Mapa pojęć
Our world has always been full of inequalities. Those with money have better access to education and healthcare, and can afford services which others cannot even dream about. Those affected by the crisis of poverty, on the other hand, lack basic facilities. Sometimes, though, there are people around us who struggle to make ends meet and we may not even know about it. Poverty has many faces.
Świat wokół nas od zawsze był pełen nierówności. Ci, którzy mają do dyspozycji pokaźne sumy pieniędzy, mają też lepszy dostęp do edukacji i opieki zdrowotnej oraz mogą pozwolić sobie na korzystanie z przyjemności, o których inni nawet nie marzą. Jednak są też tacy, którym brakuje podstawowych udogodnień, aby mogli prowadzić spokojne życie – w kryzysie ubóstwa. Zdarza się, że żyją blisko nas. Z trudnością wiążą koniec z końcem, a my możemy nie zdawać sobie z tego sprawy. Kryzys ubóstwa ma wiele twarzy.
Choose the synonyms of the word POOR. More than one answer is correct.
Study the following expressions connected with diseases of poverty. Then drag and drop the words in the correct place.
Put the expressions in the spots marked “...” by double‑clicking on the text and typing in the correct word from the list below.
AFFORDABLE
CRAMPED
CONTAMINATED
SOCIAL
MEDICAL
PATTERNS
TRAP
CROPS
TERTIARY
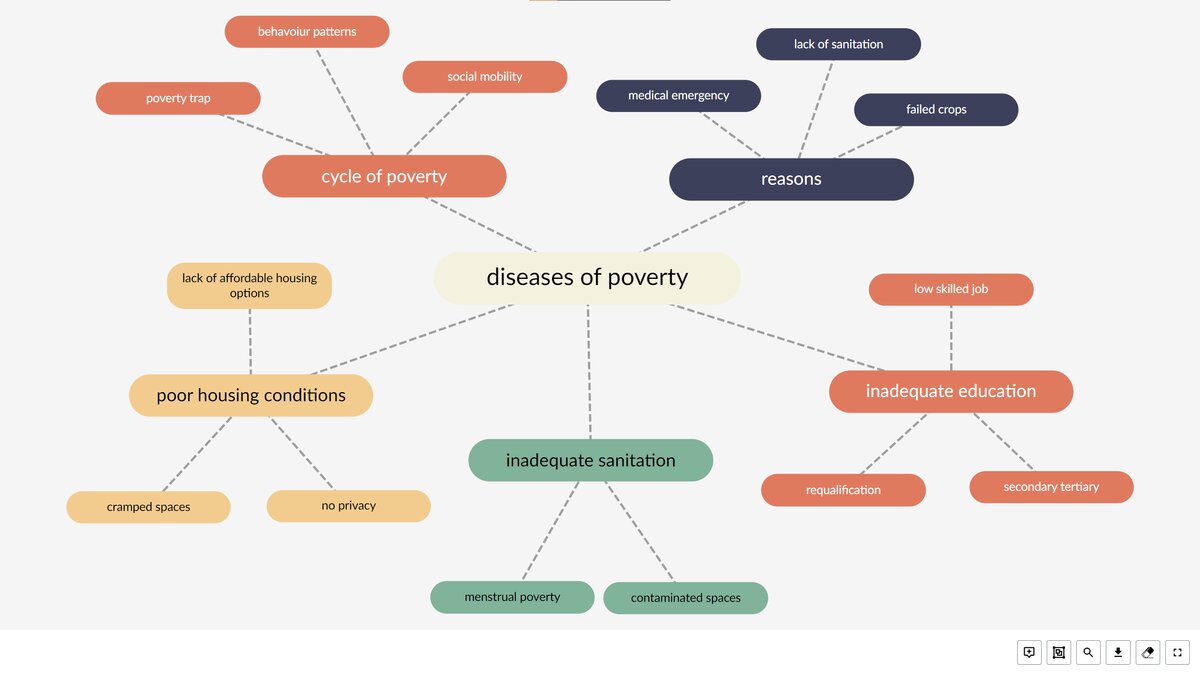
Click the numbers referring to different aspects of diseases of poverty, play the recordings and learn more about them. Then do the exercises below.
