China - the most populous country in the world
that Chinese civilization belongs to the oldest ones in the world;
that China is the most populous country in the world;
that China is a great manufacturer of versatile products which are exported to many countries around the world.
identify the geographic location of the Peoples' Republic of China;
specify the main characteristics of natural environment;
characterize the distribution of population in China;
indicate the directions of economic development and the importance of China in the world economy.
Geographic location of China and main characteristics of natural environment
China lies in East and Central Asia. It is the third largest country in the world by surface area after the Russian Federation and Canada. It has the surface area of 9 million 573 thousand square km, which means it is slightly smaller than Europe and slightly larger than Australia. China occupies 6.4% of the Earth's land area.
People's Republic of China is the official name of today's state which was formed in 1949 after the damaging civil war. It is the most populous country in the world, counting a 1 billion 390 million (data of 2017), which constitutes 18.7% of the total Earth's population.
State | Surface area | Participation in the total |
Russian Federation | 17.1 | 11.5% |
Canada | 10.0 | 6.7% |
People's Republic of China | 9.6 | 6.4% |
United States of America | 9.5 | 6.3% |
Brazil | 8.5 | 5.7% |
Looking at China's hypsometric map you can see a high differentiation of the features of Earth's surface. The huge areas of mountains and highlands are clearly marked in the west and center, while yhe lowlands are in the east. The map shows a significant predominance of mountains and highlands - areas located above 500 meters above sea level take up 75% of the China's territory.
The highest areas include the mountain ranges of the Himalayas and Karakorum in the south‑western part of the country. These are the highest mountains on Earth, the only ones with peaks reaching above 8 thousand meters above sea level. Mount Everest (8850 m above sea level) in the Hymalayas and K2/Czogori (8611 m above sea level) in Karakorum are the two tallest summits in the world. Slightly lower altitudes (5 - 6 thousand m above sea level) are reached by the neighboring vast Tibetan Plateau. The region of Tibet is the highest plateau on Earth and for that reason it is often called the roof of the world. Within the Tibetan Plateau there are latitudinally arranged mountain ranges, which locally exceed the altitude of 7 thousand meters above sea level. – Kunlun with the summit of Muztag (7723 m above sea level).
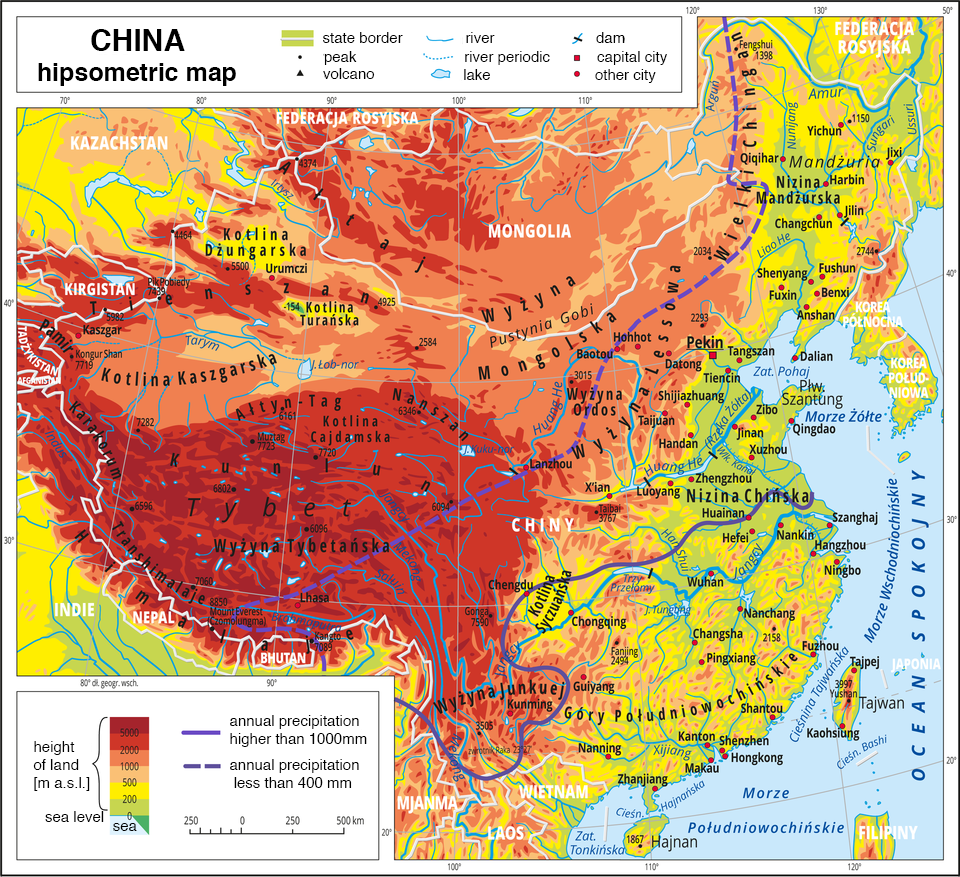
It is in Tibet that the great Chinese rivers flowing eastward – Huang He and Yangtze, as well as other great rivers flowing in the south‑east direction have their springs: Mekong, Irawadi, Brahmaputra.
Large internal valleys spread to the north of Tibet. Two largest include: Kashgar Valley and Dzungarian Valley are separated from each other with another range of high mountains - Tien‑shan. These are arid and semi‑arid areas where deserts and semi‑deserts are found. The rivers that spring in the neighboring mountains end their course in the bottoms of the valleys which do not have the outflow. Tarim is the largest of those.
In the northeastern part of China, adjacent to Tibet are The Mongolian Plateau with Gobi desert and the Loess Plateau being the largest loess area in the world. The thickness of the loess bed reaches 250 m there. It is from the yellow loess dust that the river Huang He takes its name, which means Yellow River.
