How to calculate molecular weight
that atomic mass unit is used to determine the atomic weight, i.e. 1 unit = 1,66 · 10Indeks górny -24-24 g;
that atomic weight is a weight of an atom expressed using atomic mass units;
that atomic weight of a chemical element is an averaged value which depends on the percentage of individual isotopes.
to calculate molecular weight of simple chemical compounds;
to determine mass ratios of elements in chemical compounds;
to determine percentage composition of a chemical compound.
What is atomic weight of a chemical element?
The atomic weight is very small and constitutes only a small part of gram (approx. 10Indeks górny -24-24 g). That is why it is expressed using atomic mass units, called the units. One unit is equal to 0.00000000000000000000000166 g (1.66 · 10Indeks górny -24-24 g).
Atoms of the same element may differ in their weight as there are certain varieties with different number of neutrons in nucleus. That is why atomic weight of an element is the weighted average of its isotopic masses. In order to calculate it, the percentage of isotopes of a given element is taken into account. The average atomic weights of elements are listed in the periodic table.
The atomic weight is a unique feature of given element and there are no two different elements with the same atomic weight. That is why if you know atomic weight, you can identify the element.
Use the periodic table to find chemical elements with the following atomic weights: 32 u, 23 u, 4 u and 40 u. Then state their names and chemical symbols.
How to calculate molecular weight of a chemical compound?
Chemical compounds are made of molecules or form crystal structure with ions in a specific quantitative ratio. Molecular formula of a compound shows molecular structure of a molecule or – if it is an ionic compound – it corresponds to the simplest stoichiometric ratio of ions present in this compound. The mass of these smallest structures of chemical compounds, expressed using atomic mass units, is called molecular weightmolecular weight. Although the term consists of a “molecular” part, its scope is not limited only to molecular compounds but also covers ionic compounds.
