Five kingdoms
organisms are made up of cells;
most cells have a cell nucleus.
to give examples of eukaryotes and prokaryotes;
to classify the selected organism to one of the five kingdoms, using the features of the individual kingdoms;
Criteria for the division of organisms
In modern systematics, five kingdoms of organisms are distinguished: bacteria, protists, fungi, plants and animals. The main criteria for the division of organisms into five kingdoms are: the presence or absence of a cell nucleus, the number of cells making up the organism, the presence of chloroplasts as well as the presence and chemical composition of a cell wall.
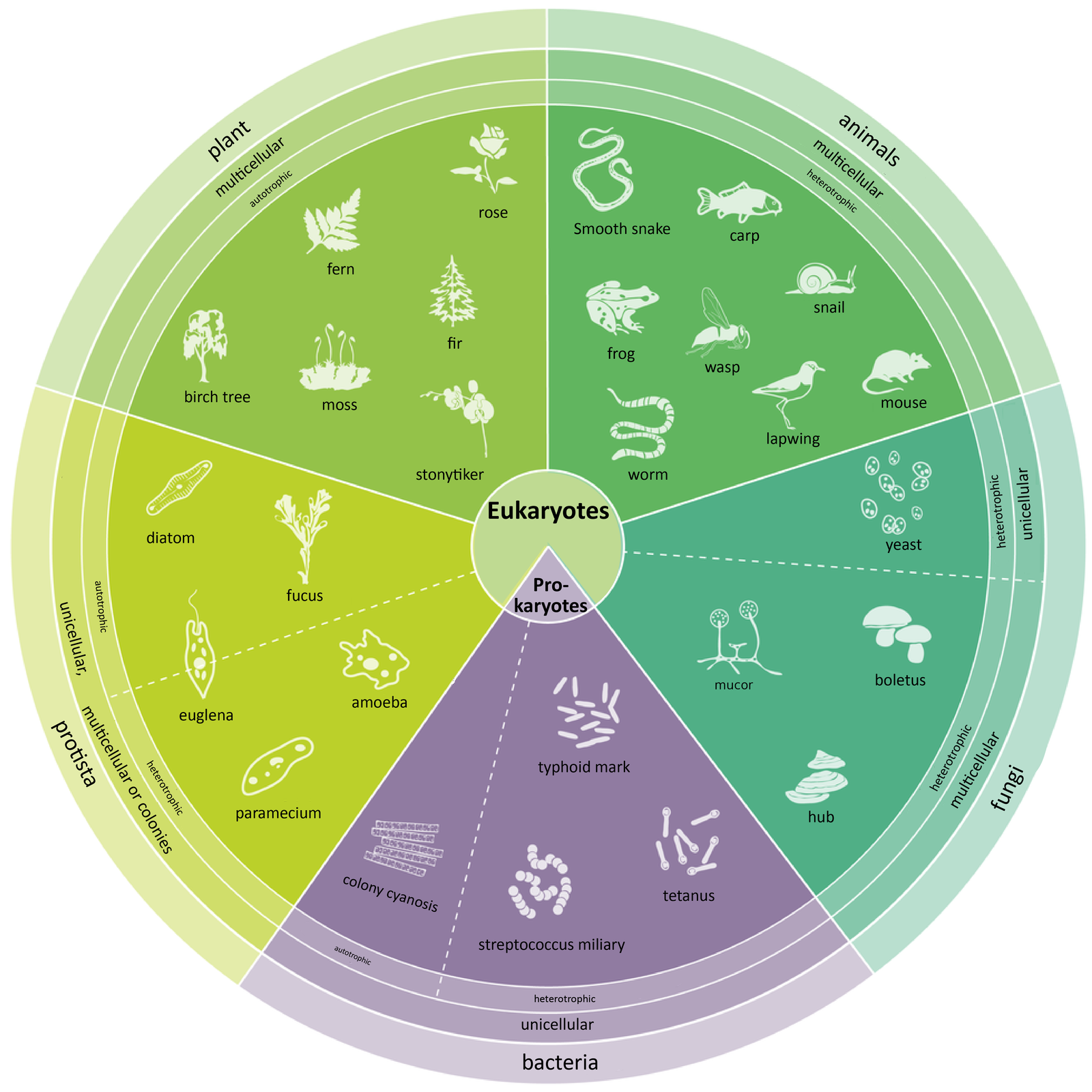
Bacteria include microscopic unicellular organisms, usually living in colonies. They have a cell wall. They may have chloroplast equivalents and nourish through photosynthesis (cyanobacteria). Most bacteria are, however, heterotrophic. There is no cell nucleus in their cells. The genetic information stored in the DNA thread is contained in the cytoplasm. Due to the lack of a cell nucleus, bacteria are called prokaryotesprokaryotes. The remaining kingdoms are made up of eukaryoteseukaryotes, i.e. organisms whose cells have cell nuclei.
Protists are a very heterogeneous group. These include unicellular organisms (e.g. amoeba), multicellular organisms (e.g. Fucus) and colony organisms (e.g. Volvox). They can be autotrophic (e.g. Fucus and Volvox) or heterotrophic (amoeba). Some protists, especially autotrophic ones, such as Fucus, have a cell wall, which is most often made up of cellulose. Most of the protists live in water. Many of them are autotrophic algae inhabiting the oceans, ponds and lakes. These algae can also be found on land, but only where there is a lot of moisture. Their cells resemble plant cells, which is why they are called plant protists.
Among fungi there are both unicellular and multicellular organisms. All of them are heterotrophic – there are no chloroplasts in their cells. The fungal cells are surrounded by a cell wall. In most species, it is made up of the same compound as insect shells, i.e. chitin.
Plants are multicellular, autotrophic organisms whose cell wall is made up of cellulose.
Animals, on the other hand, are heterotrophic, multicellular organisms, not having cell walls.
Create a simple key to mark the representatives of five kingdoms. Take into consideration the main criteria of division of organisms.
Tick the true sentences.
- There is no cell nucleus in bacteria and fungi cells.
- Fungi and animals are heterotrophic.
- Protists are organisms that most often live in water.
- Fungi belong to the kingdom of plants.
Conclusion
Organisms can be divided into eukaryotes and prokaryotes on the basis of the presence or absence of a cell nucleus.
In modern systematics, the organisms are divided into five kingdoms: bacteria, protists, fungi, plants and animals.
How was this lesson? Did you like it? Finish selected sentences.

Keywords
kingdom of organisms, prokaryotes, protists, fungi, plants, animals
Glossary
organizmy jądrowe – organizmy eukariotyczne; jedno- lub wielokomórkowe organizmy, których komórki posiadają jądro komórkowe (otoczone podwójną błoną białkowo‑lipidową), co jest jednym z elementów odróżniających je od organizmów bezjądrowych
organizmy bezjądrowe – organizmy prokariotyczne; mikroorganizmy jednokomórkowe, których komórka nie zawiera jądra komórkowego ani innych struktur komórkowych charakterystycznych dla organizmów jądrowych