Hydracids
how hydroxides are obtained, what are their structure, properties and application;
what are the indicators and what colours these turn into in water and bases.
to define the concept of acid;
to design experiments allowing to obtain hydracids by various methods;
to describe the structure of hydracids;
to determine the colour that the indicators turn into in acids;
to examine and describe the properties and application of selected hydracids.
pH indicators in acidic solutions
Under the influence of some chemical compounds, the pH indicators change colour in a way that is easy to observe. The indicator is, for example, the tea brew. After adding hydrochloric acid solution to it, its colour changes to yellowish. Let's check if similar properties are shown by red cabbage brew, phenolphthalein and methyl orange.
Will the indicators change colour after being introduced into distilled water and acid?
All indicators will change colour in both distilled water and acid.
six beakers,
red cabbage brew,
phenolphthalein,
methyl orange,
water,
hydrochloric acid solution,
universal indicator stip.
Pour water into first three beakers and hydrochloric acid solution into remaining three beakers.
Add a few drops of red cabbage brew to the first two beakers (the first one with water and the second one with acid), and add phenolphthalein and methyl orange respectively to the remaining beakers.
Pour a few drops of water on one universal strip and hydrochloric acid solution on the other.
Observe the changes.
Indicator | Colour of the indicator | |
in distilled water | in acid | |
red cabbage brew | violet‑blueish | red |
universal indicator strip | yellow | red |
phenolphthalein | colourless | colourless |
methyl orange | yellow‑orangish | red |
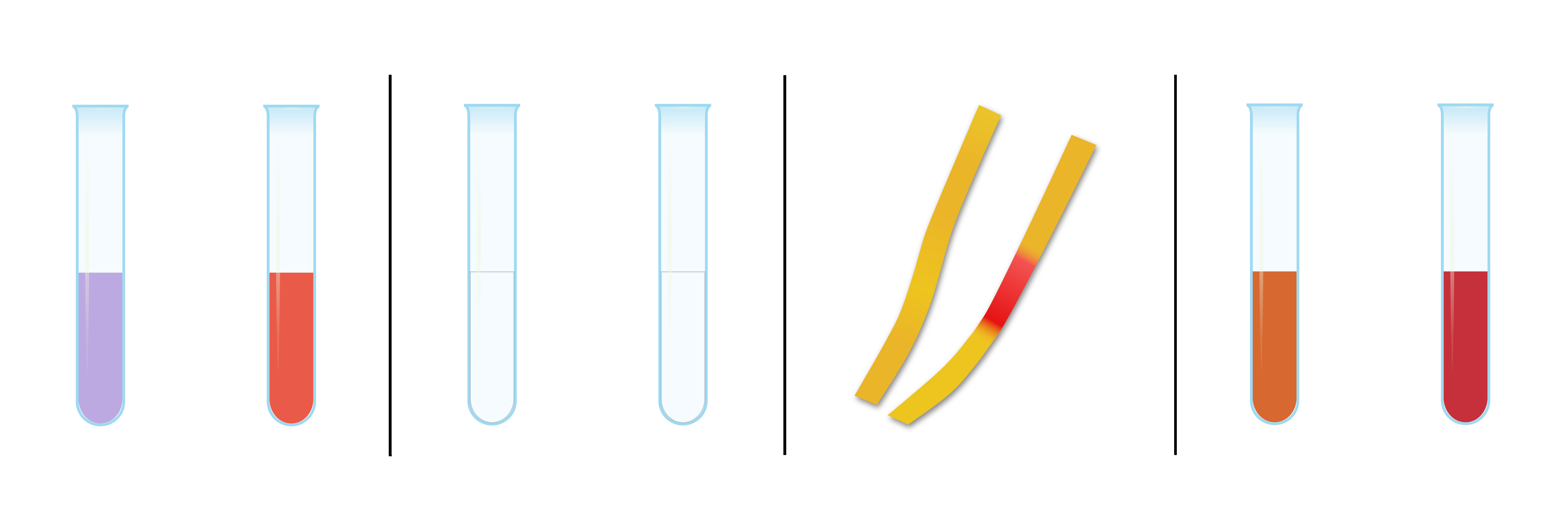
1. Red cabbage brew (water, acid) Violet liquid colour on the left indicates neutral environment, i.e. pure water. The red colour of the brew on the right indicates the presence of acid.
2. Phenolphthalein (water, acid) Two test tubes half-filled with phenolphthalein solution. The liquid in the test tube on the left side containing only the indicator and water and the liquid in the test tube on the right to which the acid has been added is also transparent.
