Europe at the height of power. Colonial conquests
to list the causes of colonialism;
to point out on the map the colonial empires of the 19th century;
to characterize the differences in the colonisation of Asia and Africa in the 19th century.
The industrial revolution has given a new face to European colonial expansion. The rapid economic development of Europe forced Europeans to look for new markets and opportunities to invest capital. ColoniesColonies were also seen as a source of cheap raw material. The most fierce competition took place in Africa and Asia. In Africa, the colonies were founded by: the British, the French, the Belgians, the Germans, the Italians and the Portuguese. In Asia, Great Britain dominated India, while the French occupied Indochina. Also Russia conquered numerous Asian areas. The weakened China has been divided into spheres of influence between many countries. Competition for colonial and subsequent conquests led to armed conflicts between the states and the native population of the colonies.
Familiarize yourself with the definition of the term colonialism. Remember what are, in your opinion, its most important elements.
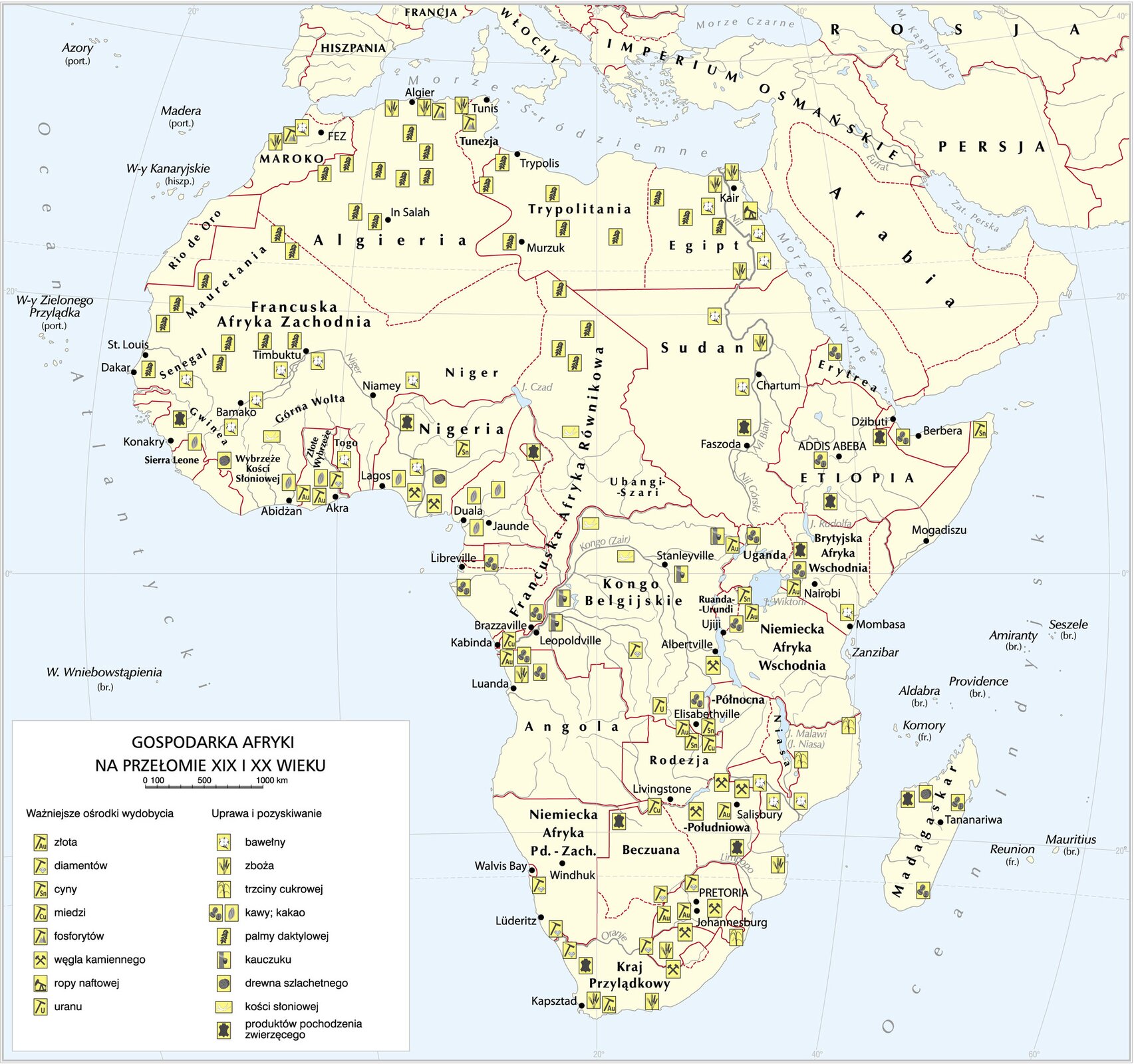
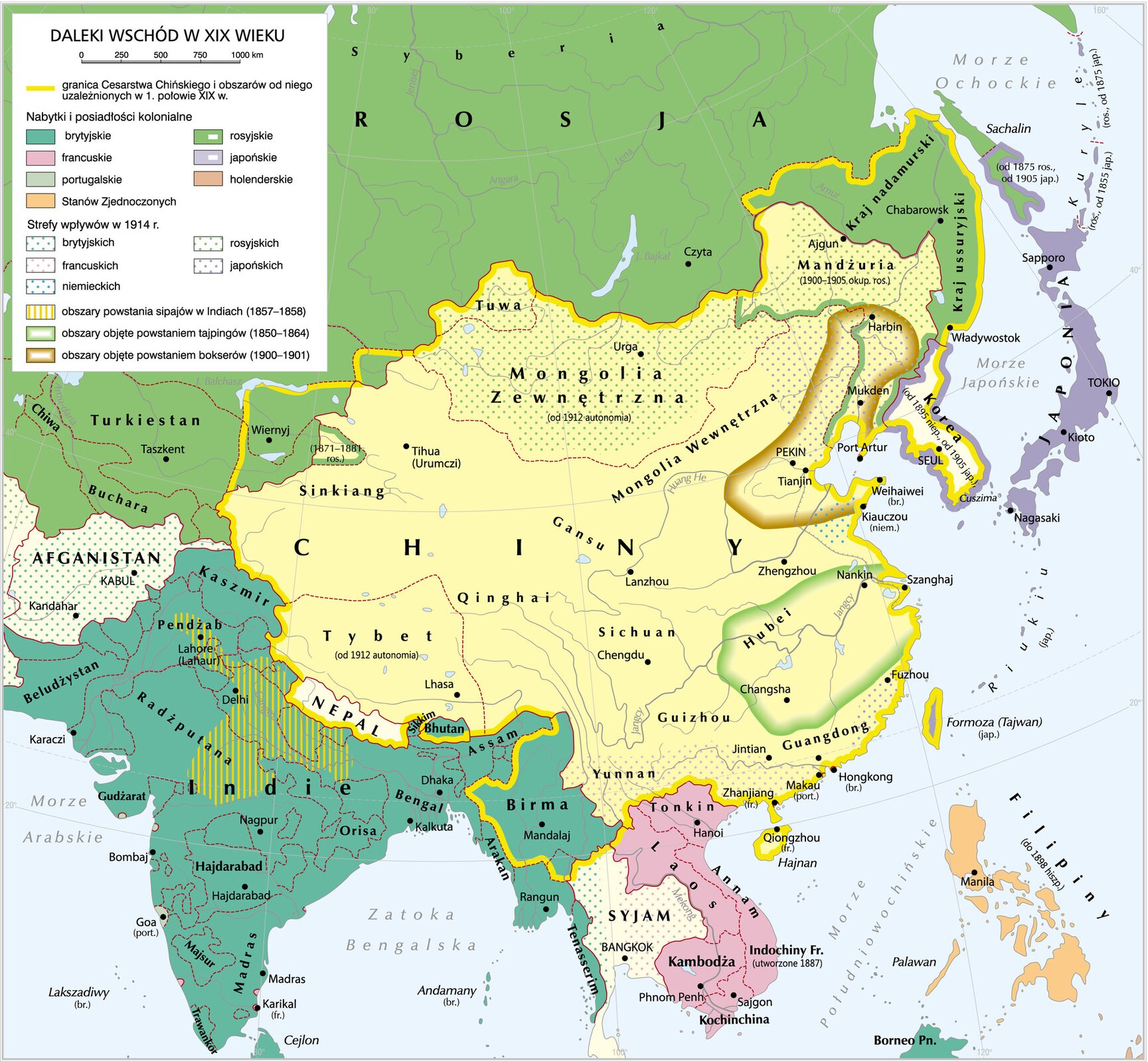
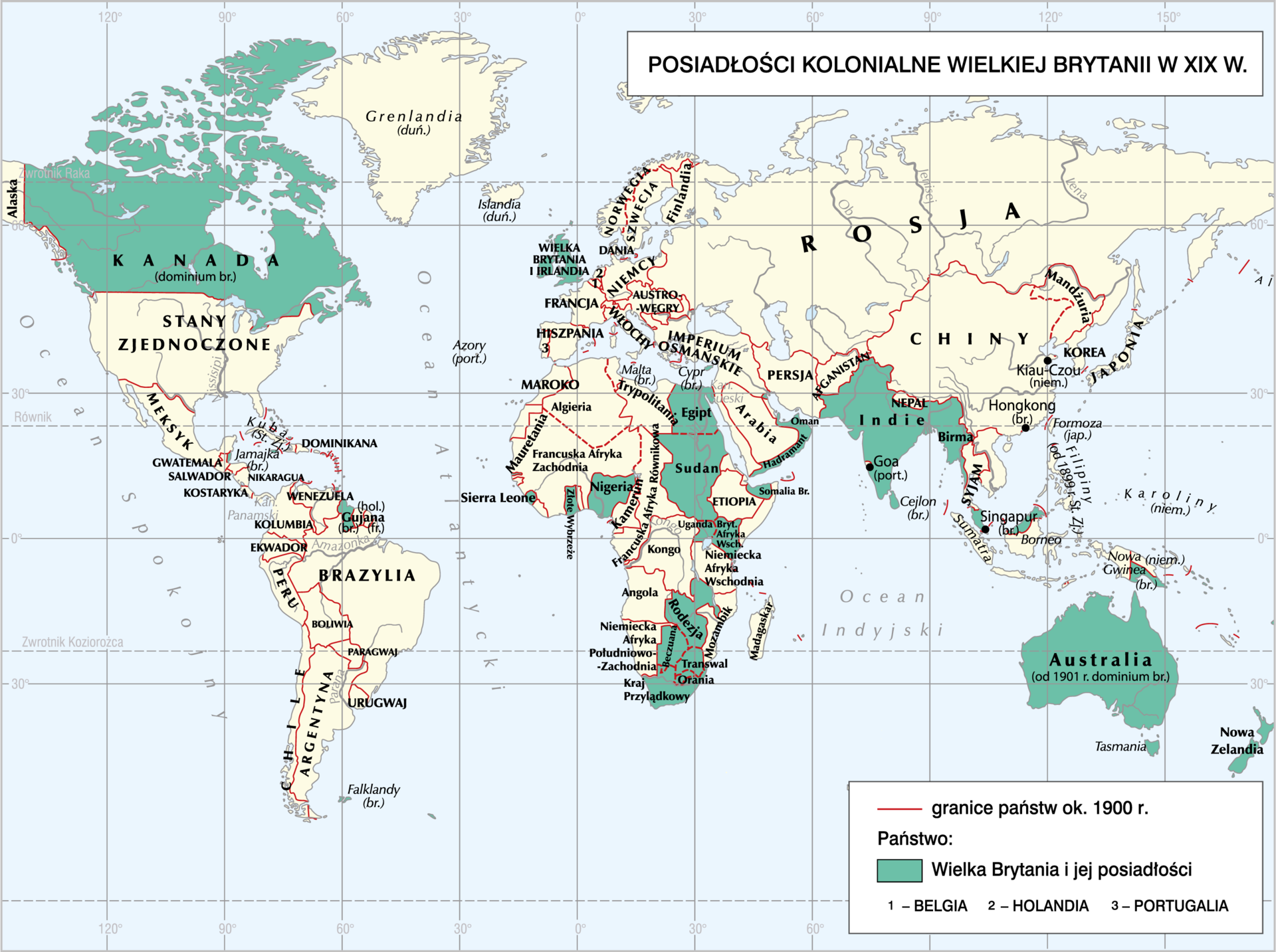
