Mixtures
that substances consist of particles;
that the properties of substances depend on the particles they are made of.
give examples of mixtures;
distinguish a compound substance from a mixture based on their molecular structure;
differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures and indicate examples of such mixtures in the environment;
propose methods for separating the mixtures components.
What are mixtures?
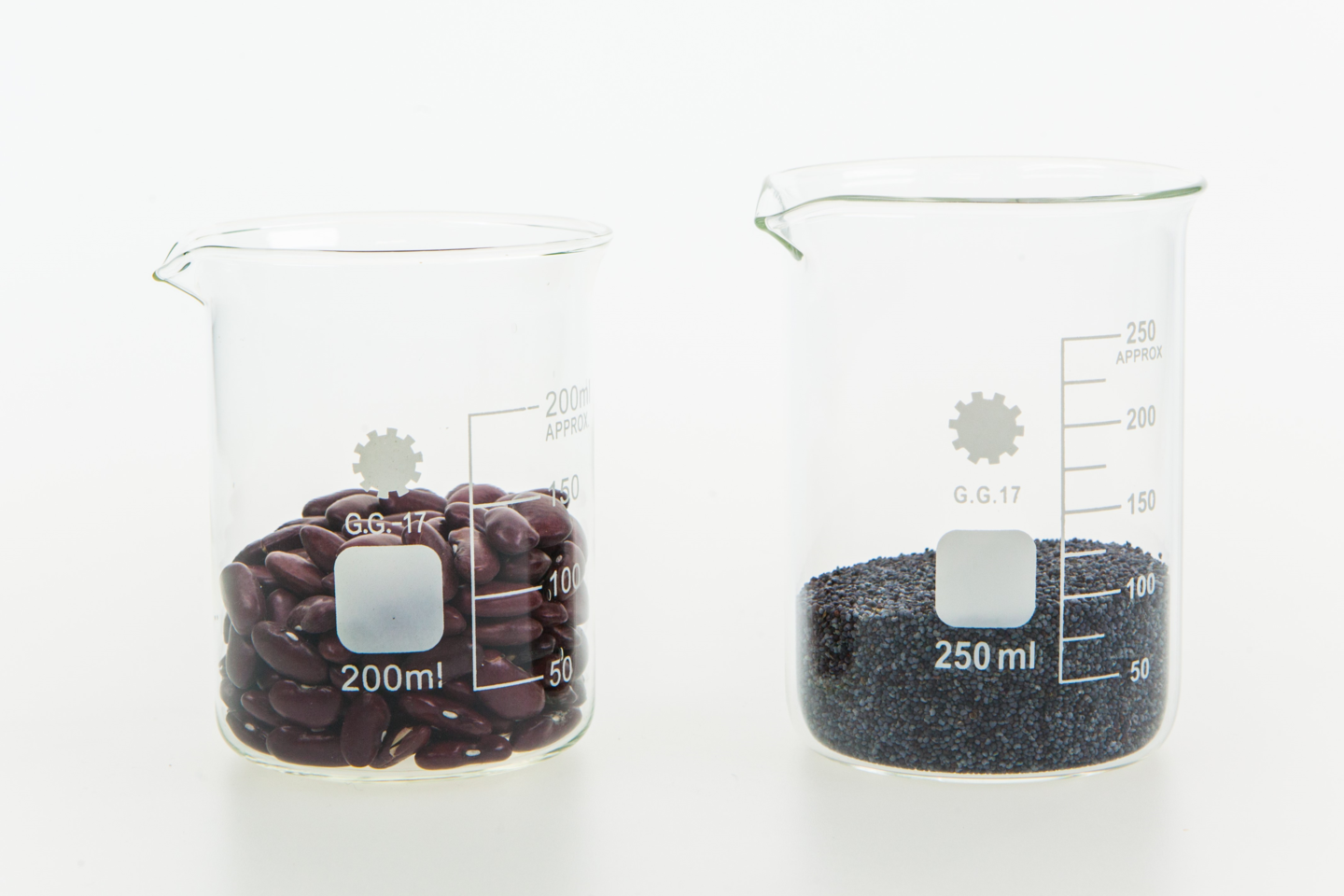
In nature, very rarely can single substances be found. More often we are dealing with mixtures. A mixturemixture is formed when we mix at least two different substances together.