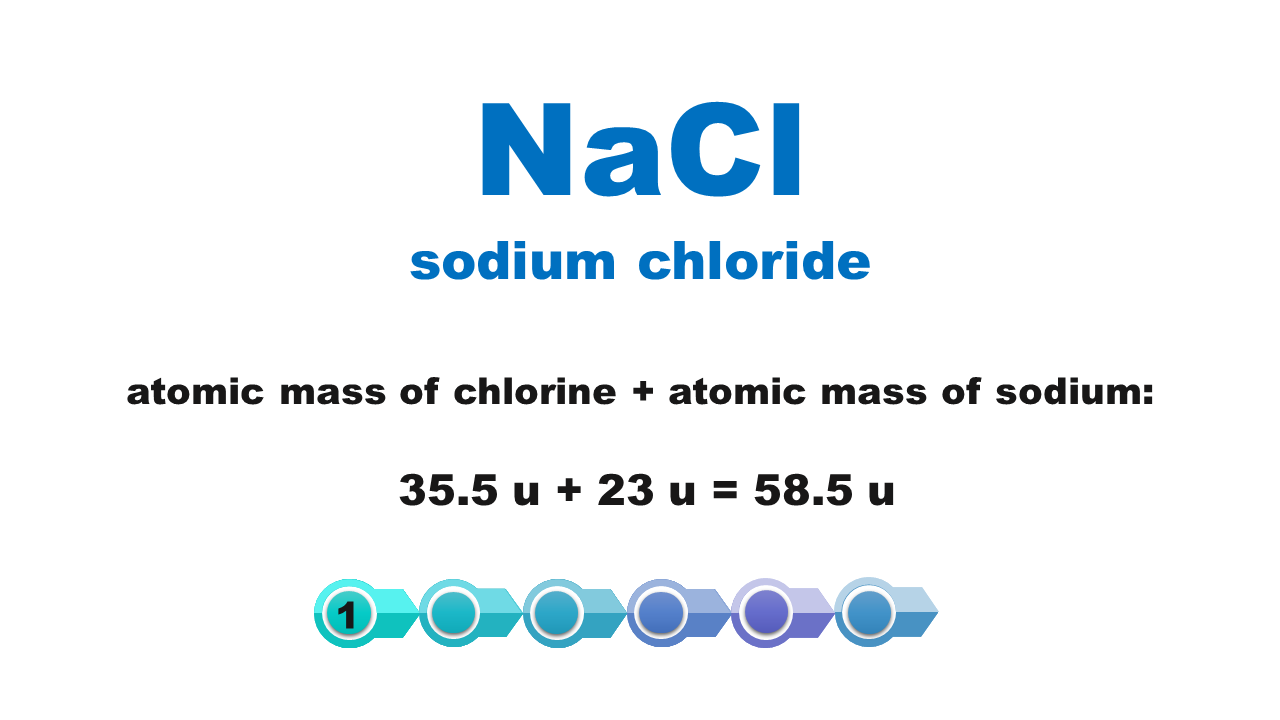
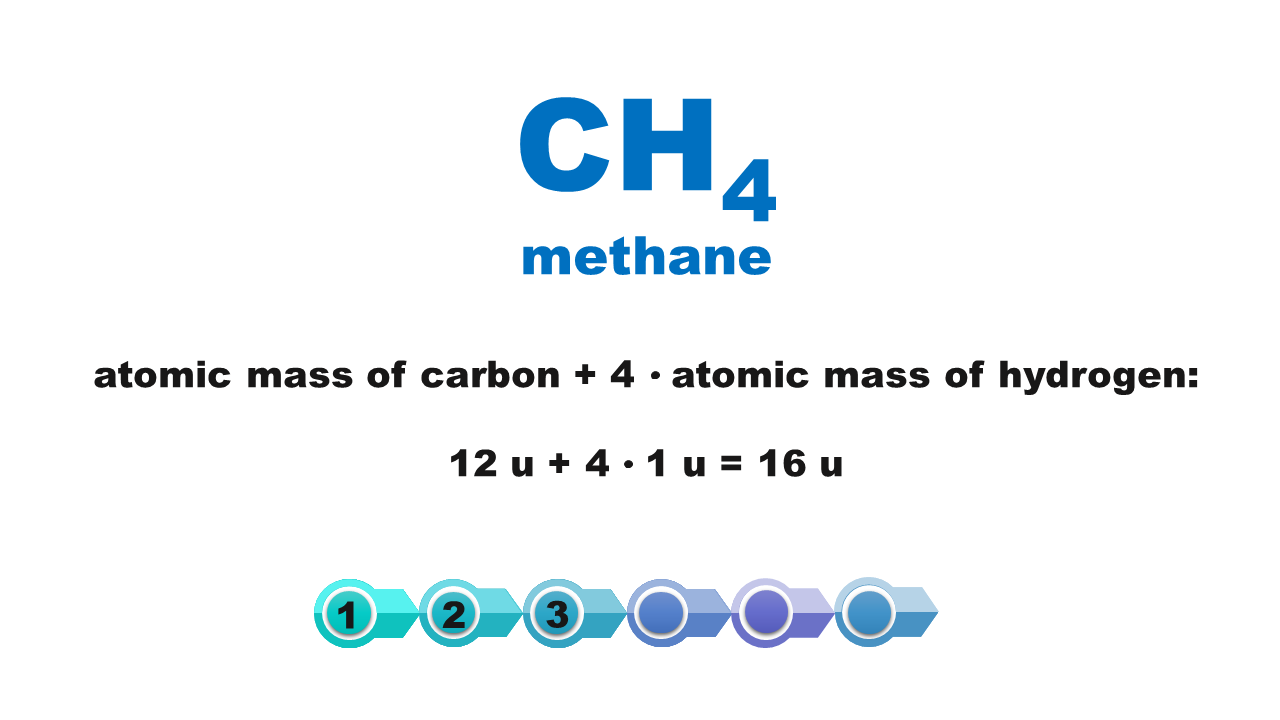
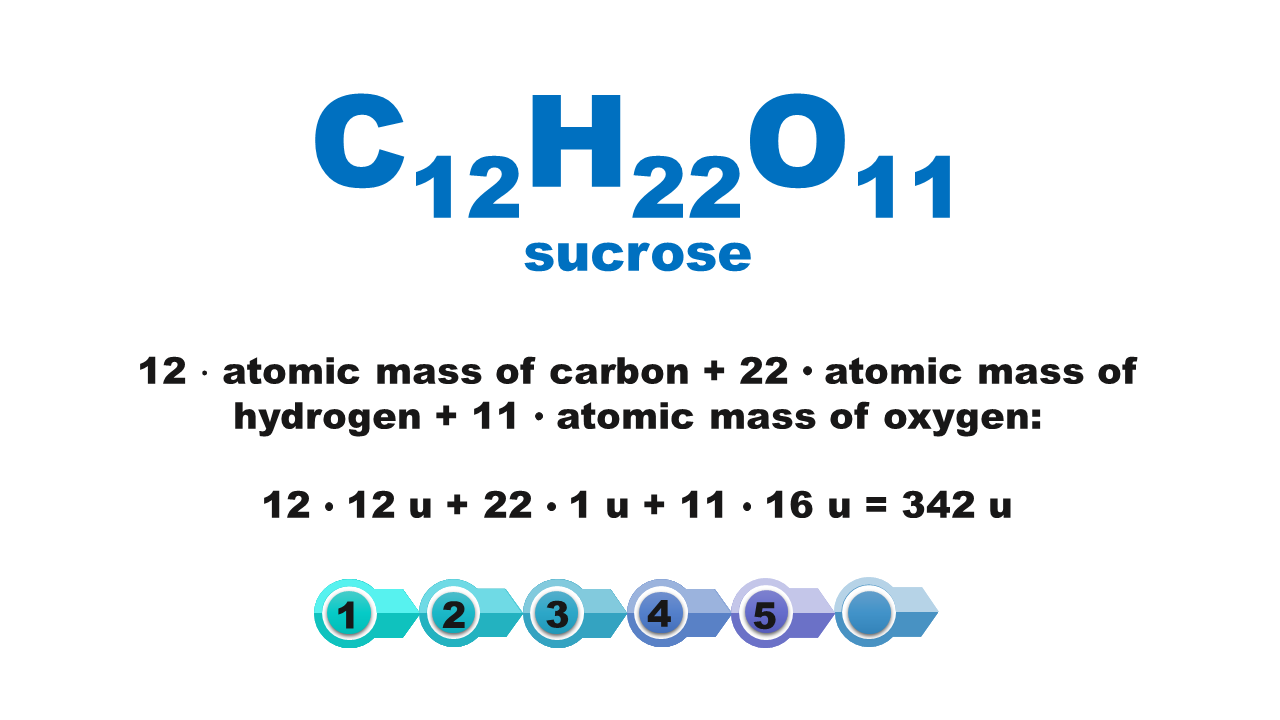
The molecular weight of a chemical compound is equal to the sum of atomic weights of elements forming the smallest structure of a chemical compound that is described using the chemical formula.
Atomic weights of particular elements can be found in the periodic table. It is usually expressed with a non‑integer with several decimal digits. In typical chemical calculations, atomic weights are rounded up to integersIndeks górny **. Atomic weights of chlorine and copper are the only exceptions:
When making approximations, you have to follow certain rules:
If the first decimal digit is less than 5, all decimal digits are rejected, for example:
If the first decimal digit is greater than 5, the number corresponding to a unit is increased by 1, for example:
In case of chlorine and copper the first decimal digit is equal to 5 (their atomic weights are not rounded up to integers).
When do we use the concept of molecular weight of a chemical element?