3. litmus paper (water, acid) The paper on the left, treated with pure water, retained its original yellow colour, while the paper on the right, treated with acid, changed colour to red at the point of contact with the acid.
4. Methyl orange The orange colour of the liquid on the left indicates the neutral environment, i.e. pure water. The intense red colour on the right indicates the presence of acid.

Film dostępny na portalu epodreczniki.pl
Film przedstawia badanie właściwości hydrochloric acid. Do badania zostały wzięte: kwas chlorowodorowy, oranż metylowy, odwar z czerwonej kapusty oraz fenoloftaleina. Substancje te zostały połączone w jednej probówce z wodą, w drugiej z kwasem chlorowodorowym. Za pomocą papieru wskaźnikowego oraz mieszadła odczytany został wynik badania.
Obtaining hydracids
Does hydrogen chloride dissolve in water?
Hydrogen chloride dissolve in water.
hydrogen chloride obtained previously – e.g. in the reaction of sodium chloride with sulphuric acid
cork with draining tube,
round bottom flask,
cork with a thin glass tube embedded in it.
Cork the flask with the previously collected hydrogen chloride with cork with a thin glass tube with a rubber hose with a squeezer at the ending. Put the tube outlet in the crystallizer with an aqueous solution of methyl orange and release the squeezer.
Observe the changes.
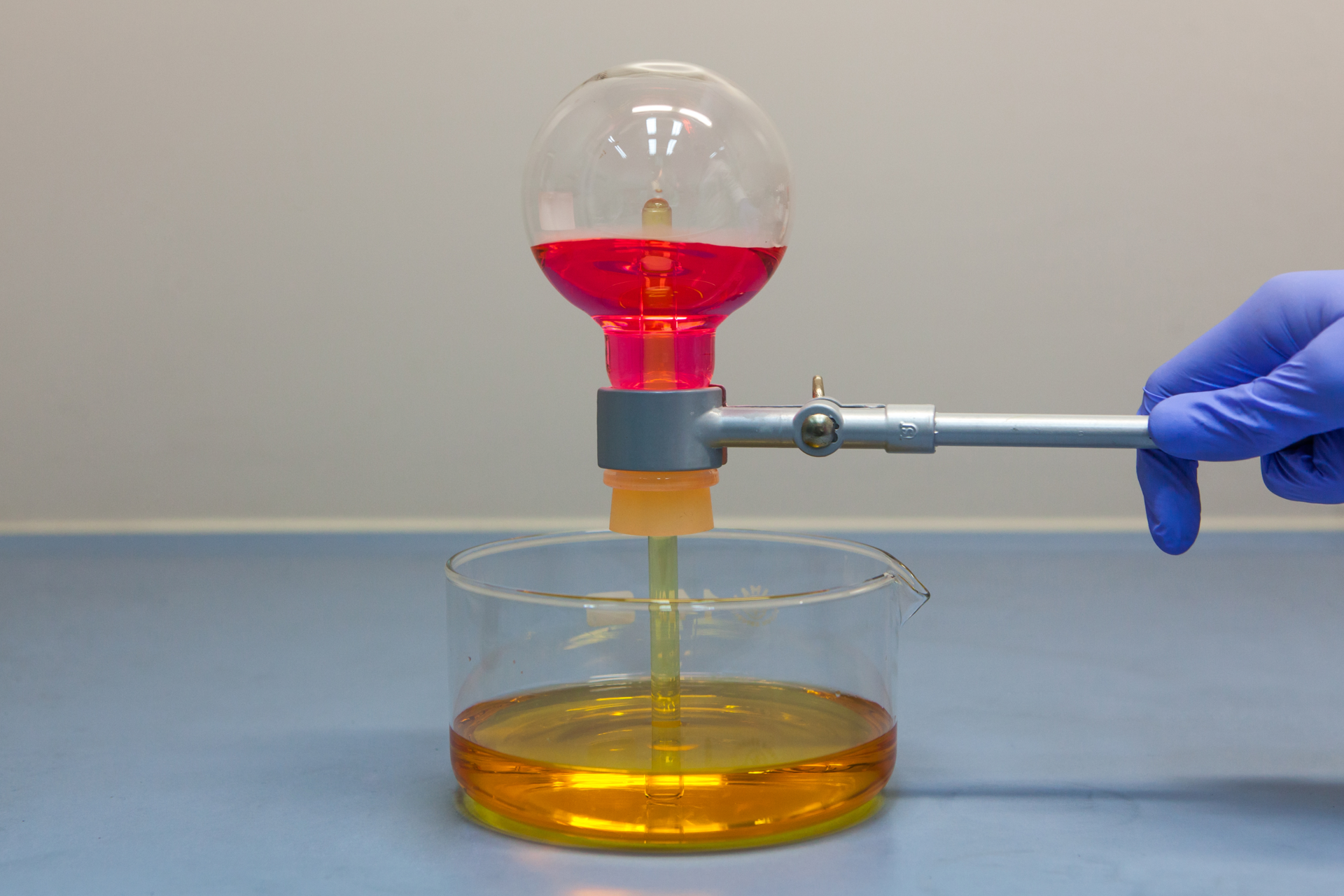

Hydracids are obtained, inter alia, by dissolving in water the chemical compound formed during the reaction of hydrogen with some non‑metals, e.g.
