Meiosis - the division leading to the formation of gametes
genetic information is found in the nucleus of the cell in the form of DNA.
discuss the importance of cell division for the functioning of the body.
Meiosis – the division leading to the formation of gametes
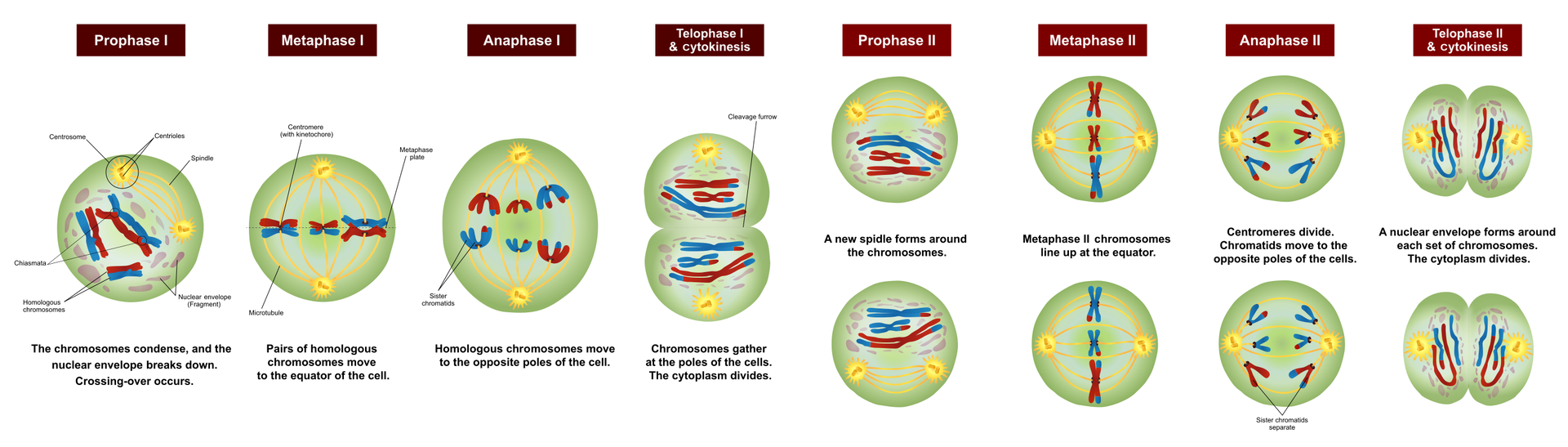
MeiosisMeiosis is the division, which leads to the creation of four daughter cells from one original cell. Each of them contains only half of the genetic material (1n) original cell (2n). As a result of meiosis, reproductive cells (gametes) arise in humans and other animals.
During meiosis, homologoushomologous chromosomeschromosomes are coming together, forming a group of 4 chromatids. Two of them in their composition have genetic material from the father, two from the mother. Chromatids twist around each other. This process can cause cracking chromatids. Such cracks are repaired immediately, but sometimes chromatid fragments are exchanged between homologous chromosomes. Next, the homologous chromosome pairs are placed in the middle of the cell, and the protein fibers pull off the individual chromosomes (made of two chromatids) in opposite directions. This division follows another, similar to mitosis.
Meiosis occurs less frequently than mitosis and is characteristic only for eukaryotic organisms. Diploid cells go through it. It is not possible in haploid cells.
The gametes produced by one and the same individual differ in their genetic material because:
the chromosomes from the father and mother divide into gametes at random;
during meiosis between homologous chromosomes of the same pair there is a process of random exchange of chromatid fragments, i.e. genetic recombinationgenetic recombination.
During fertilization, as a result of combining the sperm and the egg cell, a unique set of genes is created. Therefore, the children of the same parents differ in many features.
Specify how many chromosomes were found in the original cells from which meiosis produced descendant cells with the following number of chromosomes in the cell nucleus: 3, 18, 24.
Explain why a haploid cell can not undergo meiotic division.
Before you see the movie „ Why a plant in which somatic cells contain 3n chromosomes does not produce seeds?”, Write down the research question and the hypothesis. Make notes while watching the movie, and finally add conclusions.

Film dostępny na portalu epodreczniki.pl
Nagranie filmowe tłumaczące dlaczego rośliny zawierające 3n chromosomów w komórkach somatycznych nie produkują nasion. Widocznych jest 9 chromosomów przdstawionych w postaci piktogramów, po trzy każdego rodzaju. 3 pary chromosomów w dwóch rzędach tworzą chromosomy homologiczne, które są zdolne do wytworzenia gamet. Ostatnie 3 różne chromosomy, nie tworzą chromosomów homologicznych. Nie są one zdolne do tworzenia gamet ponieważ zawierają nieparzystą liczbę chromosomów.
Select all true statements.
- As a result of meiosis, only two daughter cells are formed.
- Each of the cells formed during meiosis contain half of the genetic material of the original cell.
- During meiosis, there may be an exchange of a DNA fragment between two homologous chromosomes.
- The gametes formed as a result of meiosis contain a random set of chromosomes from each parent.
During fertilization, as a result of combining gametes formed by meiosis, each descendant from the same parents gains a unique set of genes. What does this mean in practice?
- Due to the fact that gametes are formed in the meiosis process, genetic variation increases.
- Due to the fact that gametes are formed in the meiosis process, genetic variability remains unchanged.
- Due to the fact that gametes are formed in the meiosis process, genetic variability decreases.
Assign these features to the appropriate division (mitotic or meiotic).
the daughter cells are genetically identical to the original cell, the daughter cells have a reduced number of chromosomes relative to the origninal cell, the daughter cells are genetically identical to each other, daughter cells are genetically different, it leads to the formation of gametes, the daughter cells have the same number of chromosomes as the origninal cell, occurs only in diploid cells
| Mitosis | |
|---|---|
| Meiosis |
Adjust the number of chromosomes in the reproductive cells arising from meiosis to the number of chromosomes in the parent cell.
n = 4, does not produce gametes in the meiosis process, n = 23, n = 46, does not produce gametes in the meiosis process
| 2n = 46 | |
| 2n = 8 | |
| 3n = 33 | |
| 2n = 92 | |
| 1n = 8 |
Summary
Chromosomes consist of DNA strands and enable precise division of genetic material between daughter cells.
Diploid cells contain a double set of chromosomes, and haploid cells - a single one.
Prior to cell division, there is always a doubling of the amount of DNA in the cell nucleus.
Meiosis is the division of the nucleus, thanks to which four haploid daughter cells are formed from one diploid original cell.
Meiosis leads to the generation of reproductive cells (gametes).
During meiosis there is a genetic recombination process, thanks to which the daughter cells are not identical
Keywords
Meiosis, homologous chromosomes, genetic recombination
Glossary
chromosomy – podziałowa postać DNA; wydłużone, pałeczkowate struktury powstające w jądrze tuż przed podziałem komórki i widoczne w czasie podziału jądra
chromosomy homologiczne – chromosomy o tym samym kształcie i wielkości; zawierają podobną informację genetyczną; układają się w pary na początkowym etapie mejozy; w każdej parze jeden z chromosomów pochodzi od matki, a drugi od ojca
mejoza – proces podziału jądra komórkowego, w wyniku którego z jednej komórki powstają cztery komórki potomne o zredukowanej o połowę (w porównaniu do komórki macierzystej) ilości materiału genetycznego; przebiega dwufazowo – pierwsza faza jest redukcyjna (redukcja liczby chromosomów)
rekombinacja genetyczna – proces wymiany fragmentów chromatyd między chromosomami homologicznymi, w wyniku którego zwiększa się zmienność genetyczna