Some chemical elements, such as: hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, chlorine, bromine or iodine, occur in the form of diatomic molecules. In order to determine their weight, we use molecular weight of an elementmolecular weight of an element. The molecular weight of a chemical element is a product of its atomic weight and a number of atoms that make up a molecule.
For example, the molecular weight of nitrogen is made up of diatomic molecules with the formula is as follows:
Name of the elements | Structure of a molecule | Calculations of molecular weight | Molecular weight [u] |
nitrogen | 28 | ||
oxygen | 32 | ||
fluorine | 38 | ||
chlorine | 71 | ||
bromine | 160 | ||
iodine | 254 | ||
phosphorus | 124 | ||
sulphur | 256 |
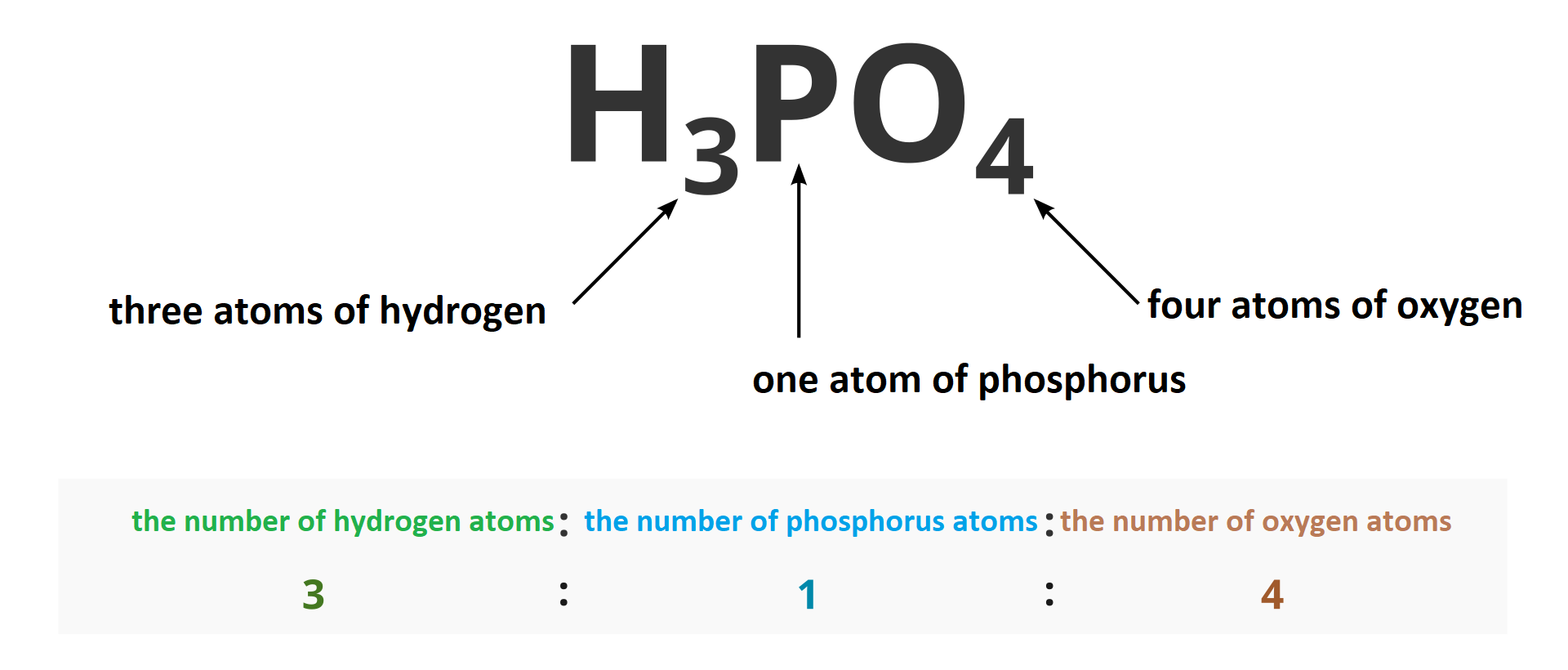
How to calculate the ratio of the number of atoms in individual elements in a chemical compound?