HIndeks dolny 22 + ClIndeks dolny 22 → 2HClIndeks dolny (g)(g)
where:
– means that substance is a gas,
– means that substance is an aqueous solution.
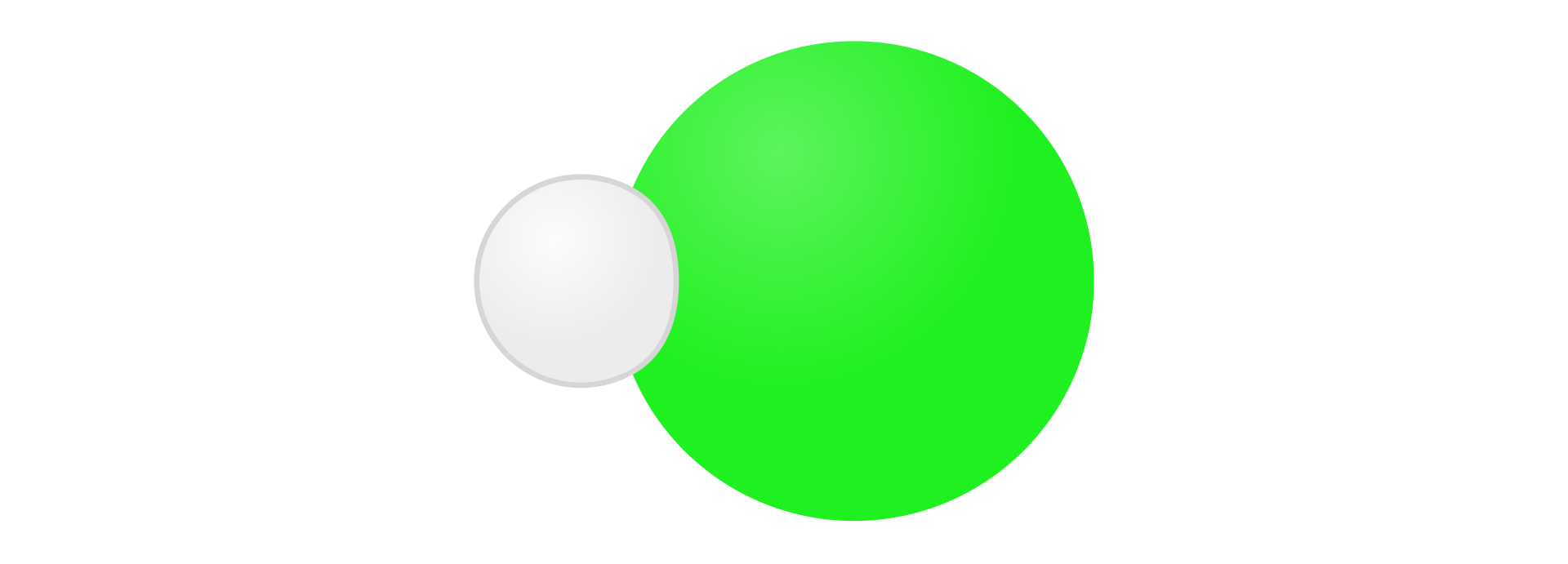
Hydrogen sulphideHydrogen sulphide can be obtained by hydrogen and sulphur synthesis as following:
HIndeks dolny 22 + S → HIndeks dolny 22SIndeks dolny (g)(g)
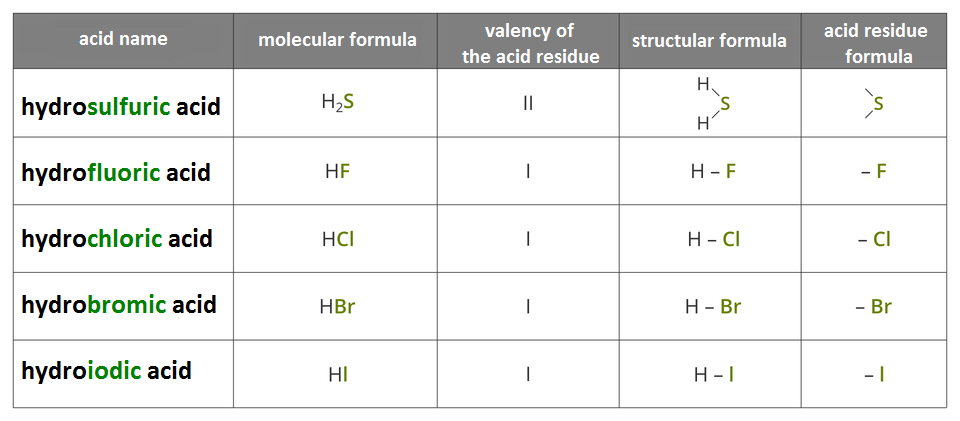
Hydracids form also other chemical elements of the 17th group of the periodic table: fluorine, bromine and iodine. In the name of hydracids you add ending ic instead of ine (exception: sulphur) to the name of the non‑metal and add prefix hydro in front of it.
– hydrobromic acid
– hydrochloric acid
– hydroiodic acid
General formula of acid is:
where:
– number of atoms in the acid molecule,
– acid residue (for hydracid these are non‑metal atoms).
Acids are chemical compounds whose molecules are made of hydrogen atoms and an acid residue. In molecules of hydracids, hydrogen atoms bond directly to the non‑metal atom.
Properties of hydracids
Hydrogen chlorideHydrogen chloride it is a colourless gas with a sharp, choking smell. It dissolves very well in water. The aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride is called hydrochloric acidhydrochloric acid or muriatic acid.
What are the characteristic properties of concentrated muriatic acid?
Concentrated muriatic acid it has an unpleasant smell and it causes charring of paper and fabric.
concentrated muriatic acid,
beaker,
two Petri dishes,
paper (tissue paper),
pieces of fabrics,
pipette or dropping funnel.
Carefully open the bottle with concentrated hydrochloric acid and pour a small amount of it into the beaker. Observe the changes.
Place paper and pieces of fabric on Petri dishes.
Using a pipette, apply a few drops of concentrated hydrochloric acid on the tested materials.
