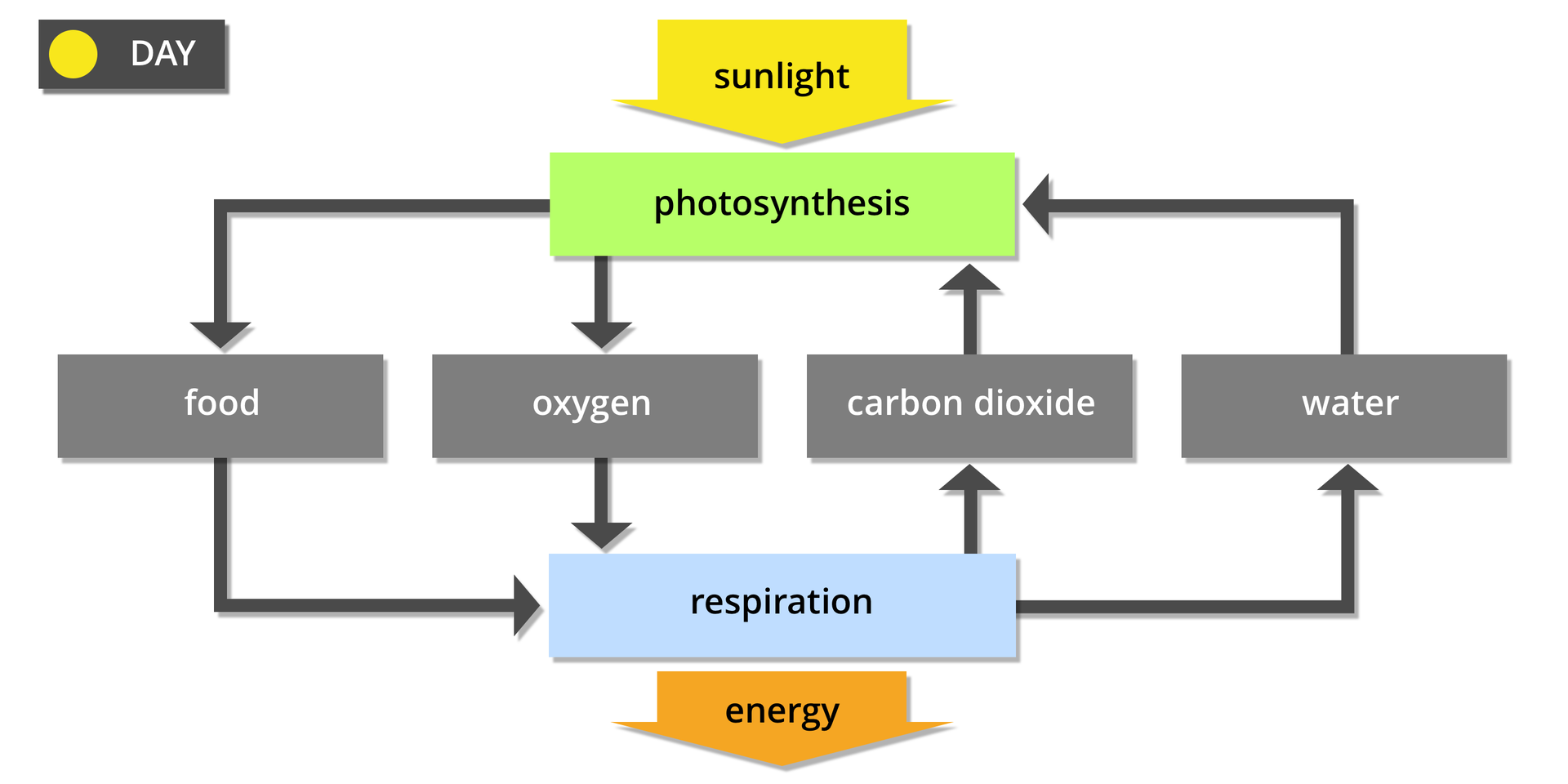
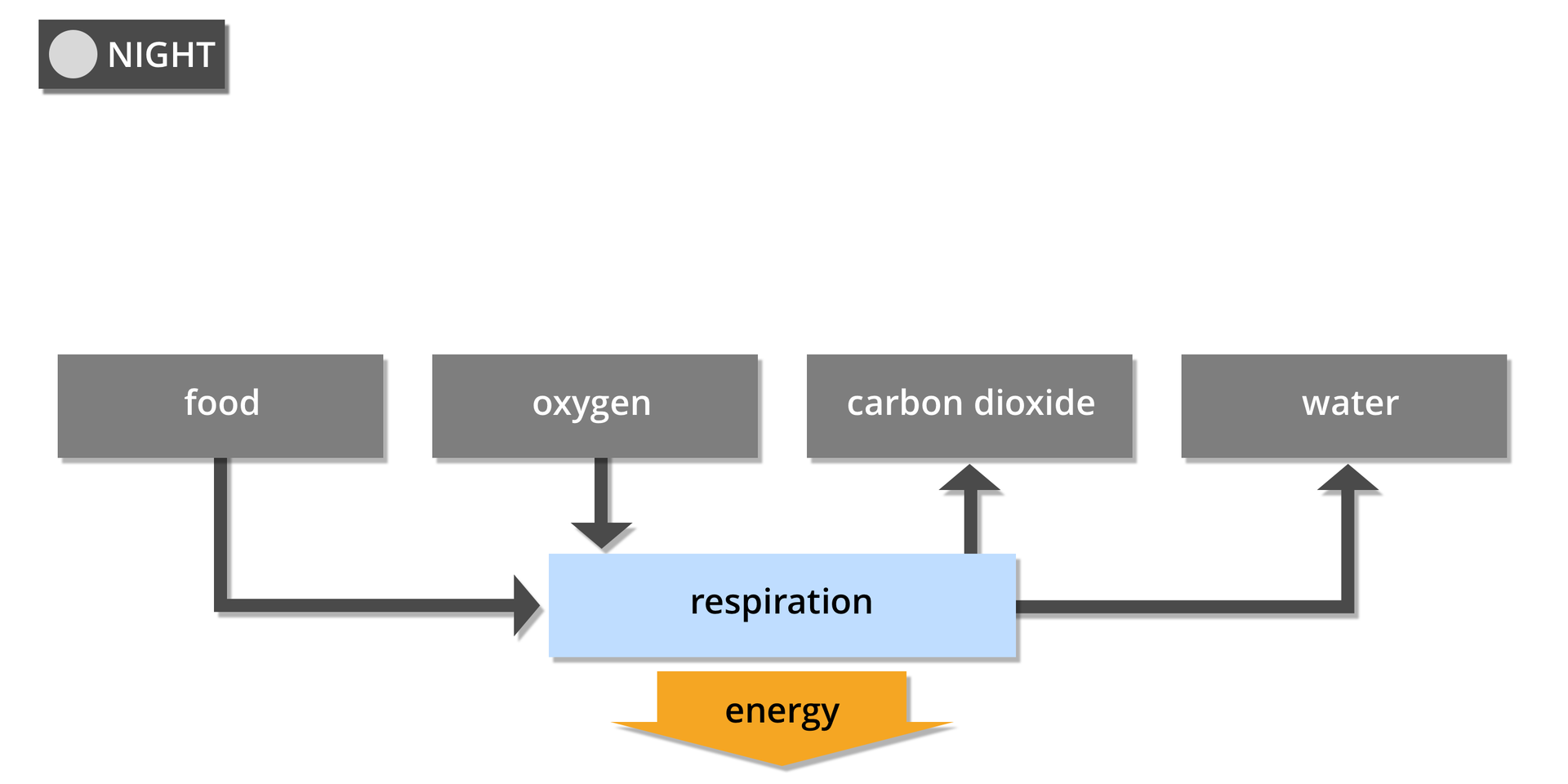
Cellular respiration
during the nutrition process, organisms acquire organic compounds, which are a source of energy for them.
to explain the cellular respiration process;
to specify the conditions of aerobic and anaerobic respiration as well as substrates and products of this process;
to show a correlation between the photosynthesis and respiration processes.
Cellular respiration
Respiration is the process that determines life, because it allows the organism to use the energy contained in the nourishment. All beings need energy to perform their vital functions – thanks to it they can move and nourish, excrete, response to stimuli, conduct biochemical processes in cells, reproduce and grow. Birds and mammals also need energy to maintain a constant body temperature, independent of ambient temperature.
Organic compounds contain chemical energy and are therefore nourishment for the organisms. Release of energy from the nourishment takes place in each living cell and is called cellular respirationcellular respiration. In the cells of eukaryotes, this process takes place in mitochondria – structures whose function can be compared to that of a power plant. They contain enzymes capable of conducting this process.
