Fermentation in food preparation processes
that the basic components of food products are proteins, carbohydrates and fats;
that sugars can be divided into simple (glucose) and complex (sucrose, starch);
how are alcohols and organic acids built and what are their properties.
to explain the concept of fermentation;
to list the types of fermentation you know;
to name the conditions that must be met for the fermentation process to take place;
to name food products that have been produced in fermentation processes;
to show examples of everyday life in which fermentation processes occur;
to justify that a given fermentation process is desirable and explain when it is not desired;
to write in words and with the aid of molecular formulas, equations of the alcoholic and acetic fermentation reaction equation.
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
Nagranie dźwiękowe. Proces fermentacji, zachodzące w nim procesy. Nagranie przedstawia trzy omówione w lekcji rodzaje fermentacji: alcoholic fermentation, lactic acid fermentation, acetic fermentation.
Alcoholic fermentation
FermentationFermentationIndeks dolny is used for centuries to process food. It consists in the practical use of transformati Indeks dolny koniecis used for centuries to process food. It consists in the practical use of transformations occurring under the influence of enzymes produced by yeasts and bacteria. It is one of the basic biotechnological processesbiotechnological processes.
Before you conduct the experiment „Identification of gas emitted during yeast activity”, formulate a research question and a hypothesis.
Which gas is the product of the yeast fermentation process?
One of the yeast fermentation products is carbon dioxide.
10 dag of yeast,
sugar,
water,
limewater,
conical flask with cork and draining tube,
beaker,
teaspoon.
In a 200 cmIndeks dolny 33 flask mix approx. 10 dag of yeast with a small amount of water and sugar.
Close the flask with a cork with draining tube.
Immerge the tube outlet in the beaker with limewater.
Observe the changes (the effect may be visible after several minutes).
Alcoholic fermentationAlcoholic fermentation occurs under the influence of enzymes produced by yeast that break down sugar (e.g. from fruit juice) into ethanol (ethyl alcohol) and carbon dioxide.
The alcoholic fermentation proceeds according to the equation:
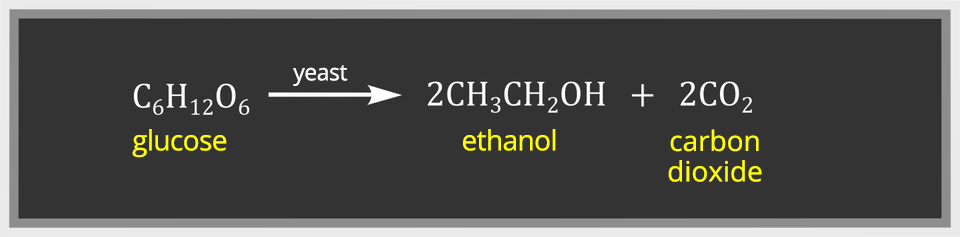
Alcoholic fermentation is used, among others in the production process of beer, wine and high‑grade alcoholic beverages.
Watch the movie to learn about industrial alcohol production

Film dostępny na portalu epodreczniki.pl
Nagranie filmowe przedstawiające produkcje alkoholu w przemyśle. Film rozpoczyna się o prezentacji silosów w których przetrzymuje się pszenicę na alkohol. W specjalistycznym urządzeniu do fermentacji pszenica mieszana jest z wodą i mieszana. Następnie uzyskany roztwór jest podgrzewany oraz mieszany. Następnie roztwór przelewany jest systemem rur do kolejnego naczynia w którym oddzielany jest alkohol.
Lactic acid fermentation
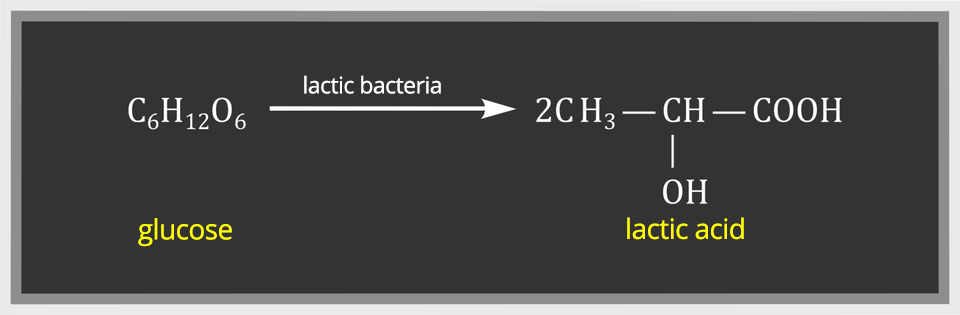
Lactic acid creates a flavour of dishes such as kefir, curd, cucumbers in brine, sauerkraut or white borscht. Lactic acid is formed in the process of anaerobic lactic fermentationlactic fermentation of sugars caused by the action of special bacteria (Bacillus acidi lactici). The protein present in milk congeals under the influence of acid (colloquially it is called „curdling”). After heating of curdled milk, you can separate the cheese and get so‑called whey, which consists of lactic acid and small amounts of lactose, protein and fats.
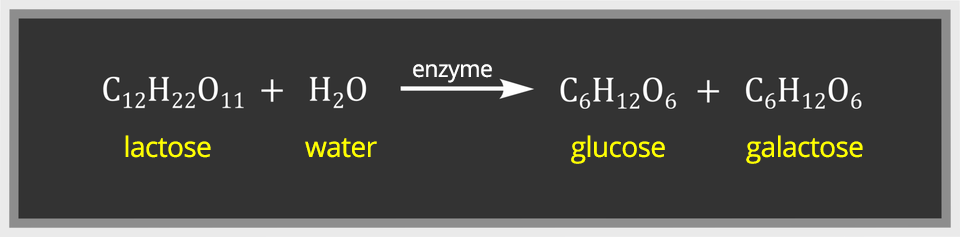
The milk fermentation process has two stages:
The first stage is the hydrolysis of the disaccharide (lactose) contained in the milk into simple sugars (the reaction takes place with the participation of appropriate enzymes).
