Illumination of the Earth throughout the year
what the Earth’s revolution and rotation are;
that the Earth’s axis is tilted in relation to its orbit around the Sun;
that the day and night cycle changes throughout the year.
to explain the following terms: vernal equinox, autumnal equinox, summer solstice and winter solstice.
to describe the illumination of the Earth on equinox days and solstice days;
to explain the relationship between the inclination of the Earth’s axis and the change of seasons.
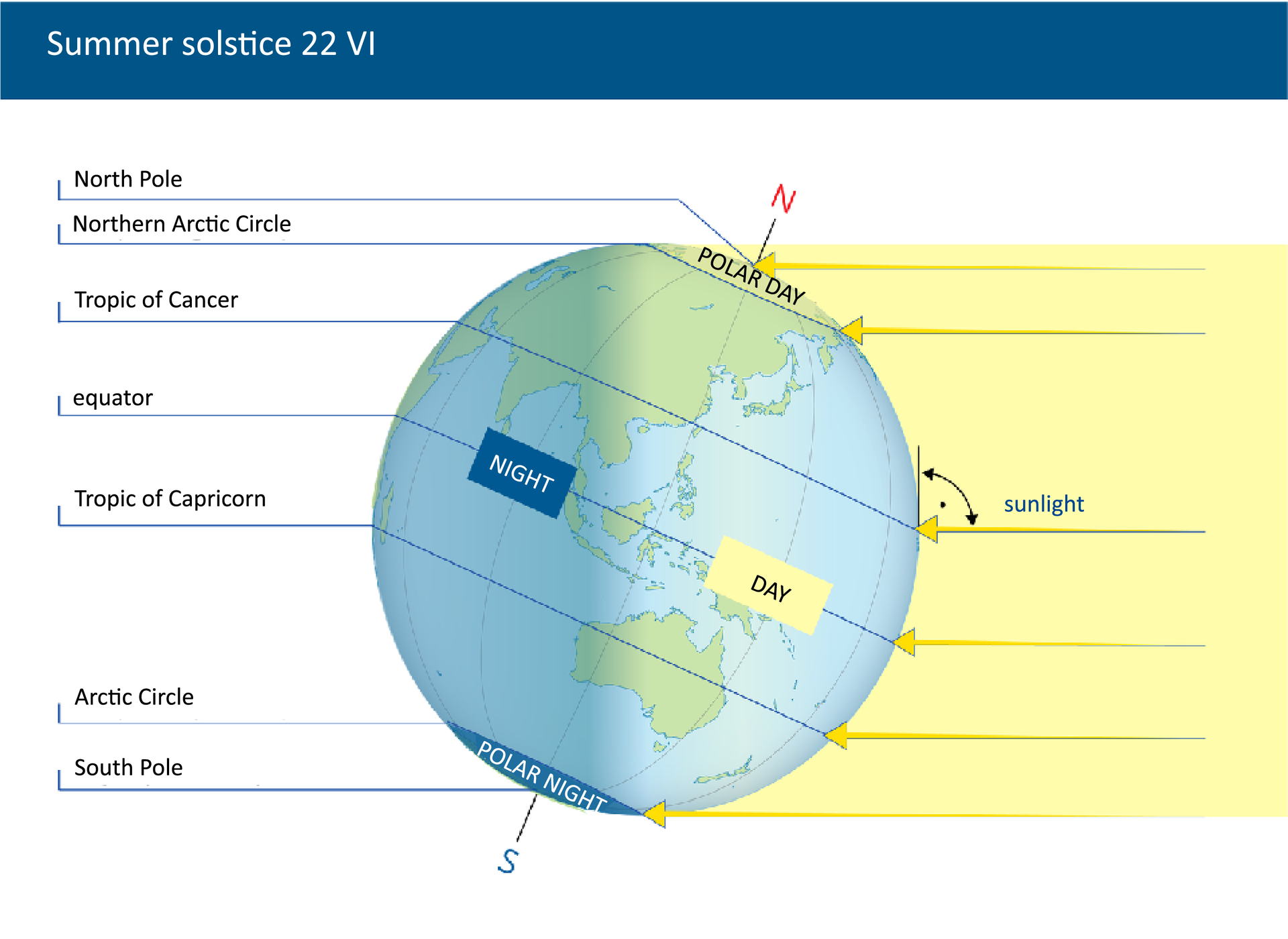
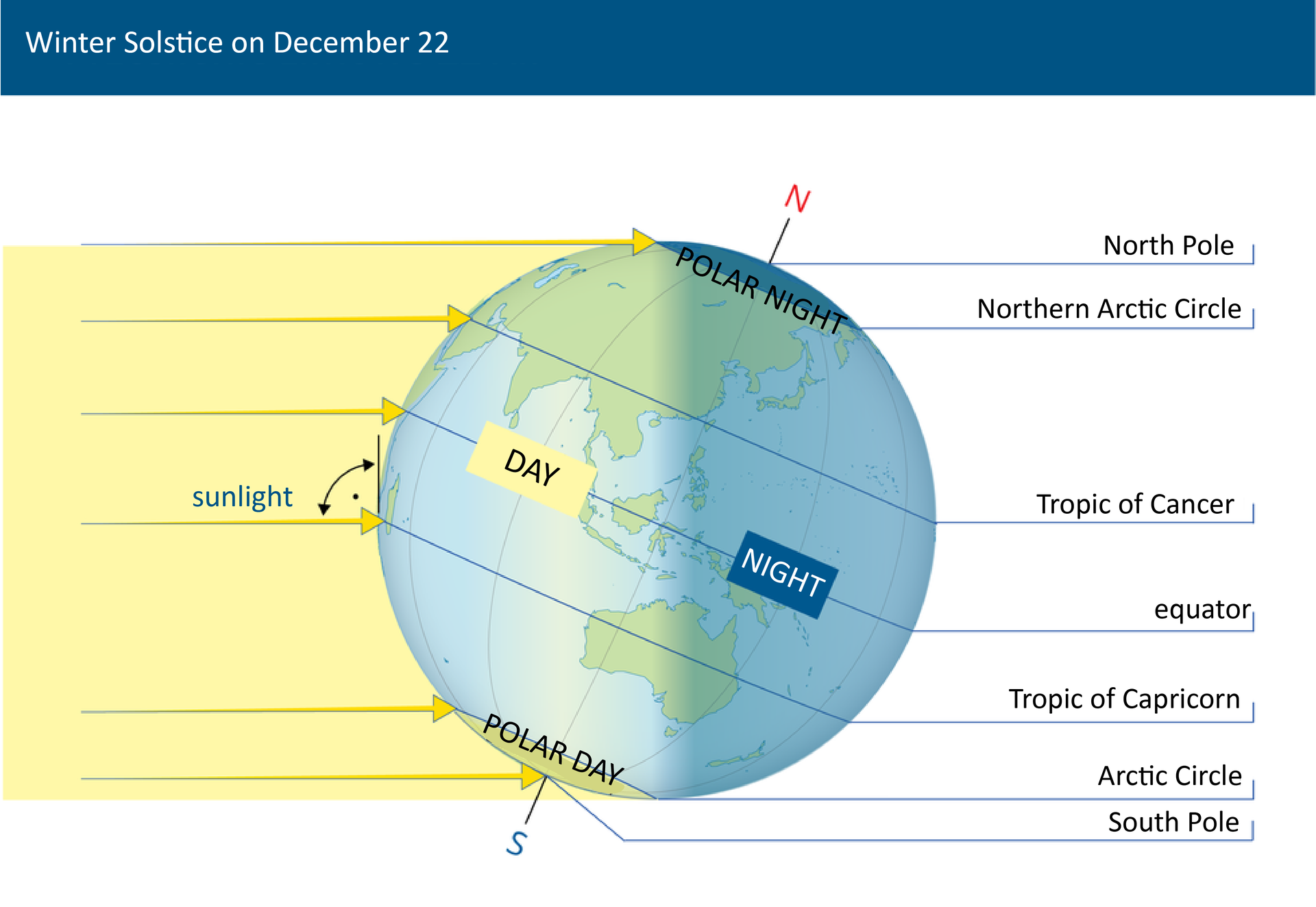
The Earth’s North Pole is tilted towards the Sun for half of the year, and its South Pole is tilted towards the Sun for the other half. It's the result of the inclination of the Earth's axis and its circular motion. For this reason, for half of the year the northern hemosphere receives more light and heat from the Sun and the southern hemisphere receives less, and then the situation is reversed. The moment when the axis is the most tilted towards the Sun with its nothern tip (summer solsticesummer solstice) occurs on June 22nd. After half a year the situation is reversed and it’s the southern hemisphere that receives more light. That moment falls on December 22nd (winter solsticewinter solstice). In Poland, that day is the shortest day of the year, whereas beyond the Arctic CircleArctic Circle there’s polar night.