Sugar – glucose is an organic compound which is an energy source. When there is no glucose in the organism, the reserve substances are broken down. Mainly other sugars and fats, and when these reserves are exhausted, even proteins are broken down. The use of proteins as “fuel” is a result of prolonged hunger and, for example, in animals, it leads to muscle atrophy.
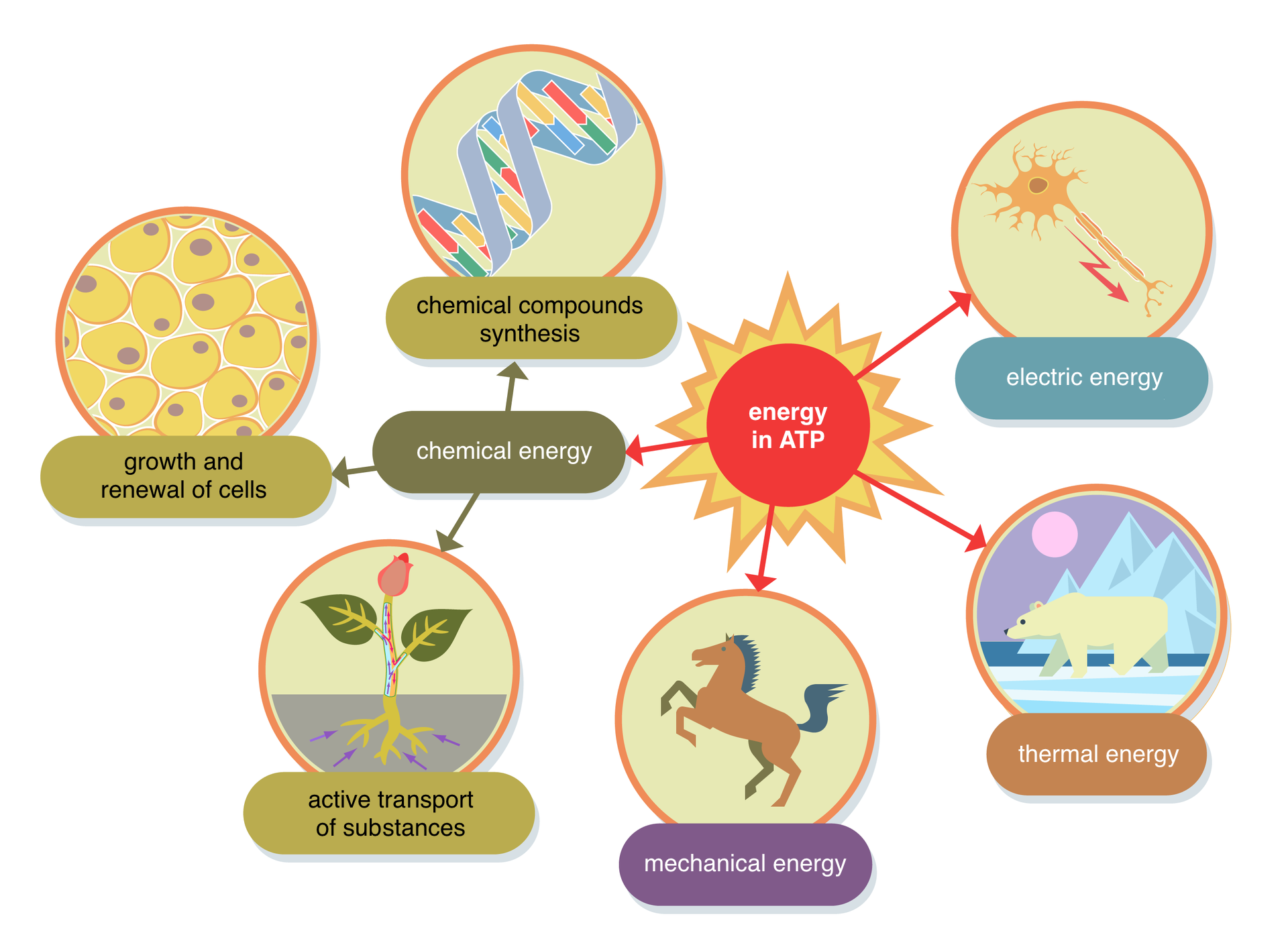
In the respiration process, chemical energy is converted. A significant part of it is dissipated in the form of heat, while the rest is stored in molecules of a chemical compound called ATPATP. It can be transported throughout the cell and then used where there is a demand for energy.
