Countries of people’s democracy
how the communists took power in Central and Eastern Europe;
what ‘people’s democracy’ and countries of people’s democracycountries of people’s democracy were;
who the communist leaders of the Eastern Bloc countries were;
when and where social and political riots against the authorities took place;
about the Hungarian Uprising of 1956 and the Prague SpringPrague Spring of 1968, and how these were suppressed.
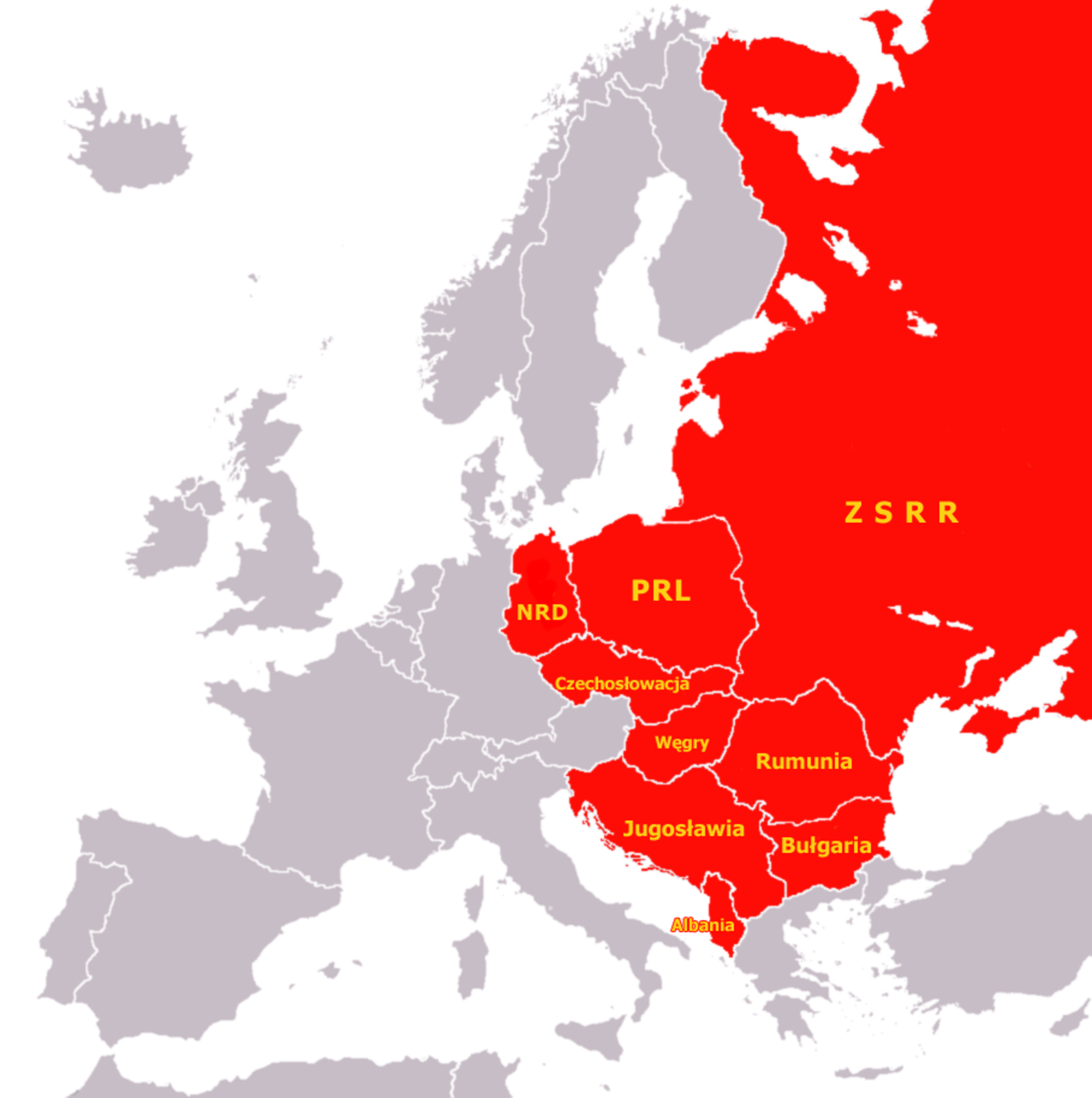
The new division of Europe, after the end of the Second World War, was the result of the arrangements made by the Big Three at inter‑allied conferences. Central and Eastern Europe found itself in the sphere of influence of the Soviet Union. Its representatives, with the help of the Red Army, quickly began to make dependent and transform the countries of the region (Poland, Czechoslovakia, Hungary, Bulgaria, and Romania) – the so‑called people’s democracies. This process was similar in all the countries. It began with the systematic liquidation of political opposition accused of conspiring and preparing for coups (salami tacticssalami tactics), followed by the holding of a fraudulent election, in which the communists gained full power, and then the adoption of a new constitution. In the meantime, the economy would be transformed (nationalizationnationalization of industry, land reform) and all forms of resistance by any kind of opposition – gradually eliminated. Another common feature was the ubiquitous indoctrinationindoctrination of the society, repressionsrepressions against the Church, and the monopoly of the authorities over information. In later years, also the required membership in the structures of CominformCominform (1947) as well as the common economic organization – ComeconComecon (after 1949) and military organization – the Warsaw PactWarsaw Pact (after 1955).