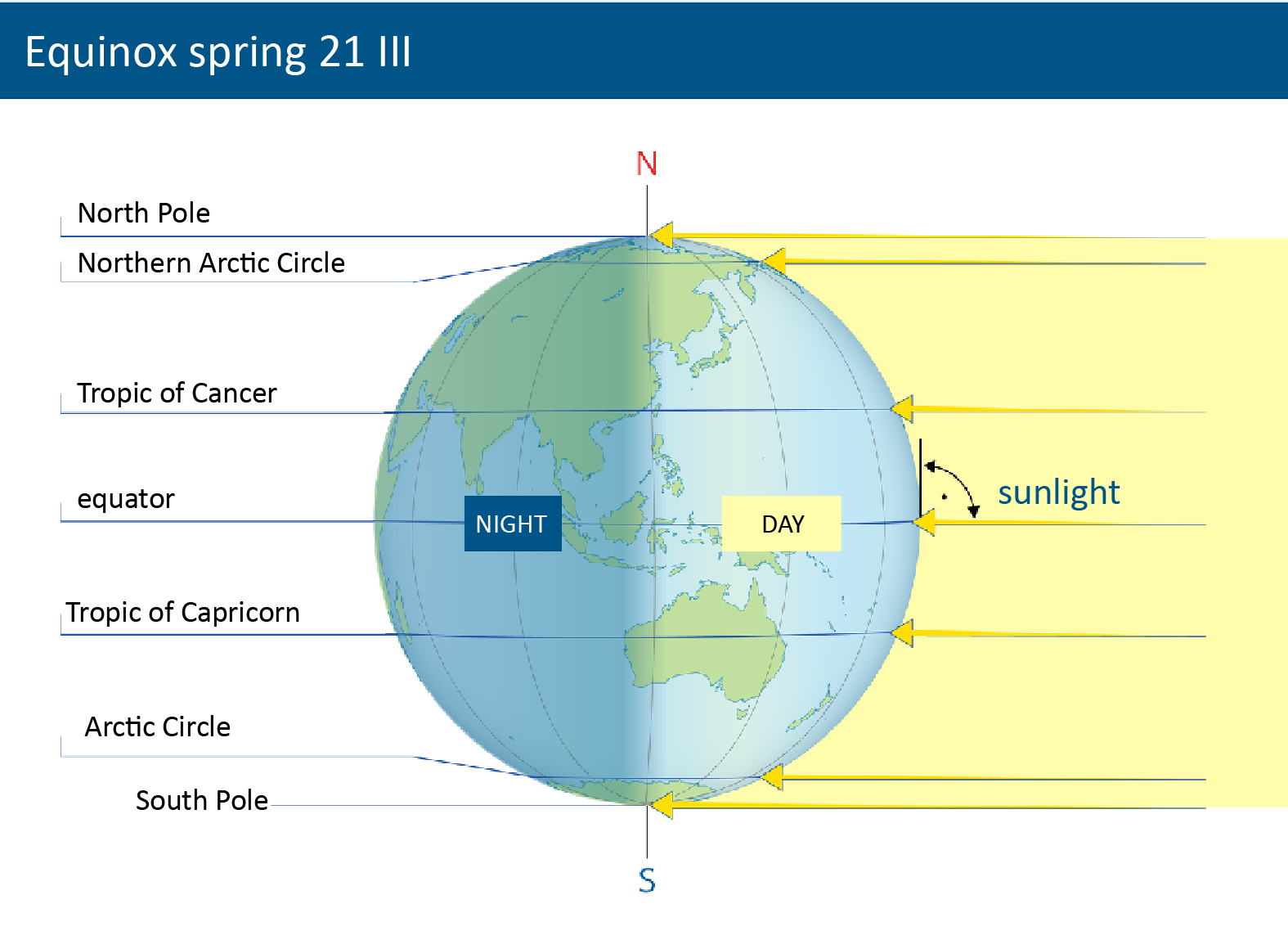
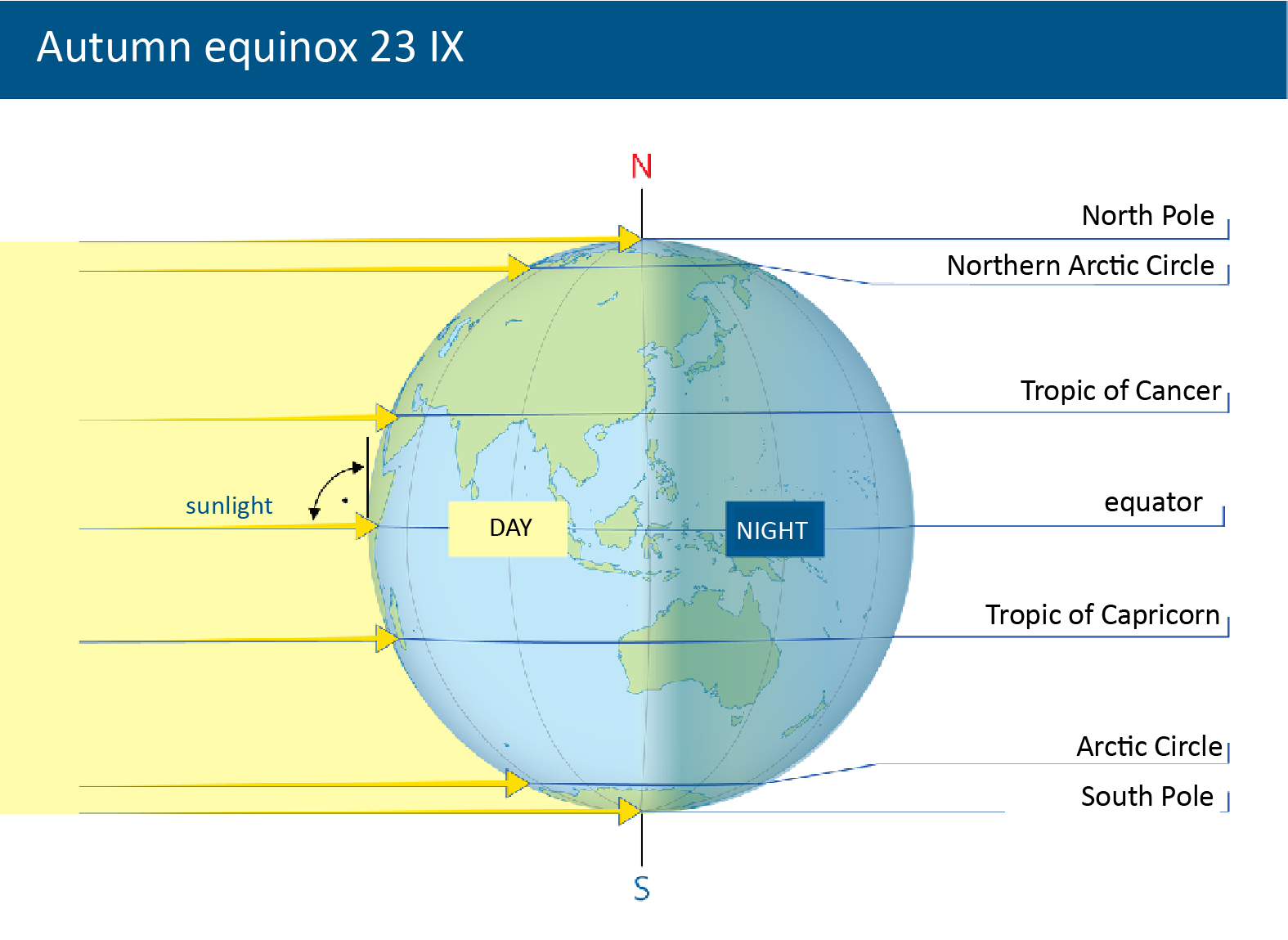
Twice a year the Earth’s axis is positioned in such a way that both hemisphere are illuminated identically: on March 21st during the vernal equinoxvernal equinox and on September 23rd during the autumnal equinoxautumnal equinox.
