How do we measure the weather?
what is atmospheric pressure;
what clouds are made of and how they are formed;
under what conditions different types of precipitation and atmospheric sediments are formed.
explain what the weather is;
differentiate types of weather components;
read the instruments which measure weather components;
monitor the weather in the local area;
recognize the basic symbols used on meteorological maps.
Weather and its components

WeatherWeather is what we call the state of the atmosphere present in a given area at a given time. Over time, you can observe constant changes in the weather. The factors which determine the weather are listed below.
Air temperature is given in degrees Celsius (°C).
Air humidityit's the content of water vapor in the air. Its value is given in percentages (%). Air humidity increases before or after rain, and decreases during sunny and dry days. If the humidity is 100%, increasing the amount of water vapor leads to its condensation.
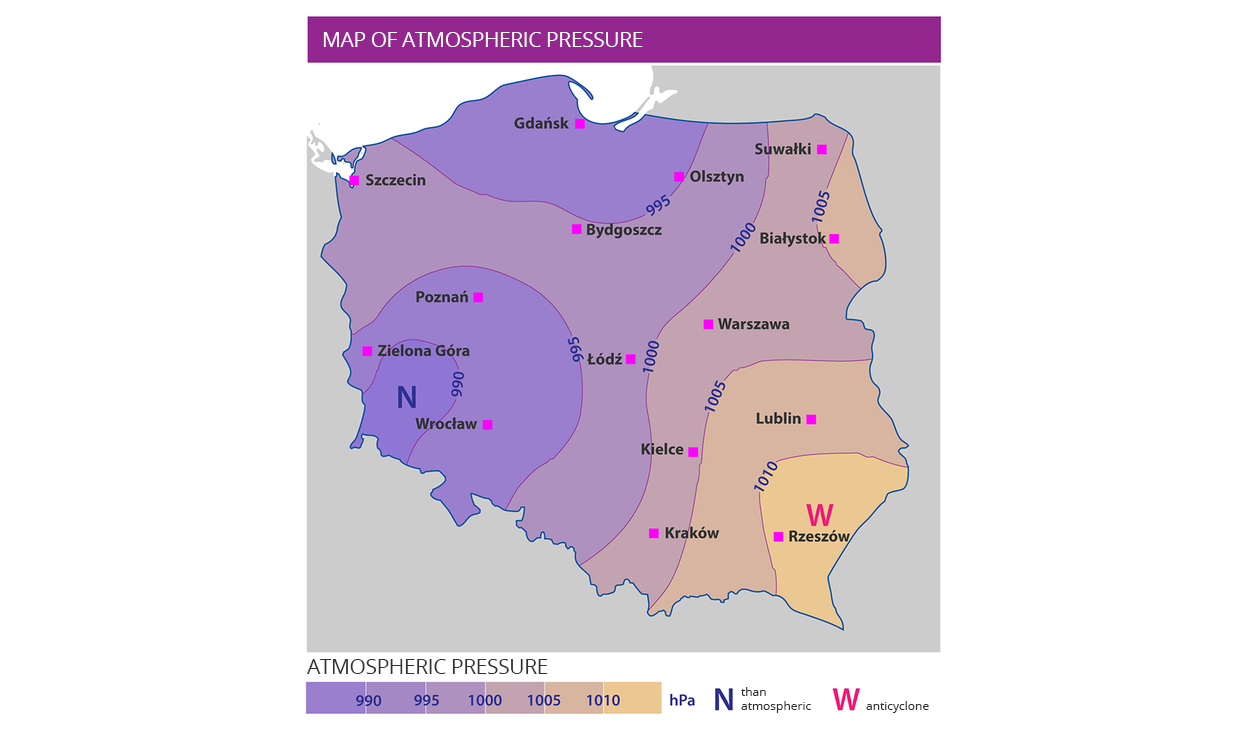
Atmospheric pressure is measured by a barometer; its values are usually given in hectopascals (hPa).