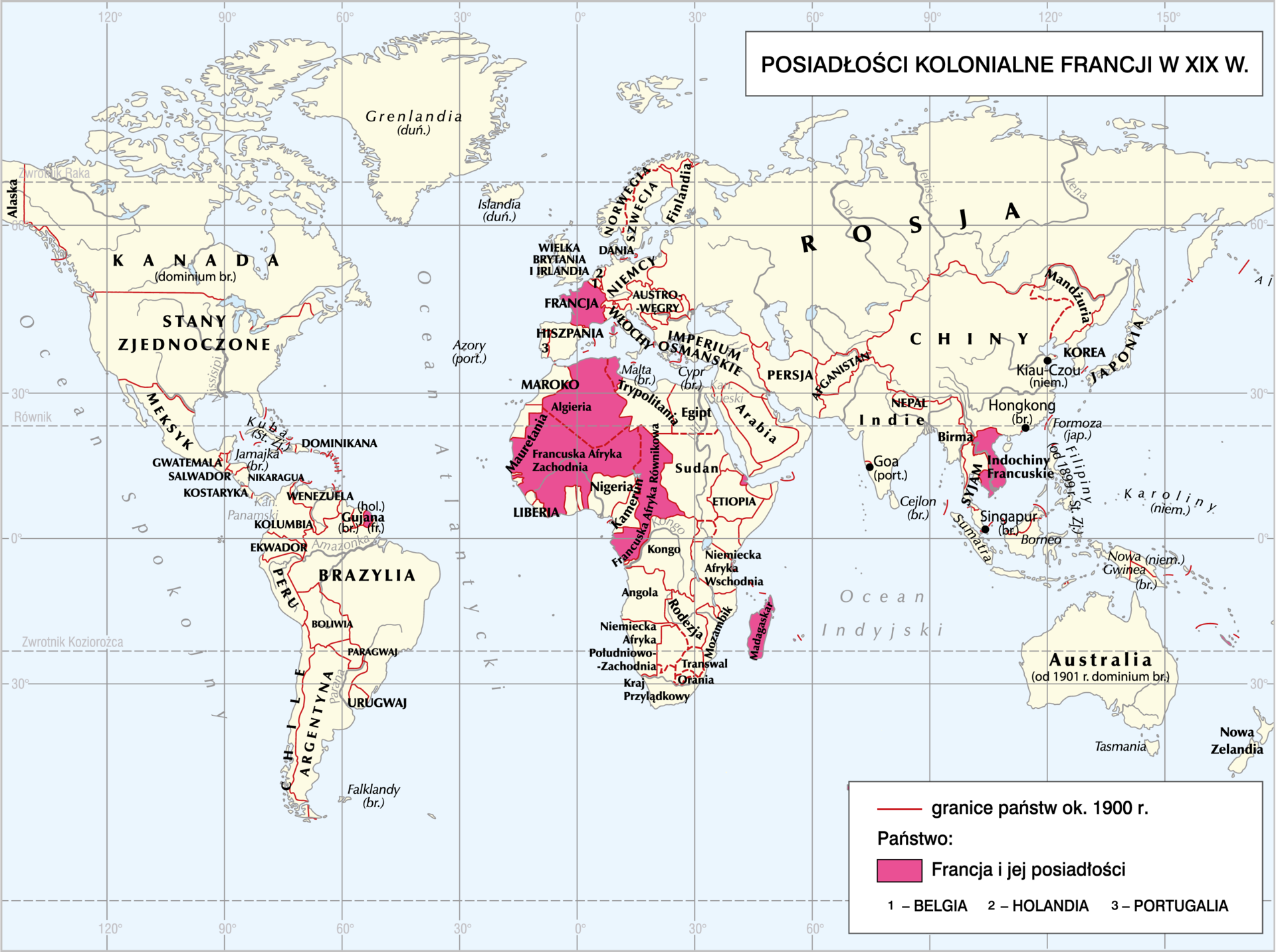
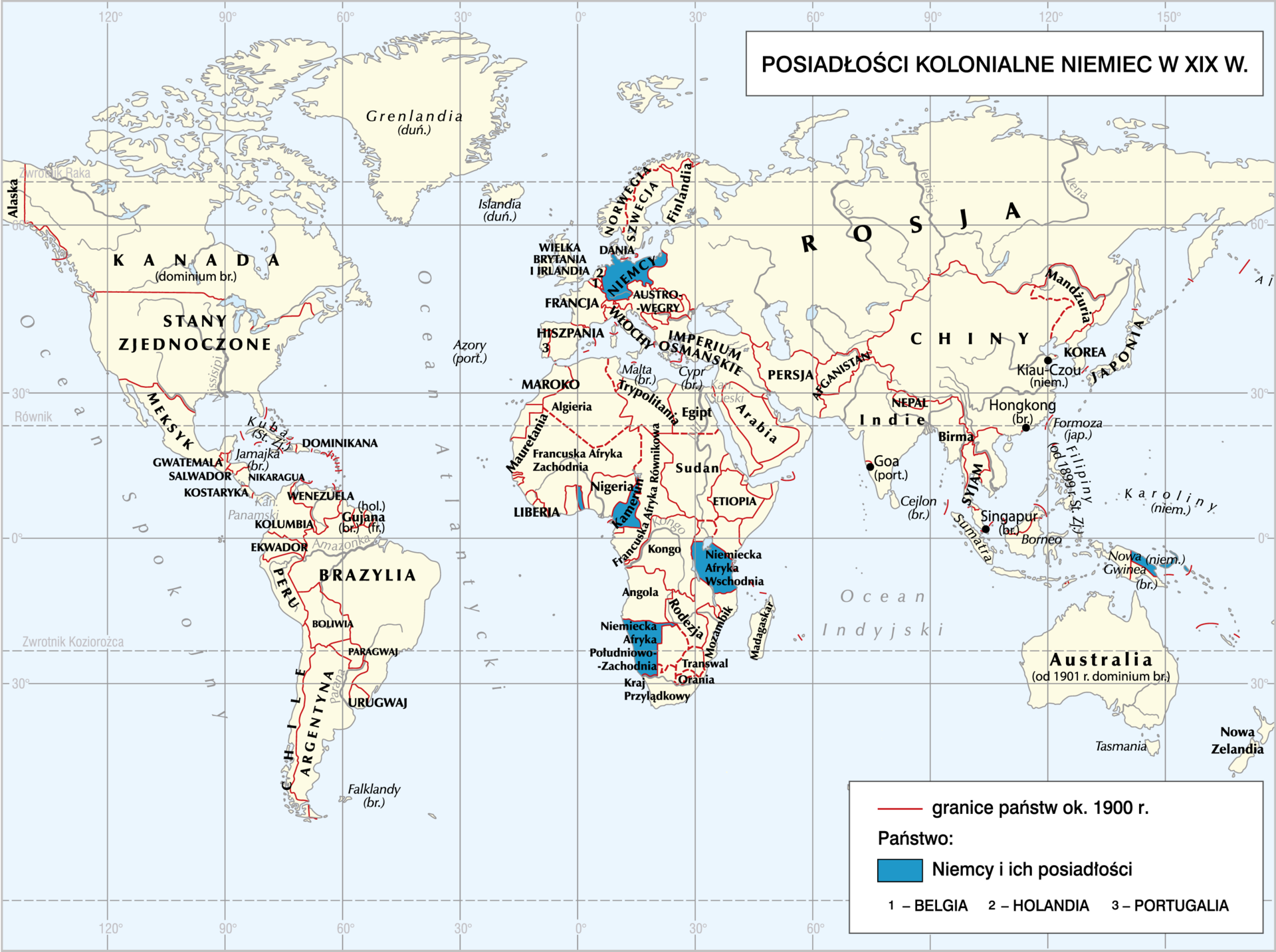
Read the text. Next, sort the names of the following countries in order – from the largest to the smallest in terms of the size of their colonial empire:
The largest of the colonial empires belonged to Great Britain. It spread over an area more than 3 times larger than the entire European continent, and the colonies of this state were located on all continents. Conquering India, South Africa and Egypt enabled Great Britain to rule over the world, and the construction of the Suez Canal created a gateway between Europe and Asia. The second largest empire was built by France. It also included colonies on all continents (without North America), the most important ones being Indochina, North Africa and Madagascar.
The Netherlands and Belgium had smaller, comparable colonial areas. Germans were placed at the very end, as it was the last country to join the race for colonies. The main area of their interest became South‑West Africa. East Africa, on the other hand, was the area of Italian expansion. The old colonial powers, Spain and Portugal, only possessing small estates, no longer played a major role in the colonial race.
Organize the names of countries - from the largest to the smallest in terms of their colonial territory:
- France
- Spain and Portugal
- Netherlands and Belgium
- Germany and Italy
- Great Britain

Keywords
colonies, protectorate, semicolony, dominiumdominium
Glossary
kolonie – zamorskie posiadłości państw europejskich
protektorat – terytorium kontrolowane przez metropolię, lecz zarządzane przez lokalne władze
półkolonia – państwo oficjalnie niepodległe, lecz uzależnione gospodarczo od Europejczyków
dominium – brytyjskie kolonie, które miały pełną autonomię w sprawach polityki wewnętrznej; a niekiedy również zagranicznej.
europocentryzm – postawa polegająca na stawianiu europejskiej kultury i wartości wyżej niż te z innych kręgów kulturowych.