Mixtures can be formed of solid substances, liquids or gases. Particles in the mixture do not change their properties. However, the mixture formed by them may differ in properties from their components.If, for example, you mix table salt and water, you will get a mixture that has a lower melting point than pure water, but the properties of the ingredients of this mixture remain the same.
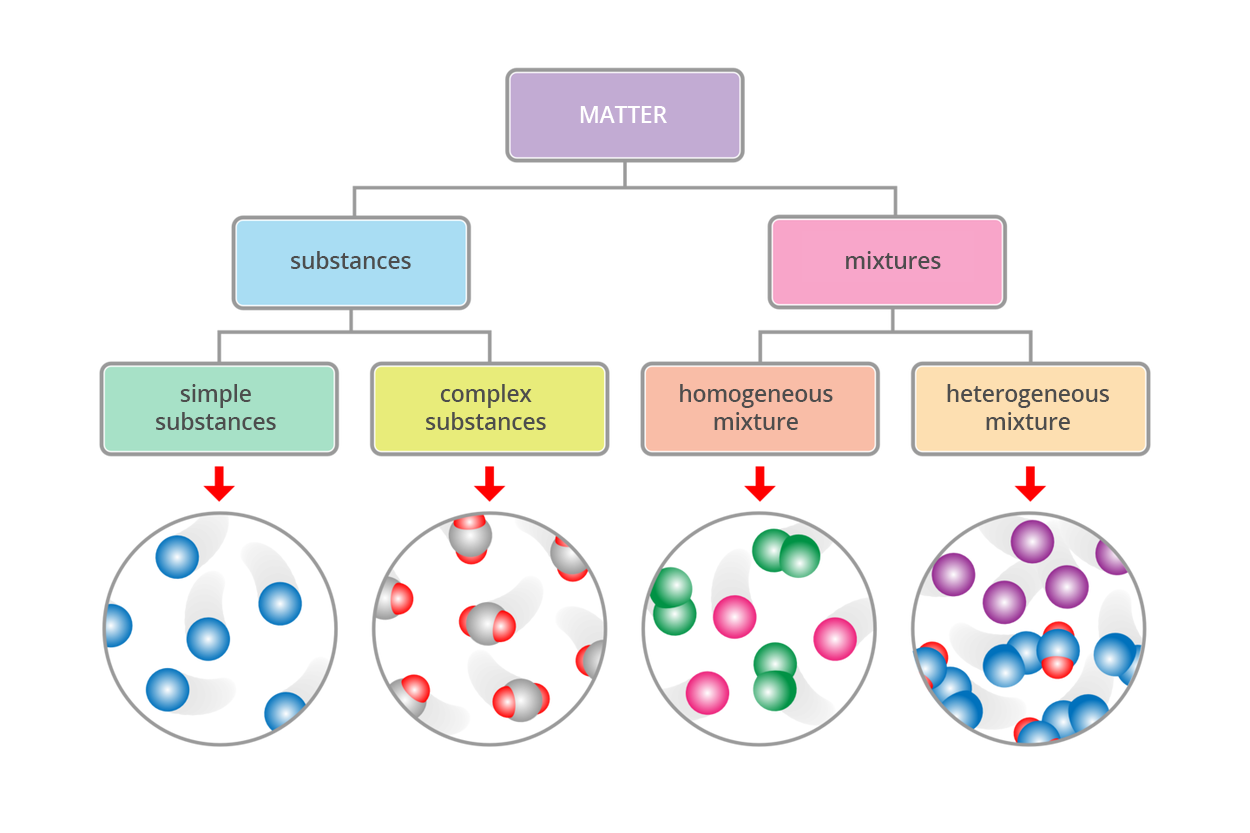
Comparison of simple substance, complex substance and mixture | |||
Characteristic | Simple substance | Complex substance | Mixture |
Components | one element | one chemical compound | two or more elements or chemical compounds |
Determination of properties | the same as the element which creates it | the same as chemical compound, but differs from the elements that make it up | able to determine the properties of individual components |