The essence of the respiration process is the release of energy from the nourishment. The chemical energy contained in organic compounds is stored in ATP molecules and gradually converted into other types of energy needed by the cell.
During respiration, sugars and fats are broken down into carbon dioxide and water. As a result of the decomposition of proteins, compounds containing nitrogen – ammonia and urea are additionally produced, and in the ammonia conversion process produced is also uric acid. These products are toxic for animals and must be removed from the organism. Plants do not get rid of nitrogen compounds, because they use them to produce their own amino acids and proteins.
In winter, when it's freezing outside, we blow on our frozen hands to warm them up. What makes the air exhaled from the lungs hotter than the ambient temperature?
Substrates of aerobic respiration | Products of aerobic respiration |
sugar | ATP |
oxygen | carbon dioxide |
water |
Cellular respiration can be compared to burning wood in a fire. Analyse both processes, taking into account:
substrates of both processes,
products.
Anaerobic respiration
Anaerobic respiration is the main source of energy for organisms living in environments with little or no oxygen. This is how some bacteria, fungi and intestinal parasites, sometimes also muscle cells, respire. Anaerobic respiration takes place in the cytoplasm and is called fermentationfermentation. The best known is the alcoholic fermentation carried out by the yeast. As a result of it, sugar is broken down into ethyl alcohol and carbon dioxide, and energy is obtained.

Aerobic respiration | Anaerobic respiration |
decomposition of organic compounds into inorganic compounds | decomposition of organic compounds into simpler organic compounds |
a lot of energy is produced | little energy is produced |
occurs in cytoplasm and mitochondria | occurs in cytoplasm |
Observing the production of carbon dioxide by yeasts.
a small lump of yeast (1/2 teaspoon),
1 tablespoon of sugar,
cool water,
small glass or plastic bottle,
balloon,
mug,
candle.
Dissolve the yeast in a small amount of water with sugar.
Pour the mixture into the bottle and stretch the airless balloon over the neck of the bottle.
Place the experimental set in a warm place.
After about an hour, remove the balloon from the bottle neck and quickly squeeze its contents into the mug.
“Pour” the contents of the mug onto the flame of the candle.
If the yeast undergo fermentation in the bottle, the balloon is filled with gas. This gas is carbon dioxide, which suppress the flame of the candle.
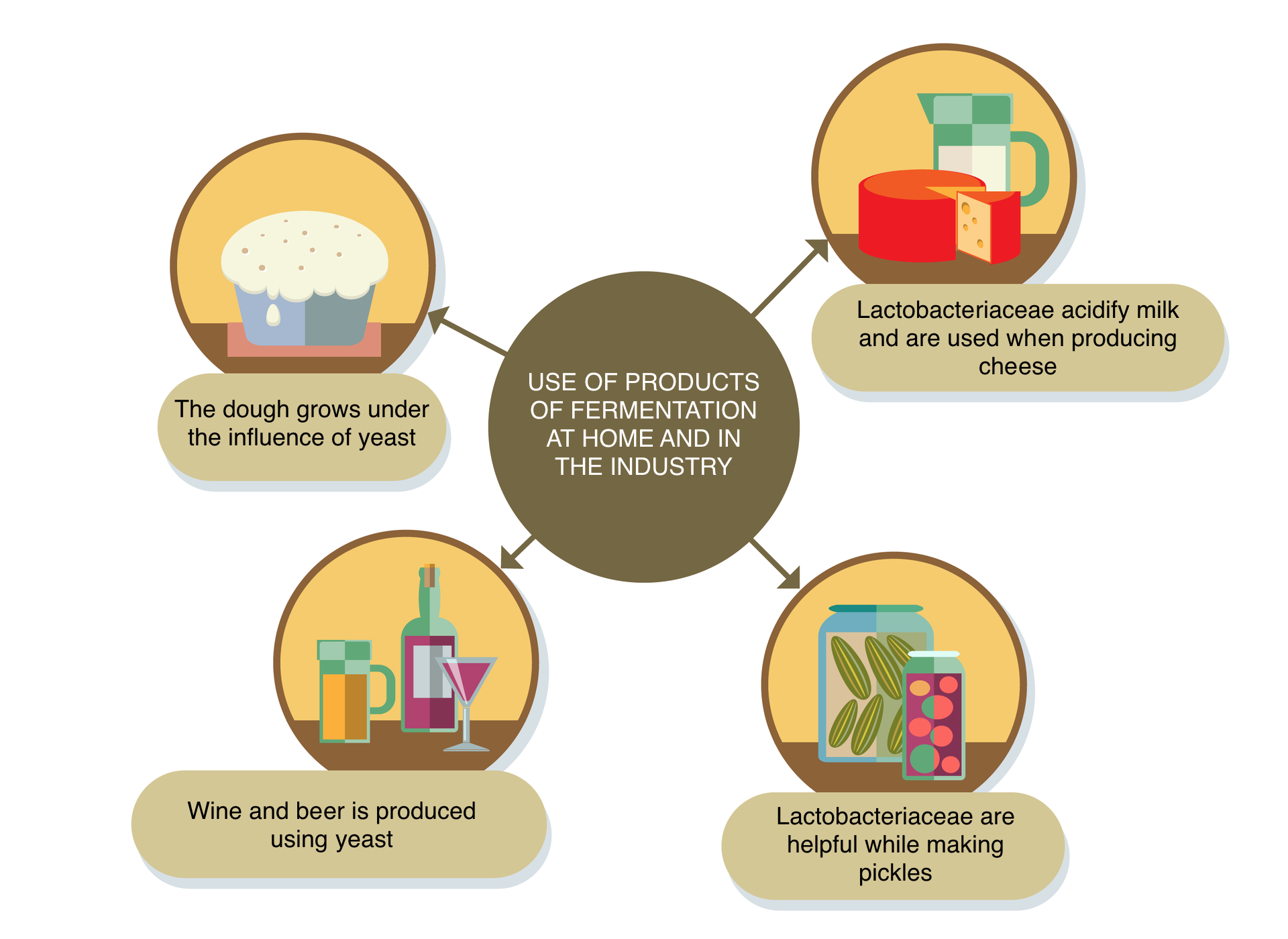
Explain why the yeast dough rises.
Cellular respiration and photosynthesis