Leave it for a few minutes. Observe the changes.
Application of selected hydracids
Hydrogen chloride is used as a chemical reagent in the process of metalworking, for the production of plastics, sugar, artificial honey, spices, homogenized cheese and curd. Hydrogen sulphide is used as a chemical reagent to detect ions of some metals.
Select correct sentence.
- Muriatic acid is used in the production of dyes
- Muriatic acid smells like rotten eggs
- Muriatic acid is obtained in the reaction of Chlorineoxide with water
- Phenolphthalein in acid turns raspberry-pinkish
Create a multiple-choice test based on today's lesson. Then exchange your questions with a friend or classmate.
Question: ...
- ...
- ...
- ...
- ...
Summary
There are no oxygen atoms in molecules of hydracids, and hydrogen atoms are bonded directly with the atoms of non‑metal.
These are formed as a result of dissolution in the water of the product of hydrogen synthesis with non‑metal.
Hydrogen chloride and hydrogen sulphide are poisonous gases. Their aqueous solutions are acidic.
Search for the information about the type of hazard and instructions for first aid in the safety data sheet.
Keywords
Hydrogen chloride, Hydrogen fluoride, Hydrogen sulphide, hydrochloric (muriatic) acid
Glossary
chlorowodór – bezbarwny, dymiący gaz o silnie duszącej woni; cięższy od powietrza, niepalny; bardzo dobrze rozpuszcza się w wodzie, tworząc kwas solny
fluorowodór – bezbarwna ciecz (tw 19,5°C) lub trujący gaz o silnie drażniącej woni; wywołuje stan zapalny błon śluzowych
siarkowodór – bezbarwny, silnie trujący gaz o ostrym, duszącym zapachu zgniłych (nieświeżych i długo gotowanych) jaj; jego wodny roztwór to kwas siarkowodorowy
kwas chlorowodorowy (solny) – wodny roztwór chlorowodoru