Cultural circles of the world
where and why the oldest civilisations came into existence;
that there are regions with different levels of development on every continent;
that social factors have an important influence on countries' development.
to describe what culture circles are, and what their place in the world is;
to name the criteria which allowed world culture circles to be distinguished;
to explain what the limitations of generalisations are;
to explain how cultural traits influence social and economic development.
What is a culture circle?
It is very difficult to give the concept of culture a precise description. In the simplest terms, it is a way of life. A person, when making a decision or a choice, whether they want to or not, is doing it under the influence of the culture in which they grew up. Language, religion, traditions, customs, eating habits, available technology – they all affect the way we perceive the world; as an enemy which must be avoided, or a friend who is worth getting to know. Language gives us the means to describe it – the Sami from northern Scandinavia have over 180 names for snow and ice.
For believers, religion is the most important priority in life. Customs, which often result from religion, define the relations between people and social norms, the way a person dresses or which products are acceptable to eat. Culture influences our perception of time as well as non‑verbal communication.
Find a different definition of culture to the one given above and decide which definition describes the culture best.
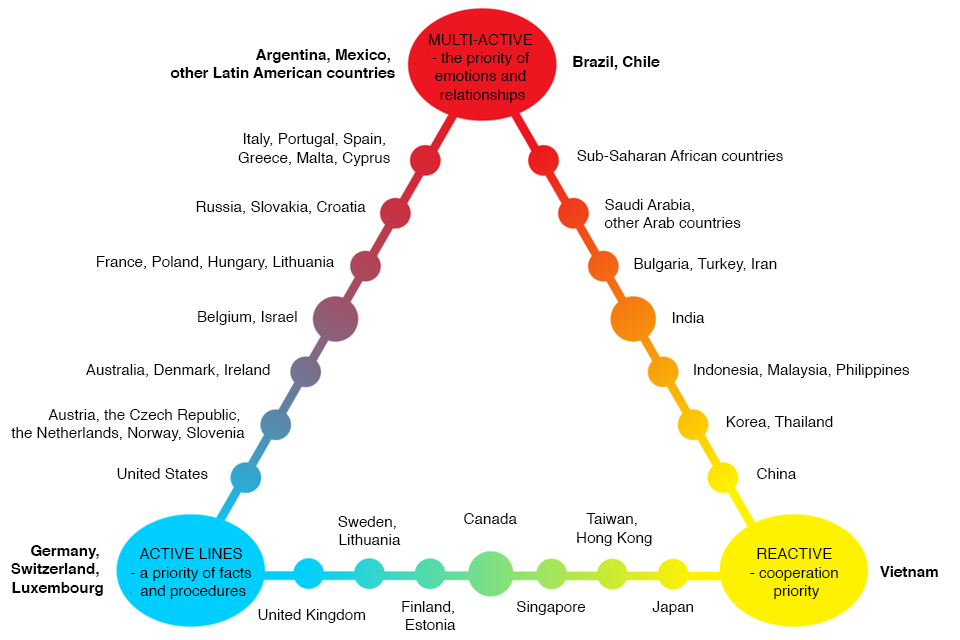
Richard D. Lewis divided cultures into 3 groups
The first of them concentrates on facts and procedures, and respects time.
The second values dialogue, interpersonal relations and emotions.
The third is oriented towards listening and seeking compromises.
Of course, there are intermediate states between these extremes.
Culture (civilisation) circles according to Huntington
Samuel Huntington's theory of culture circles (civilisations)(civilisations), which was propagated in his book The Clash of the Civilisations, was significantly more popular.
Western civilisation is characterised by high individual freedom, freedom of expression and the rule of law, as a consequence there is a high intensivity of experimentation, innovation and entrepreneurship. In Latin American civilisation, which is derived from European civilisation, Indian cultures play a certain role.
Orthodox civilisation, which originates from Byzantium, is characterised by a greater centralisation of governments and an extensive bureaucracy.