The ratio of the number of atoms (or ions) of individual elements in given compound is determined based on molecular formula of a chemical compound. For example, in hydrogen chloride with the following molecular formula: there is one atom of hydrogen per one atom of chlorine. The ratio of hydrogen atoms to chlorine atoms is 1 : 1. In case of water with molecular formula , the ratio of hydrogen atoms to oxygen atoms is 2 : 1.
Chemical | Name of the compound | Type of numerical ratio | Ratio of the number of atoms or ions in the compound |
sodium chloride | |||
aluminium chloride | |||
sulphuric acid | |||
sucrose |
Using the term “atom” to describe the numerical ratio would not be a big mistake, regardless of the compound type (covalent or ionic one).
How to calculate the mass ratio of individual elements in a chemical compound?
A molecular formula of a chemical compound contains information about elements that form this compound and quantitative ratio in which they bond with each other. If you know these information, it is easy to calculate mass ratiomass ratio of individual elements. This value is defined as the ratio of atomic weights of individual elements that form given chemical compound. In a hydrogen chloride with a formula there is one atom of hydrogen with atomic weight of 1 u and one atom of chlorine with atomic weight of 35.5 u. The mass ratio of hydrogen to chlorine in a hydrogen chloride molecule amounts to 1 : 35.5.
In a compound with general formula:
the mass ratio is as follows:
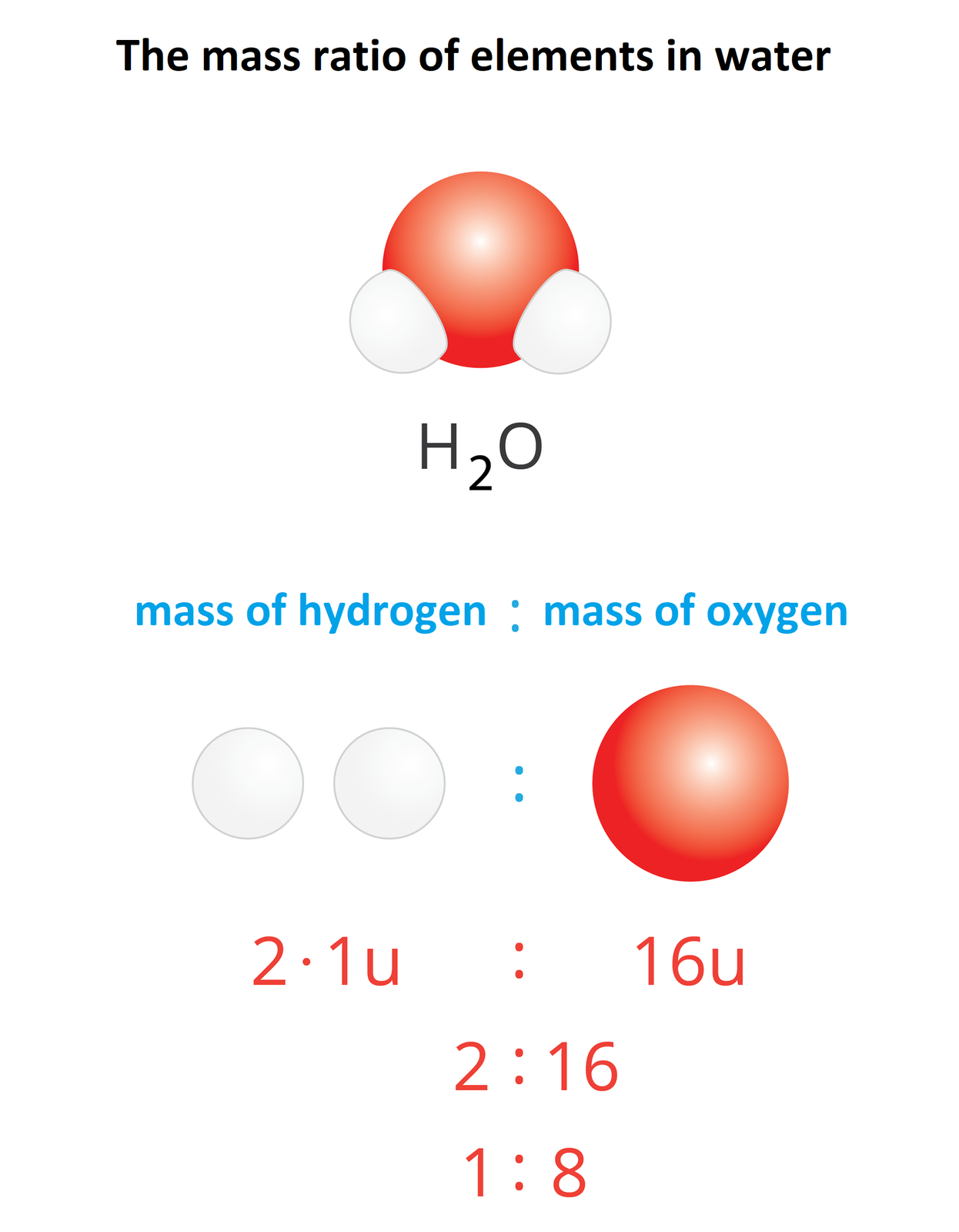
Chemical formula of a compound | Name of the compound | Expression of mass ratio | Mass ratio |
sodium chloride | |||
aluminium chloride | |||
sulphuric acid | |||
sucrose |
Watch the presentation “Molecular weights of selected chemical compounds”. Write down your conclusions and summary when you analyse the animation with your teacher.
Select the correct answer. The molecular weight of chlorine (Cl2) is:
