Classification of plant tissues
all organisms are made up of cells;
basic biological processes take place in the cells;
a plant cell has chloroplasts, a cell wall and vacuoles.
to recognise plant tissues;
to discuss the basic functions of individual plant tissues;
to show a relationship between the structure of tissues and their function;
to observe plant tissues under the microscope.
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
Nagranie dźwiękowe dotyczące klasyfikacji tkanek roślinnych
The variety of tissues is the result of the adaptation of plants to the terrestrial environment. Unstable dry land conditions, especially periodical droughts, force the plants to have elements for transporting and storing water. It is also necessary to develop coatings protecting against evaporation. Plants need elements to stiffen their flaccid bodies when they climb up to the light. Tissue formation is therefore a response to environmental factors.
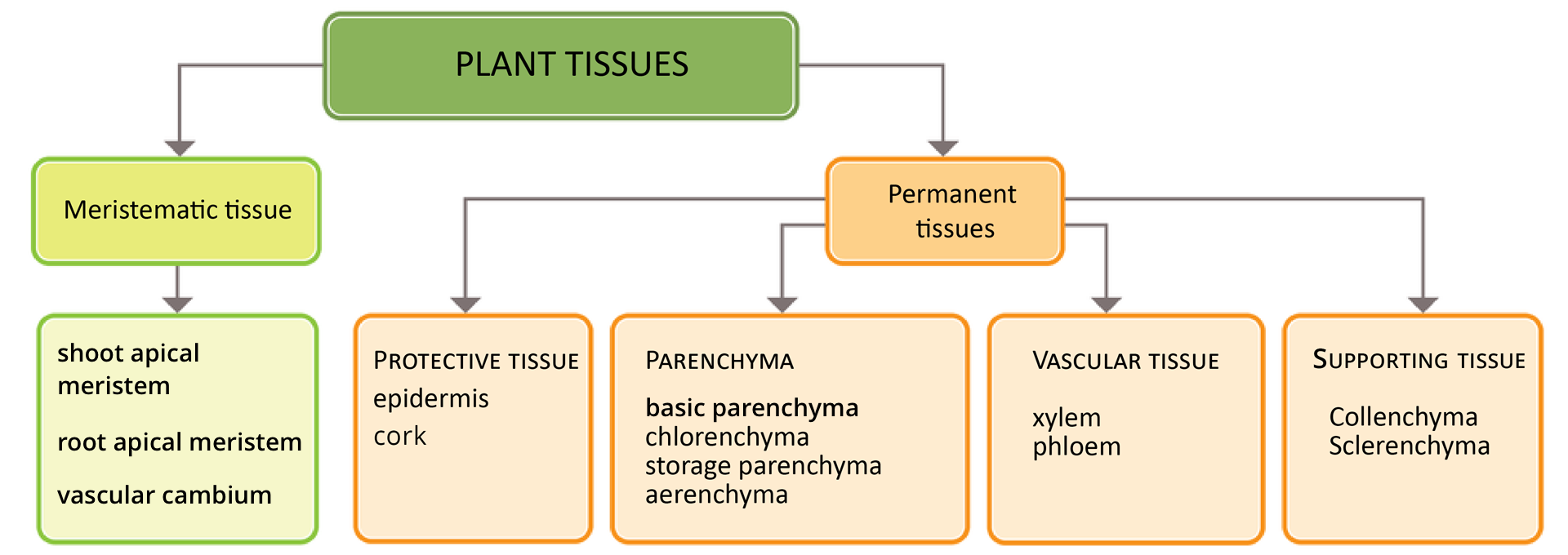
TissueTissue is a group of cells of similar origin and structure that has a specific function in the body. In modern plants, meristematic and permanent tissues are distinguished. Meristematic tissue cells have the ability of continuous divisions. Permanent tissue cells are specialised for a specific function, they do not multiply, they can only grow and have the shape characteristic of a given tissue.
Look at the structure of a plant leaf without using a magnifying glass and microscope. Think about what tissues it is made of. Indicate these parts of the leaf where you expect them to be found.
Assess whether the following sentences are correct.
| True | False | |
| Plant tissue is a collection of cells that perform different functions in a plant. | □ | □ |
| Plant tissue consists of a group of cells with a similar structure. | □ | □ |
| Tissues perform strictly defined functions in the plant. | □ | □ |
| The best way to look at plant tissues is through the microscope. | □ | □ |
Complete the places of occurrence of particular plant tissues.
plant surface, all parts of the plant, mainly long stems, tip of stem and root, leaves and coarse plant organs
Meristematic tissues: responsible for plant growth ............................................................
Vascular tissues: transport water and dissolved in it mineral substances as well as water and dissolved in it nutrients .............................................................
Parenchyma: photosynthesis takes place in them, water and nutrients are collected in them .............................................................
Protective tissues: protect the plant against external factors ............................................................
Mechanical supporting tissues: stiffen the plant and protect it against breakage .............................................................
A set of cells of similar origin and structure that perform certain functions in the body is called:
- a tissue.
- an organ.
- a leaf.
Conclusion
The plant body is filled with tissues, i.e. collections of cells of similar structure specialised for performance of specific functions.
Keywords
plant tissues, types of plant tissues, leaf
Glossary
tkanka – zespół komórek o podobnym pochodzeniu i budowie, pełniących określone funkcje w organizmie