Contemporary African civilisation is greatly influenced by the European civilisation. Colonial powers left their language, legal system and religion. Very strong family and tribal ties still affect the ways in which the countries are governed.
According to Huntington, Islamic civilisation is the reverse of European civilisation by, for example, limiting religious, economic and personal freedom. There is no separation between religious and secular spheres.
Chinese civilisation, as well as Japanese civilisation which originates from it, are characterised by weak religious foundations, however, they have a highly developed hierarchy, traditionalism and collectivity of action – they prioritise the good of society over individualism. Hence China, Japan and South Korea's economic success, as well as that of Chinese and Vietnamese societies all over the world. To representatives of this culture circle, shared work is a matter of course as is loyalty to a group or company. Long‑term goals are important to them and not instant success, which is why they make a long‑lasting effort and plans for years ahead. However, a reluctance to stand out, at least by expressing individual opinions, limits innovation.
In Hindu tradition the general good has more importance than individuals. This culture is characterised by a society strongly divided into castes, which causes great social inequalities and very limited opportunities to reduce them. Attempts at economic advance undermine the religiously sanctioned world order.
Buddhist civilisation is based on striving for nirvana by limiting needs, meditation and self improvement. It opposes western consumerism, for example.
Huntington's model has been criticised for not taking the internal diversity of culture circles into account, as well as establishing strict borders instead of transition zones.
Match the civilisations to their traits.
The Spanish and Portuguese languages, and Christianity dominate; Religion is a combination of the beliefs of the indigenous people, African slaves and catholics., Its foundation is Christianity; The most important values are individual freedom, respect for human dignity and considerable tolerance towards other cultures., Respect for authority; An exeptional work ethic; The karoshi phenomenon occurs - death from overwork., Officially recognised poligamy; Women remain in men's shadow; Women must be strictly obedient to their husbands., There is a considerable influence from Confucianism, in which the ruler cares for his subjects and they in turn are completely obedient to him; Discipline and the ability to make sacrifices.
| Western | |
| Japanese | |
| Chinese | |
| Latin American | |
| Islamic |
Add a civilization circle to each country.
| Australia | Western |
| Spain | Western |
| Poland | Western |
| Canada | Western |
| Libya | Islamic |
| Tunisia | Islamic |
| The United Arab Emirates | Islamic |
| Oman | Islamic |
| Iraq | Islamic |
| Kazakhstan | Islamic |
| Afganistan | Islamic |
| Brazil | Latin American |
| Mexico | Latin American |
| Venezuela | Latin American |
| Peru | Latin American |
| Russia | Orthodox |
| Serbia | Orthodox |
| Romania | Orthodox |
| Zimbabwe | African |
| Tanzania | African |
| Namibia | African |
| India | Hindu |
| Mongolia | Buddhist |

Choose which civilisation Thailand belongs to.
- Chinese
- Hindu
- Buddhist
- Islamic
Choose two countries from one of the culture circles and identify their cultural similarities and differences.
Summary
Culture is a society's material and spiritual wealth which is accumulated through the centuries and determines its people's way of life.
Culture is made up of, among others, historical memory, language, customs, traditions, cuisine, music, attire and technology.
World cultures are higly diverse; culture circles (civilisations) are distinguished on the basis of common or similar traits.
Cultural diversity influences contemporary economic and social life.
Keywords
culture circle, Lewis' cultural model,
Glossary
cywilizacja - w etnologii termin oznaczający obszar występowania jednego lub więcej cech lub elementów kulturowych, niekoniecznie ze sobą powiązanych.
fuzja kulturowa - proces przenikania elementów między co najmniej dwiema kulturami, lub wewnątrz kulturowo zróżnicowanego społeczeństwa, poprzez kontakty członków kultury dawców i kultury odbiorców. Uwarunkowane m.in. rozwojem komunikacji: transportu, łączności satelitarnej oraz Internetu i turystyki oraz nasilaniem się procesów integracyjnych a także zacieśnianiem współpracy międzynarodowej.