In the Eastern bloc, the only exceptions were Albania and Yugoslavia. Albania, after the communists took full power and succumbed to the will of the USSR, withdrew from the socialist economic and military arrangements in 1961 and became isolated from the world. In Yugoslavia, after Josip Broz Tito, a hero of the communist resistance movement, assumed full power, a conflict with Stalin ensued. Condemned and excluded from the communist structures, the country turned to Western countries, concluding economic agreements with them (the US and UK), which positively influenced its development. However, it remained a socialist state until its disintegration in the 1990s .
Despite the full power and subjugation of the societies of the Eastern bloc, there were many social protests and riots against their difficult economic situations, lack of basic freedoms, and the presence of the Red Army troops. These were brutally suppressed (Berlin 1953, Poland and Hungary 1956, Czechoslovakia 1968).
Match the terms to the definitions.
a systematic process of instilling certain political, religious, or social messages and ideologies in the society, control and restriction of the freedom of speech by verifying and publicizing only information that is consistent with the authorities’ point of view, an order to leave the place of residence against one’s will, unfair punishments imposed by the state on citizens, or persecution in the form of retaliation against a specific group, a political and military alliance formed in 1955 by the Eastern Bloc. The dominant role in it was played by the USSR, the taking over of property, companies, and private capital by the state, an economic system in which decisions concerning production and investments are made by central authorities in the form of economic plans
| Planned economy | |
| Nationalization | |
| Censorship | |
| Repressions | |
| Warsaw Pact | |
| Displacement | |
| Indoctrination |
Find information on the Internet about the current building of the CMEA.

Keywords
Planned economy, nationalization, censorship, repression, Warsaw Pact, displacement, indoctrination
Glossary
Demoludy – potoczne określenie krajów „demokracji ludowej” w bloku wschodnim. Były one podporządkowane ZSRS, a ich ustrój zmieniono na wzór radziecki. Określenie „demokracja ludowa” miało wskazywać na rzeczywistą władzę ludu.
Gospodarka planowana – system gospodarczy, w którym decyzje dotyczące produkcji i inwestycji podejmowane są przez władze centralne w postaci planów gospodarczych. Najczęściej występuje w okresie wojny oraz w krajach socjalistycznych. Jest przeciwieństwem wolnego rynku.
Nacjonalizacja – inaczej upaństwowienie, przejęcie przez państwo majątków, przedsiębiorstw i kapitału prywatnego.
Cenzura – kontrola i ograniczenie wolności słowa polegające na weryfikacji i przekazywaniu tylko zgodnych z punktem widzenia władzy informacji. Występuje najczęściej w krajach niedemokratycznych i w czasie konfliktu zbrojnego.
Represje – niesprawiedliwe kary nakładane przez państwo wobec obywateli lub prześladowania w formie odwetu na jakiejś grupie.
Rada Wzajemnej Pomocy Gospodarczej (RWPG) – międzynarodowa organizacja gospodarcza państw socjalistycznych istniejąca w latach 1949‑1991.
Układ Warszawski – sojusz polityczno‑wojskowy utworzony w 1955 r. przez blok wschodni. Dominującą rolą odgrywał w nim ZSRS. Oficjalnie miał charakter obronny, w rzeczywistością był odpowiedzią na rozszerzenie NATO o RFN i przeciwwagą dla zagrożenia z jego strony Paktu. Istniał do 1991 r.
Wysiedlenie – przymusowy nakaz opuszczenia miejsca zamieszkania. Często jest związany ze zmianami granic w wyników konfliktów.
Taktyka salami – potoczne określenie stopniowego eliminowania przedstawicieli partii opozycyjnych do komunistów oraz przejmowanie przez nich władzy. Odnosiła się do krajów demokracji ludowej.
Kominform – Biuro Informacyjne Partii Komunistycznych i Robotniczych; utworzone w 1947 r. w Szklarskiej Porębie celem „koordynowania walki z imperializmem” oraz wymiany doświadczeń między partiami komunistycznymi oraz wzajemna pomoc krajom demokracji ludowej.
Indoktrynacja – systematyczny proces wpajania społeczeństwu określonych treści i ideologii politycznych, religijnych lub społecznych. Wykorzystywano w tym celu propagandę w środkach masowego przekazu i systemie nauki szkolnej.
Praska Wiosna – okres politycznego odprężenia i liberalizacji w 1968 r. stłumiono przez inwazję wojsk Układu Warszawskiego.