Wind force is usually given with two elements: direction and speed expressed in meters per second or kilometers per hour.
Precipitation is determined by giving it's type and amount in millimeters.
Cloud cover is determined on the basis of how much the sky is covered by clouds and is defined on a scale from 0 to 8. The types of clouds and the order in which they appear is also given.
Sunshine it's the time that solar rays fall on a specific place. They are given in hours. Sunshine hours are lower in winter and higher in summer.
MeteorologistsMeteorologists investigate the events and processes taking place in the atmosphere. They do it based on observations carried out in weather stations. These stations are equipped with various types of equipment that measures the weather components listed above. In Poland, all collected weather data goes to the Institute of Meteorology and Water Management (or IMGW). There are forecastersforecasters who prepare weather forecasts, or they predict its state for a limited time. This information is placed on special weather mapsweather maps, which are presented on television, radio stations, newspapers and the Internet. Thanks to them, we know whether we should expect a storm or strong winds or maybe even beautiful, sunny weather on a given day. In order to prepare the forecast, the forcasters must study the weather in an area much larger than only the area of our country. Unfortunately, the weather is constantly changing, therefore the short‑term forecast (for example, two days) sometimes works with accuracy to the hour, but the long‑term (eg 4 - 5 days) may differ from reality.
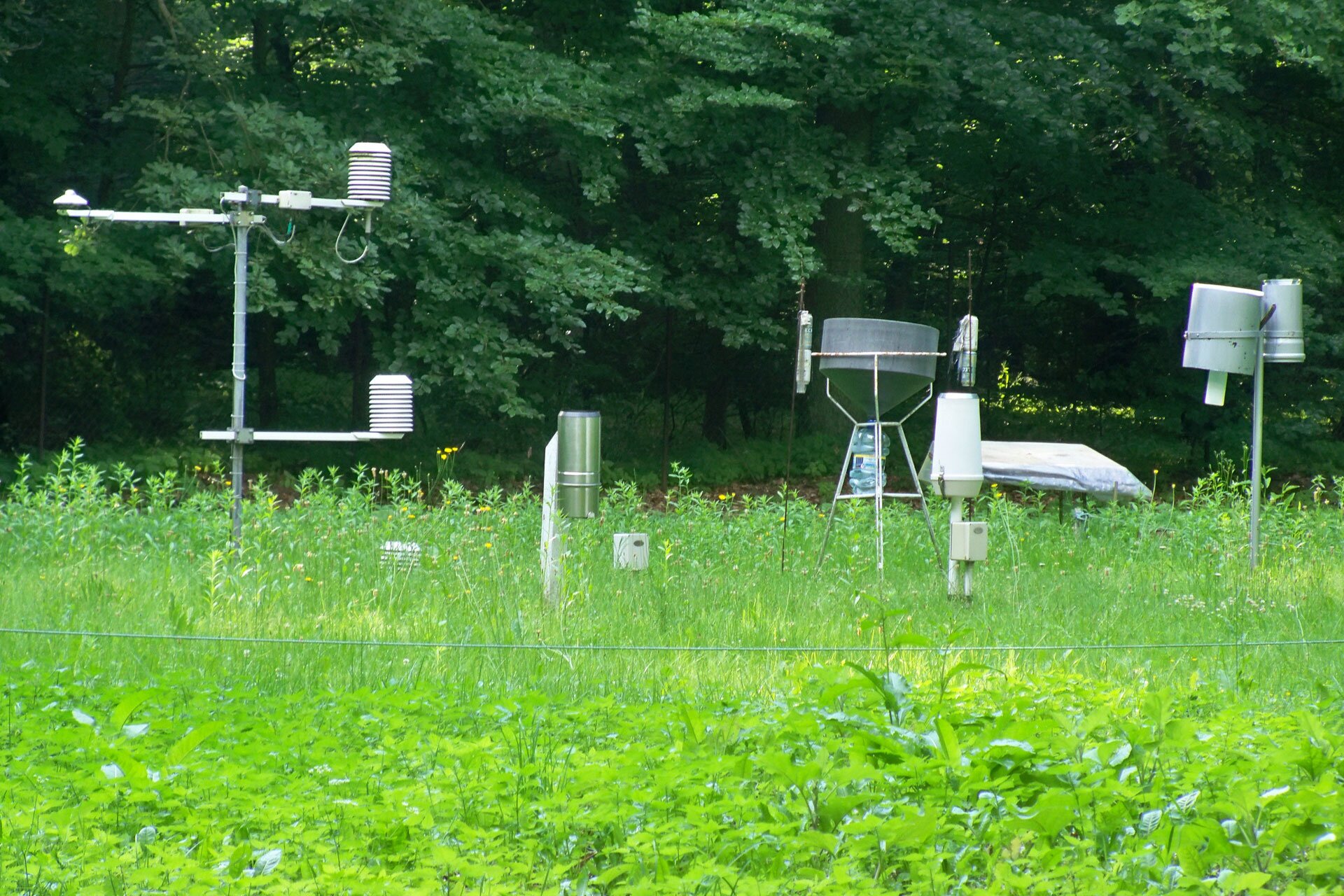
Meteorological Gardens
Measurements of all weather components should be carried out in a designated place and at the same fixed time, and the operation of measuring devices should not be disturbed by, for example, excessive lighting. That is why the instruments used for observing the weather are placed in special meteorological Gardens. In such a garden you should find the following equipment:
several thermometers (to obtain high accuracy of measurement) – to measure the minimum and maximum air temperature and ground temperature;
hygrometerhygrometer – to measure air humidity;
barometer–for determining atmospheric pressure;
anemometer – it indicates both the direction and the speed of the wind;
pluviometerpluviometer – collecting water from rain and measuring its quantity.