Using available sources, find out where and how the Sun is positioned at the poles on equinox and solstice days.
Earth's circulation time around the Sun takes 365 days 5 hours and about 49 minutes. That’s slightly more than a calendar year. That’s why it became necessary to add one day in February every four years. Every four years a year has 366 days and is called a leap year.
When setting the Earth's axis allows identical illumination of both hemispheres of Earth?
- each day of the year
- once a year on the day of the vernal equinox
- once a year on the day of the autumnal equinox
- twice a year: on the day of the vernal equinox and on the day of the autumnal equinox
Mark all true statements.
- When the North Pole experiences polar night, the South Pole experiences polar day.
- On the days of summer and winter solstice, both poles experience a polar day.
- Both poles experience polar day for half a year and polar night for the other half.
- On the winter solstice day, the entire northern hemisphere experiences polar night and the entire southern hemisphere experiences polar day.
Do the randomly selected elements create a true statement?
|
Polar night on the North Pole lasts
|
from the vernal equinox (21 III)
|
to the autumnal equinox (23 IX).
|
|
Polar day on the South Pole lasts
|
from the vernal equinox (21 III)
|
to the vernal equinox (21 III).
|
|
Polar day on the North Pole lasts
|
from the autumnal equinox (23 IX)
|
to the vernal equinox (21 III).
|
|
Polar night on the South Pole lasts
|
from the autumnal equinox (23 IX)
|
to the autumnal equinox (23 IX).
|
Summary
The Earth’s revolution around the Sun takes 365 days 5 hours and approx.
The inclination of the axis of the Earth’s rotation in combination with its revolution lead to the Earth having seasons.
Twice a year the Earth’s axis is positioned in such a way that both hemisphere are illuminated identically: on March 21st during the vernal equinox and on September 23rd during the autumnal equinox.
Using available sources of information, describe the behaviour of storks and where they stay during the spring, summer, autumn and winter. Demonstrate the link between the storks’ behaviour and the seasons of the year.
Keywords
summer solstice, winter solstice, autumnal equinox, vernal equinox
Glossary
koło podbiegunowe – równoleżnik ziemski o szerokości geograficznej 66°33'39”N (na półkuli północnej) lub 66°33'39”S (na półkuli południowej)
przesilenie letnie – na półkuli północnej to moment, gdy biegun północny znajduje się najbliżej Słońca, a biegun południowy najdalej; Słońce w tym dniu góruje w zenicie nad zwrotnikiem Raka; w tym samym momencie na półkuli południowej jest przesilenie zimowe
przesilenie zimowe – na półkuli północnej to moment, gdy biegun północny jest najbardziej oddalony od Słońca, a biegun południowy znajduje się najbliżej; Słońce w tym dniu góruje nad zwrotnikiem Koziorożca; w tym samym momencie na półkuli południowej trwa przesilenie letnie
równonoc jesienna – na półkuli północnej to moment, gdy Ziemia osiąga punkt na swojej orbicie, w którym promienie słoneczne padają prostopadle na równik i są równocześnie styczne do jej powierzchni na biegunach; począwszy od tego momentu Słońce zaczyna bardziej oświetlać południową półkulę Ziemi
równonoc wiosenna – na półkuli północnej to moment, gdy Ziemia osiąga punkt na swojej orbicie, w którym promienie słoneczne padają prostopadle na równik i są równocześnie styczne do jej powierzchni na biegunach; począwszy od tego momentu Słońce zaczyna bardziej oświetlać północną półkulę Ziemi tellurium