- 35,5u
- 36u
- 71u
- 72u
Select the correct answer. The molecular weight of aluminum hydroxide (Al(OH)3) is:
- 78u
- 75u
- 44u
- 46u
Select the correct answer. The molecular weight of iron(III) sulphide (Fe2S3) is:
- 88u
- 208u
- 144u
- 152u
Find out which chemical element is denoted by letter , if you know that molecular weight of its oxide with a formula amounts to 108 u.
Summary
Molecular weight, mass ratio of individual chemical elements and percentage content of these elements can be calculated based on formula of given chemical compound.
Molecular weight of chemical compound is equal to the total weight of atoms of elements making up the molecule (if it is a covalent compound) or the smallest set of repetitive ions (if it is an ionic compound). It is expressed using atomic mass units.
The mass ratio of individual elements making up a chemical compound is called mass ratio.
Arrange chemical compounds listed below by growing molecular weights: , , .
Keywords
molecular weight of an element, molecular mass of a chemical compound, mass ratio of elements
Glossary
masa cząsteczkowa pierwiastka – masa cząsteczki pierwiastka chemicznego wyrażona w atomowych jednostkach masy
masa cząsteczkowa związku chemicznego – masa cząsteczki (związek kowalencyjny) bądź najmniejszego zbioru powtarzających się jonów o przeciwnych znakach (związek jonowy) wyrażona w atomowych jednostkach masy
stosunek masowy pierwiastków – stosunek mas poszczególnych pierwiastków wchodzących w skład związku chemicznego
zawartość procentowa pierwiastka w związku – udział masowy danego pierwiastka w związku chemicznym; stosunek masy atomów pierwiastka w najmniejszej strukturze związku chemicznego do masy cząsteczkowej związku pomnożony przez 100%; za najmniejszą część związku chemicznego uważa się cząsteczkę (w przypadku związków kowalencyjnych) bądź najmniejszy zbiór powtarzających się jonów (w związku o budowie jonowej)