Thermometers and hygrometers are placed in the meteorological box in order to separate them from the influence of external factors that disrupt the operation of the measuring devices, e.g. sunlight. You certainly know the terms „temperature in the shade” and „temperature in the sun”. To make the air measurement accurate, it can not be disturbed by excessive sunshine – The sun would heat the air, which would result in erroneous measurement.
Natural signs of weather
People have been trying to determine the weather for thousands of years, at least for the next day. They noticed that plants and animals often feel minor weather changes that they do not. Observing nature, you can get a lot of valuable information about how the weather will change. For example, livestock become restless before storms . While swallows before the rain starts, fly low to the ground, because at higher altitudes are no insects.
To the given terms, select the unit in which they are expressed.
percent (%), millimeters(mm), (m/s), hours (h), hectopascals (hPa)
| Air humidity | |
| Atmospheric pressure | |
| Wind meter per second | |
| Precipitation | |
| Sunshine |
Choose the weather components.
- wind direction and speed
- temperature and humidity
- height above sea level
- distance of the Earth from the Sun.
- atmospheric pressure
- body temperature
Summary
Weather is the state of the atmosphere at a given moment in a specific area.
Weather components are cloud cover (cloudiness), sunshine, air humidity, air temperature, Precipitation (rainfall), wind force and atmospheric pressure.
A weather forecast should be based on the analysis of all its components.
Measurements and weather observations are dealt with by weather stations.
On the weather map, the weather for the area is marked for a specific time.
Keywords
weather, forecast, weather map
Glossary
deszczomierz – przyrząd do pomiaru ilości opadów atmosferycznych
higrometr – przyrząd do mierzenia wilgotności powietrza, czyli zawartości pary wodnej w powietrzu
mapa synoptyczna – mapa przedstawiająca prognozę pogody dla danego obszaru w danym czasie
meteorolog – naukowiec zajmujący się badaniem zjawisk i procesów fizycznych zachodzących w atmosferze ziemskiej
pogoda – stan atmosfery w danym czasie na danym obszarze; wpływają na nią procesy zachodzące w warstwie atmosfery najbliższej powierzchni ziemi
synoptyk – meteorolog zajmujący się opracowywaniem prognoz pogodowych