Separation of ingredients | impossible to break down into simpler substances | the possibility of separation only through chemical changes (changing the properties of the substance) | can be separated into components by physical changes (eg. change of temperature) |
Examples | oxygen, hydrogen, mercury, gold | water, quartz, carbon dioxide, kitchen salt | tea, fruit drink, milkshake, air, fog, foam |
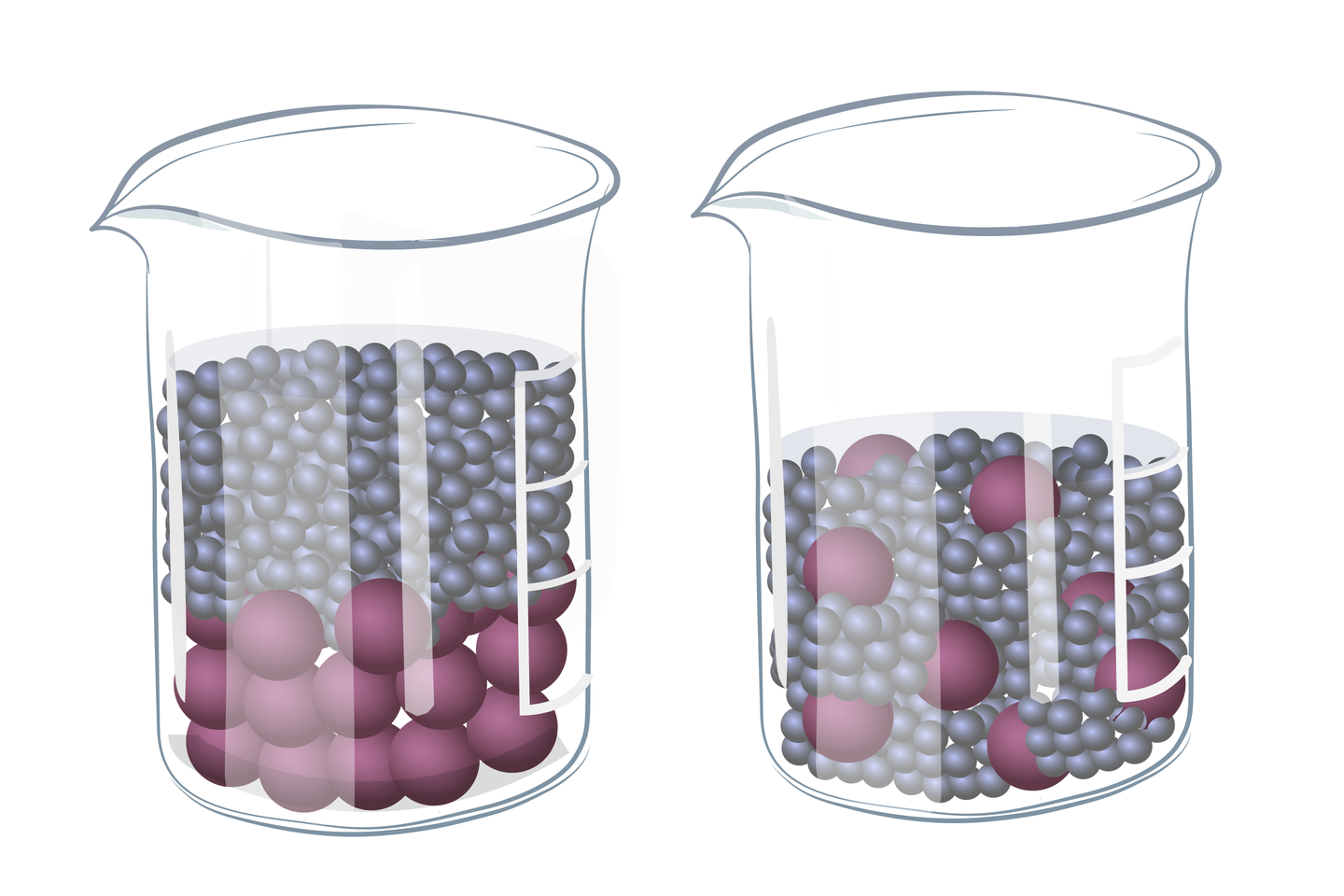
Types of mixtures
Sometimes, when we mix two substances, eg water and sand, we can distinguish the components of the mixture.We then we have a heterogeneous mixtureheterogeneous mixture. We see that the sand slowly sinks to the bottom. The situation is different when mixing table salt with water. The salt dissolves in water and we get a clear liquid. If we are unable to distinguish the components of a mixture, it is a homogeneous mixturehomogeneous mixture.