In the second stage, with the participation of lactic bacteria from glucose, lactic acid is formed.
Beverages consisting of fermented milk have many advantages. These are characterized by higher absorption of nutrients, these contain less lactose in comparison with milk (important for people with lactose intolerance) and have valuable taste values.
Acetic fermentation
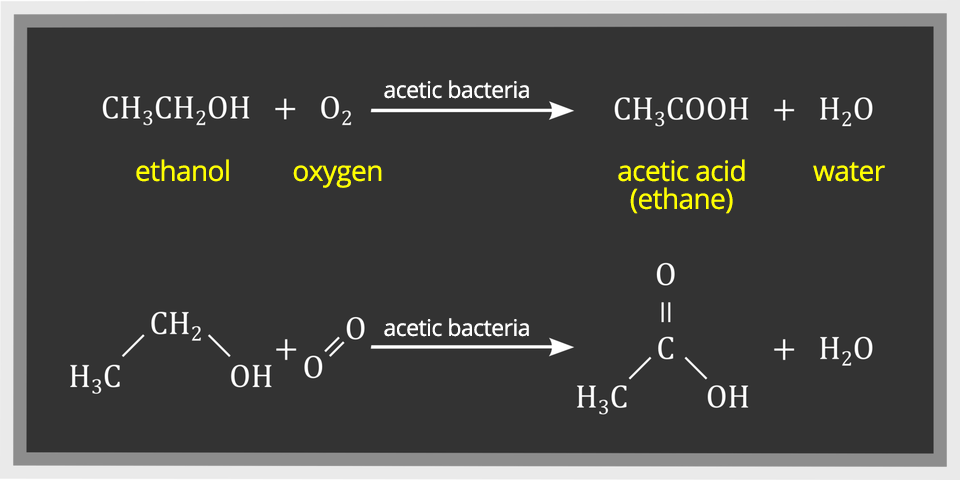
Sometimes beverages with a low alcohol content, such as wine and beer, left for a long time in open vessels, sour. This process involves converting ethyl alcohol to acetic acid and is called acetic fermentationacetic fermentation. Acetic fermentation occurs under the influence of oxygen from the air, involving microorganisms (bacteria or fungi). This process can be presented in the form of the following equation:
In nature, fermentation is a way of breathing in an anaerobic environment. By conducting the fermentation, organisms, such as some bacteria and yeasts, obtain the energy necessary for life. The energy obtained in this way enables the course of various biochemical processes, called metabolic changes, serving the growth and development of these organisms and their life activities, such as movement, reaction to stimuli or reproduction.
Fermentation processes may occur under limited oxygen access – anaerobic fermentations, e.g. alcoholic fermentation, lactic acid fermentation, but also with oxygen – aerobic fermentation, e.g. acetic fermentation.
Alcoholic fermentation occurs according to the following process:
- C6H12O6 → C2H5OH + CO2↑
- C6H12O6 → 2C2H5OH + 2CO2↑
- C6H12O6 → C2H5OH + 2CO2↑
- C12H21O11 → 4C2H5OH + 4CO2↑
Create a multiple-choice test based on today's lesson. Then exchange your questions with a friend or classmate.
Question: ...
- ...
- ...
- ...
- ...
Summary
Fermentation processes occur with the participation of microorganisms (bacteria and yeasts). These are used in food production.
Alcoholic fermentation (with the participation of yeast) is the basis for the production of wine, beer and other types of alcohol. This process is also used when baking yeast dough (the carbon dioxide formed as a result of fermentation scarifies the dough).
Lactic acid fermentation makes it possible to produce such milk products as kefir and yogurt.
Alcoholic and lactic acid fermentation are processes occurring under anaerobic conditions.
In the acetic fermentation process, under aerobic conditions, with the participation of acetic acid bacteria, ethyl alcohol is transformed into acetic acid (ethanoic).
Ask a person who knows how to cook for a recipe where fermentation processes are used.
Write down this recipe in a notebook. Pay attention to the conditions recommended for the preparation of the food/products to guarantee the culinary success.
Use the acquired knowledge to explain the legitimacy of the procedure proposed in the recipe.
Keywords
Alcoholic fermentation, lactic acid fermentation, acetic fermentation, biotechnological process
Glossary
fermentacja – reakcja biochemiczna zachodząca pod wpływem enzymów drobnoustrojów zwykle w warunkach beztlenowych; niektóre procesy produkcji związków organicznych z wykorzystaniem mikroorganizmów nazwane są fermentacją, pomimo iż zachodzą z udziałem tlenu, np. fermentacja octowa; nazwa pochodzi od łac. fermentatio – zakwaszenie, burzenie się
fermentacja alkoholowa – proces zachodzący pod wpływem enzymów (zawartych w drożdżach), polegający na przemianie cukrów prostych w etanol
fermentacja mlekowa – proces zachodzący z udziałem bakterii kwasu mlekowego, polegający na przemianie cukrów w kwas mlekowy
fermentacja octowa – proces polegający na utlenieniu etanolu do kwasu octowego; zachodzi pod wpływem enzymów wytwarzanych przez bakterie kwasu octowego
proces biotechnologiczny – proces technologiczny zachodzący z udziałem organizmów żywych lub ich składników (głównie bakterii), np. podczas kiszenia kapusty czy produkcji serów