Ilustracja przedstawia mapę myśli z zaznaczonymi kategoriami, posiada pięć punktów interaktywnych, po naciśnięciu których pojawiają się nagrania. Transkrypcja do nagrań znajduje się poniżej.
Nr 1 CYCLE OF POVERTY
Nr 2 REASONS
Nr 3 INADEQUATE EDUCATIONS
Nr 4 INADEQUATE SANITATION
Nr 5 POOR HOUSING CONDITIONS
a) people find it impossible to change their material situation due to
a number of hindrances.
b) children don’t see their parents as role models.
c) recession makes many people unemployed.
d) parents don’t support their children in finding better employment.
2. Which situation is unlikely to result in people ending up in poverty?
a) having to pay for a costly medical treatment.
b) rainy days.
c) being made redundant suddenly.
d) floods or wildfires.
3. Children raised in poor areas:
a) are less likely to find good jobs.
b) never finish school.
c) go to college or university less often than their peers from other districts.
d) only work in low-skilled jobs.
4. Which statement is NOT true about poor sanitation?
a) It may lead to diseases and death.
b) It stops people from attending to their daily duties.
c) It prevents people from improving their material situation.
d) It makes people contaminate water.
5. Living in inadequate housing conditions:
a) makes it more difficult for kids to acquire education.
b) makes people have cramps.
c) makes people spend more money.
d) is always the ramification of being poor.
Answer the question. What can be done to help communities in crisis to help break the poverty cycle. Write 6–7 sentences.
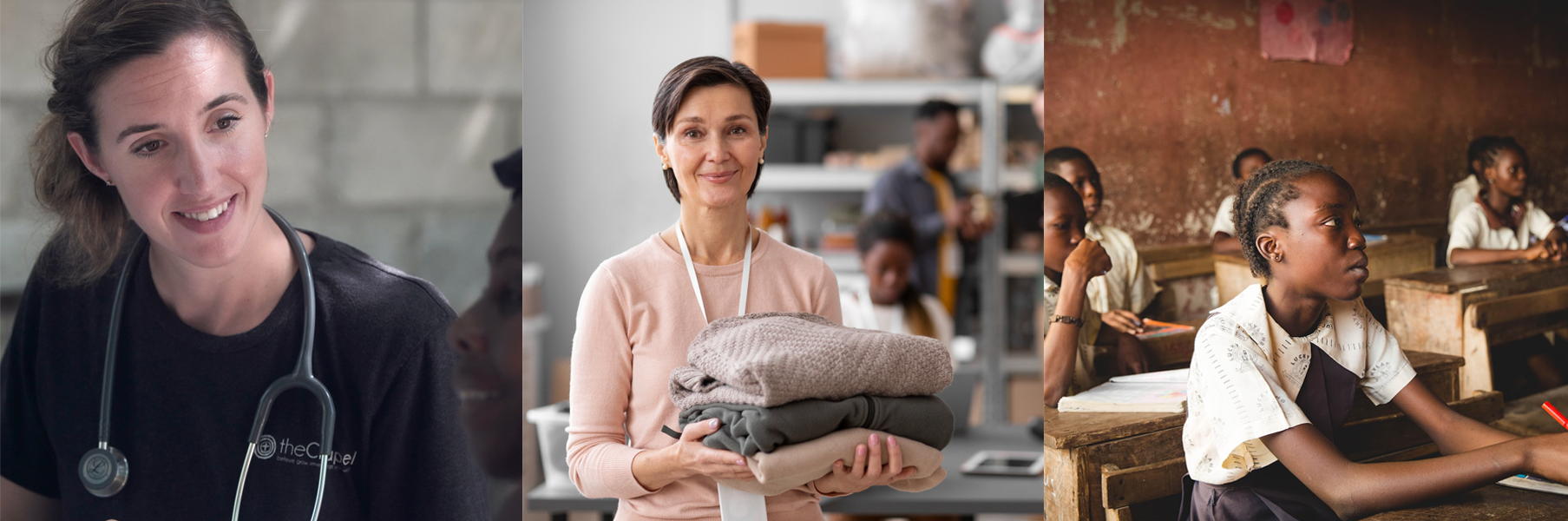
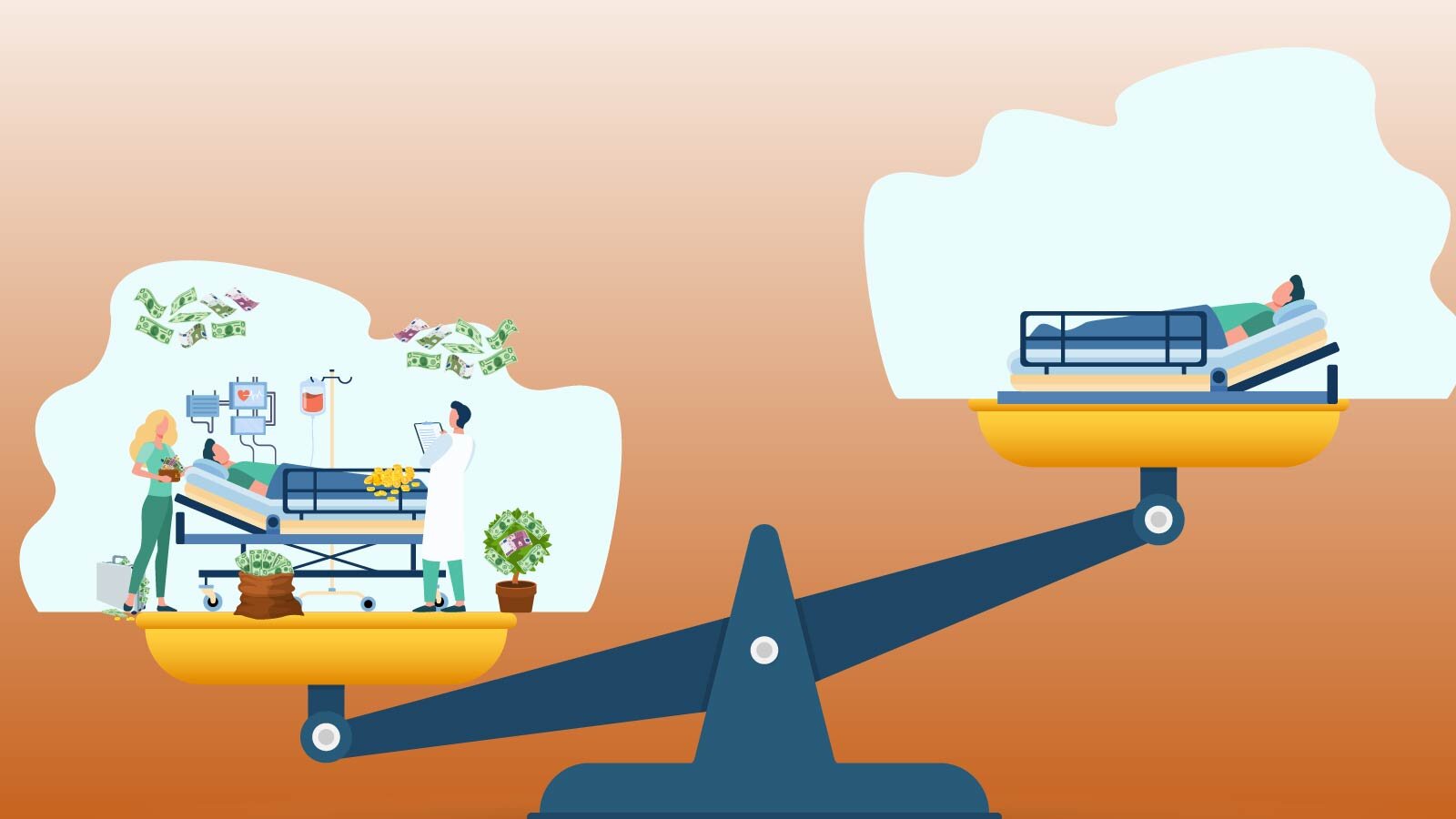
Analyse the pictures below. They show some aspects of supporting countries afflicted by the poverty crisis. Refer to 2 of the pictures and describe what can be done to help communities in crisis to help break the poverty cycle. Write 6–7 sentences.