Separation of mixtures
The components of many mixtures can be separated. The separation method is selected based on the properties of the components.
The mechanical method consists of separating the ingredients by hand or with the help of tools. Mechanical separationMechanical separation can be used on a heterogeneous mixtures of solids. The process consists of removing larger pieces of a substance with tweezers or sieving the mixture. If one of the components of the mixture is liquid, then we can use filtrationfiltration. It consists of filtering a heterogeneous mixture through an appropriate filter. The filter keeps the solids and the liquid flows into the container under it.
It is more difficult to separate the components of a homogeneous mixture. One of the methods that can be used for a mixture of homogeneous solid and liquid, is evaporation. It consists of heating a mixture, the result of which is that the liquid, e.g. water, turns into steam, and a solid substance remains in the container (in this way the salt in salt water can be obtained).
Separation of mixture components.
water,
sand,
a few small stones,
strainer,
chalk,
teaspoon,
a plate
4 glasses,
2 funnels,
filter paper.
Fill two glasses halfway with water.
Put a small teaspoon of sand and a few pebbles in the first glass and mix the contents of the glass.
Put half a teaspoon of crushed chalk into the second glass. Mix the contents.
Wait a few minutes. Prepare the filters. To do this, cut 2 circles with blotting paper and fold them so that you get 1/4 of a circle. Place the filters in the funnels which are on the empty glasses.
Pass the contents of the first and second glasses through the filters.
The components of the first mixture that have settled on the filter, spread on the paper and leave to dry for a few hours.
Pass the dry ingredients through a sieve. Place a plate under the sieve.
To separate fine solids (sand, powdered chalk), from liquid is best done by filtering. Larger elements (pebbles) can be separated from mixtures with a sieve.
Before you watch the film „Separation of components of homogeneous mixtures”, write down the research question and the hypothesis. Make notes while watching the movie, and finally make conclusions.