Respiration and photosynthesis are interdependent processes. During photosynthesis, plants produce organic compounds and oxygen, which are essential both for them and for heterotrophic organisms to release energy during the respiration process. Products of respiration – carbon dioxide and water – are substrates of the photosynthesis process. Plants respire continuously during the day and at night. During the day, carbon dioxide produced during respiration is used by plants for photosynthesis. However, its amount is not sufficient, so plants additionally take up this gas from the environment. These organisms use only a small proportion of the oxygen produced by photosynthesis to respire, the rest being released into the atmosphere. It is worth knowing that at night, when photosynthesis stops, plants - like other organisms - consume oxygen and produce carbon dioxide.
Specify the likely effects of keeping a large number of potted plants in the bedroom.
What is aerobic respiration?
- Gas exchange takes place in lungs
- It takes place in cells
- It uses oxygen
- It uses carbon dioxide
- It stores energy
- It releases energy
- It produces water
- It produces carbon dioxide
- It takes place in mitochondria
- It takes place in chloroplasts
Conclusion
Aerobic respiration is the process of obtaining energy through the decomposition of sugars and is carried out according to a simplified scheme:

Aerobic respiration is more energy efficient than anaerobic respiration.
Substrates of respiration are products of photosynthesis, and the products of photosynthesis are substrates of the cellular respiration process.
Gas exchange is the process accompanying aerobic respiration.
Anaerobic respiration is a type of cellular respiration that occurs without oxygen; the type of anaerobic respiration is fermentation.
Keywords
cellular respiration, gas exchange, lime water
Glossary
ATP – organiczny związek chemiczny; nośnik energii chemicznej biologicznie użytecznej, który pełni funkcję magazynu energii w procesach fotosyntezy i oddychania komórkowego; zawarta w nim energia jest bezpośrednio wykorzystywana do przeprowadzania procesów życiowych
fermentacja – beztlenowy rozkład cukrów związany z uwalnianiem energii, w którym produktami końcowymi są alkohol (fermentacja alkoholowa) lub kwas mlekowy (fermentacja mlekowa)
oddychanie beztlenowe – rodzaj oddychania komórkowego zachodzący bez udziału tlenu; rodzajem oddychania beztlenowego jest fermentacja
oddychanie komórkowe – ciąg reakcji biochemicznych zachodzących w każdej żywej komórce, polegających na rozkładzie substancji pokarmowych i uwolnieniu zgromadzonej w nich energii
oddychanie tlenowe – rodzaj oddychania komórkowego wymagający obecności tlenu; w jego wyniku powstają dwutlenek węgla i woda