How genetic information is written
genetic information is written in the DNA;
a gene is a DNA fragment.
on the basis of the DNA explain how proteins are formed, followed by specific features of an organism;
to distinguish between the terms 'genetic code' and 'genetic information';
to present how genetic information is written in the DNA;
to describe the genetic code.
Features of an organism depend on the type of its proteins. The instruction of protein construction, i.e. genetic informationgenetic information, is written in the DNA. A DNA molecule is made up of billions of nucleotide pairs. Nucleotide sequenceNucleotide sequence is not random. It is a special code. The alphabet of this code is made up of just 4 characters that are actually 4 nitrogenous bases, which form 4 types of nucleotides. Depending on the number and sequence of the nucleotide arrangement, the genes that they make up contain instructions for the formation of different proteins. The rules of the code writing are called genetic codegenetic code.
Explain what is the difference between the genetic code and the genetic information.
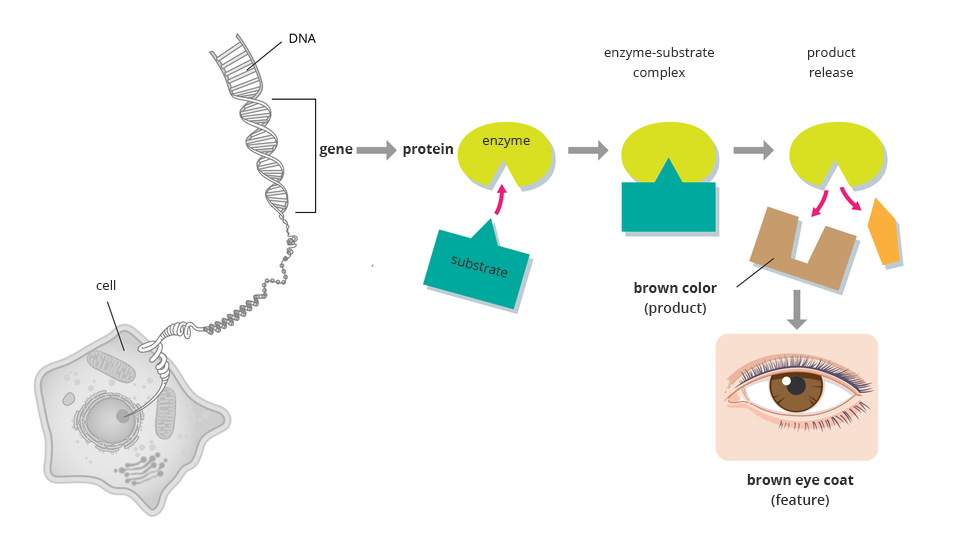
Human DNA contains more than 20 thousand genes, and almost each of them controls production of a different protein. These include proteins that build structures of the organism, enzymes that enable various chemical reactions in cells, some hormones that regulate the function of tissues and organs and those that control growth and development. For example, eye colour to be created needs a special protein – an enzyme – that can transform colourless substrate into brown melanin. This enzyme is produced based on the instructions contained in the particular gene. The people in whom the gene coding for this enzyme is inactive will have no melanin in their irises. Their eyes will usually be red. This is because blood vessels are visible through colourless iris tissue with no melanin.
In fact, people have eyes of various colours. This diversity is due to the presence of various genes. Each of them contains information regarding how much melanin should be produced in irises. The more melanin, the darker the colour of the eyes. Since the colour of the human iris is determined by several genes, it has an infinite number of variants. Coloured irises are a common trait of all people (with few exceptions), but eye colour is an individual personal feature.
Explain why the DNA encodes information about the structure of proteins rather than sugars.
What is the role of these groups of chemical compounds?
How many characters are used to write the genetic code? Identify the correct number.
- 2
- 4
- 8
- 16
- 32
- 64
Arrange the following items in the correct order to recreate the cause-and-effect chain from the gene to the occurrence of a specific trait
- appearance of a trait in the phenotype of an organism
- synthesis of the appropriate enzyme
- reading genetic information written in the gene
- involvement of the enzyme in the production of a protein controlling a specific trait
Complete the following text by dragging the appropriate words into the gaps.
amino acids, Genetic information, genetic code, protein, trait
...................................... is encoded in the DNA nucleotide sequence. This is why its sequence cannot be accidental. Amino acids attach to one another forming a ....................................... Their kind and sequence are written in the ....................................... If the sequence of the ...................................... was changed, or if one of them was replaced with another, it would result in the synthesis of a completely different protein that would control the occurrence of a different .......................................
Summary
The genetic code is a way of writing information about the structure of proteins.
The genetic code is a triplet code, i.e. one amino acid is coded by three nucleotides called a codoncodon.
The gene contains information about the structure of a specific protein, while the sequence of codons in the gene determines the sequence of amino acids in the protein.
The genetic code is universal; the genetic information is written identically in all organisms.
Keywords
genetic code, genetic information, nucleotide sequence
Glossary
informacja genetyczna – informacja o kolejności aminokwasów w białkach zakodowana w sekwencji nukleotydów DNA, mówiąca pośrednio o cechach organizmu; nośnikiem informacji genetycznej jest DNA
kod genetyczny – sposób zapisu informacji genetycznej w materiale genetycznym (DNA)
kodon – trójka kolejnych nukleotydów w sekwencji kwasu nukleinowego, kodująca jeden aminokwas
sekwencja nukleotydów – kolejność ułożenia nukleotydów w cząsteczce DNA