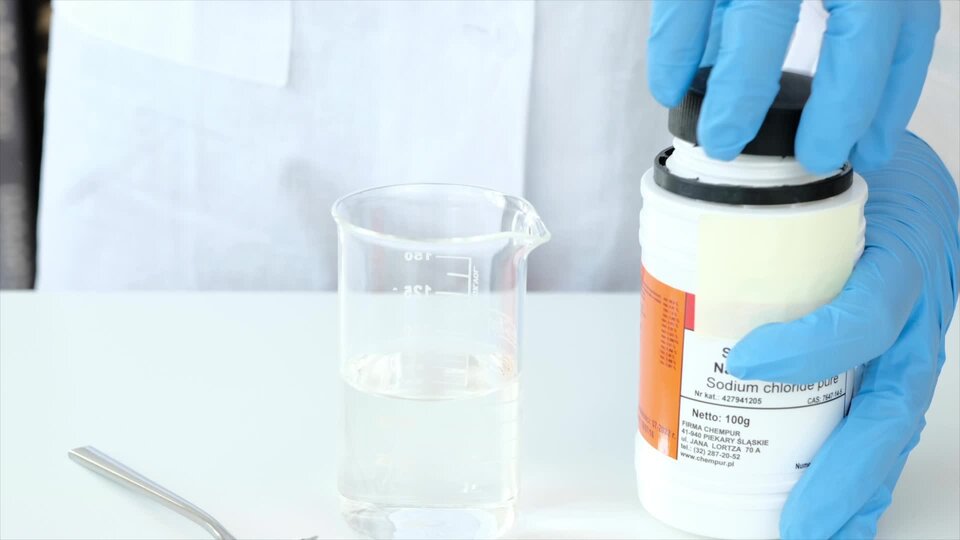

Film dostępny na portalu epodreczniki.pl
Nagranie filmowe przedstawiające eksperyment w laboratorium. Na stole znajdują się rzeczy potrzebne do przeprowadzenia doświadczenia takie jak: łyżka, zlewka z wodą oraz pojemnik z chlorkiem sodu. W wodzie rozpuszczono trzy łyżeczki chlorku sodu, część roztworu eksperymentator przelał do innego naczynia i podgrzał. W naczyniu pozostała sama sól.
More, but less
It happens that after mixing, the substances take up less space than each of them separately. This is because particles of different substances have different sizes. If they are mixed, smaller particles fill the space between larger ones.
Examine how particles are arranged in a mixture.
2 glasses,
felt‑tip pen,
beans,
poppy seeds,
ruler.
Fill one of the glasses up to 1/3 of the height with beans and the other with poppy seeds to the same height. 2.Select the level on which each glass is filled with a marker pen. Measure the height from the bottom of the glass to the line.
Sprinkle the poppy seed into a glass with beans and shake the glass.
Mark the level where the mixture of poppy seeds and beans reaches. Measure the distance from the bottom to the new line with a ruler. Is the distance the sum of the poppy seeds and the beans? Examine the resulting mixture. What do you see?
If, after pouring the poppy seeds into the beans, the mixture does not take up as much as the total volume of ingredients, it means that the poppy seeds are between the beans.
Group the examples of homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures by dragging to the appropriate fields.
pepper and salt, vegetable soup, milk, air, jelly, macaroni and cheese, water and pepper, vanila icecream with dried fruit, salt and water, tea
| homogeneous mixtures | |
|---|---|
| heterogeneous mixtures |
Assign the appropriate separation method to the mixtures.
mixture of water and table salt, a mixture of chalk and water, a mixture of rice and salt
| evaporation of water | |
| sieving | |
| filtration |
Summary
Mixtures are formed by combining two or more substances.
Mixtures are divided into: homogeneous and heterogeneous.
The components of homogeneous mixtures can not be distinguished by the naked eye or magnifying glass, whereas in heterogeneous mixtures we can distinguish at least one component.
Depending on the nature of the components forming the mixture, a variety of methods may be used for their separation, e.g. mechanical separation, filtration and evaporation.
Suggest two ways to separate a mixture of sugar and poppy seeds. Consider what properties are different and which properties can be used to separate them. Decide in practice which of the methods you suggest is better and takes less time.
Keywords
mixture, homogeneous mixture, heterogeneous mixture, filtration, mechanical separation
Glossary
mieszanina – substancja złożona przynajmniej z dwóch różnych substancji
mieszanina jednorodna – mieszanina, której składników nie można rozróżnić, np. powietrze, sok
mieszanina niejednorodna – mieszanina, w której gołym okiem lub za pomocą prostych urządzeń powiększających (np. lupy) można rozróżnić przynajmniej jeden składnik, np. mieszanina piasku i wody
filtracja – proces przepuszczania mieszaniny niejednorodnej (ciecz + ciało stałe) przez filtr; na filtrze pozostaje ciało stałe, a ciecz spływa do naczynia
rozdzielanie mechaniczne – rozdzielenie składników mieszanin niejednorodnych za pomocą narzędzi (sita, magnesu itp.)