In the northeast of China there is Manchuria, and to the south of it, in the lower flow of Huang He and Yangtze, known for the development of first civilizations, is the North China Plain.
To the south of Yangtze river there are the South China Mountains which only slightly exceed the altitude of 2 thousand meters above sea level.
Population of China
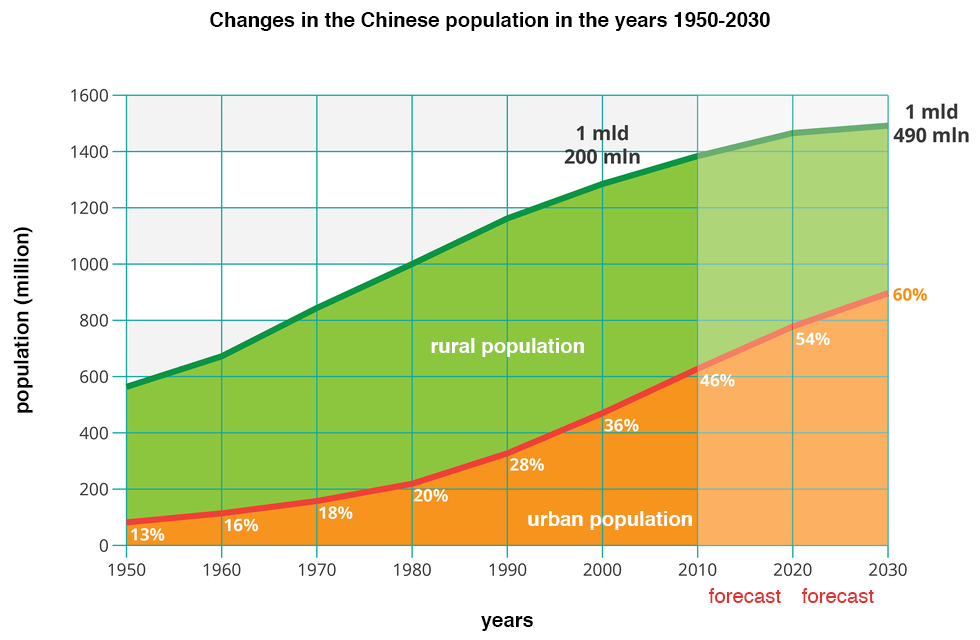
For many years China has been the most populous country in the world. Towards the end of 1930's the population of China reached 500 million. In 1981 China became the first country whose population exceeded 1 billion. Officially its population is now 1 billion 390 million (data of 2017).
The population of China is distributed very unevenly, and the main decisive factor is the differentiation of the natural environment of the country. Up to 95% of Chinese population lives in the eastern part of the country. The highest density of population is present in the North China Plain - on average it amounts to app. 800 people per 1 square kilometer. High density of population is present also in the coastal strip, where it frequently exceeds 200 people per 1 square kilometer. In the central part of China where the mountains and highlands begin, there is a drastic decrease in the density of population in the western direction. The vast areas of Tibet and the arid valleys remain very poorly populated due to difficult terrain and climate conditions.
There has been an increase in the urban population in recent years. Currently there are about 80 cities in China with the population of over 1 million inhabitants. Two of those have more than 15 million inhabitants - they are the so‑called mega cities:
Beijing – 19,5 million, capital city;
Shanghai – 23.0 million, an enormous sea port at the estuary of Yangtze river.
In the remaining 15 cities there are between 5 and 15 million people. Some of them form even more densely populated urban areas with smaller centers. China's great cities are located mainly in the coastal strip, in the Manchuria plain, in the North China Plain and in the valleys of the three great rivers: Huang He, Yangtze and Xijang.
The graph shows changes in population and the growth of urban population in China in years 1980‑2030.
The largest nationalgroup consists of the Chinese of Han nationality who constitute 92% of the total population. There are 55 other nationalities who live in China, 18 of which count more than 1 million people. The most numerous include the Chuang (15.7 million), Manchu (10.1 million) and Tibetan (4.7 million), who had their own independent state in the years 1912–1950.
Is China an economic power? Work on the topics below.
Which Chinese city is this?
- Hong Kong
- Shanghai
- Beijing
- Canton

Definition of Gross Domestic Product is...
- produkt krajowy brutto, w ekonomii, jeden z podstawowych mierników efektów pracy społeczeństwa danego kraju stosowany w rachunkach narodowych. PKB opisuje zaagregowaną wartość dóbr i usług finalnych wytworzonych przez narodowe i zagraniczne czynniki produkcji na terenie danego kraju w określonej jednostce czasu - najczęściej w ciągu roku
- to wartość strumienia produktów finalnych wytworzonych na terytorium danego kraju przez narodowe i zagraniczne czynniki produkcji w danym okresie pomniejszona o wartość amortyzacji w tym okresie.
- miernik całkowitych dochodów osiąganych przez obywateli danego kraju powiększonych o dochody netto z tytułu własności za granicą. Dochody netto są różnicą między dochodami otrzymanymi z tytułu własności za granicą a dochodami wypłacanymi z tytułu własności cudzoziemcom.
Keywords
China, GDP, Tibet, the most populous contry in the world
Glossary
PKB – produkt krajowy brutto (GDP - Gross Domestic Product), w ekonomii, jeden z podstawowych mierników efektów pracy społeczeństwa danego kraju stosowany w rachunkach narodowych. PKB opisuje zaagregowaną wartość dóbr i usług finalnych wytworzonych przez narodowe i zagraniczne czynniki produkcji na terenie danego kraju w określonej jednostce czasu - najczęściej w ciągu roku.