Mutations and their causes
sexual reproduction is the cause of genetic variation;
some diseases are the results of errors which happened in DNA.
to explain the difference between the inherited genetic variation and non‑inherited variation and give examples;
to explain what mutations are and what their connection with genetic variation is;
to give examples of mutagens.
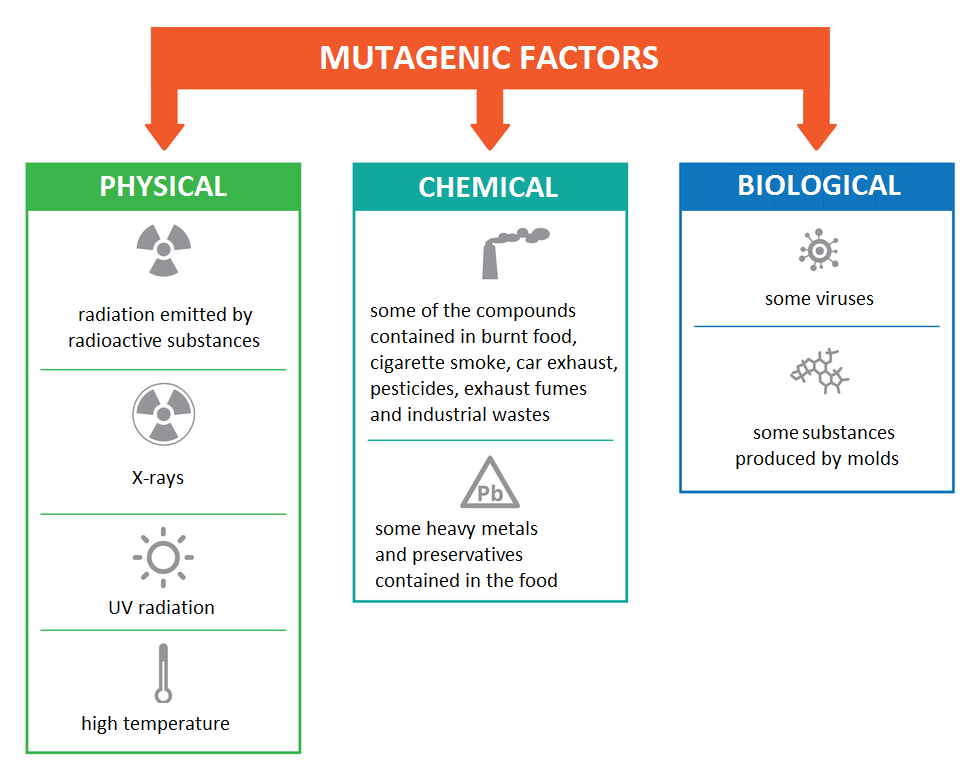
During copying of the DNA strand errors happen. As a result of those errors, genetic information changes. Those sudden changes to the genetic material of the cell, which are lasting ones (they become permanent), are called mutations.mutations. Most often, permanent changes in the DNA take place not as a result of an error in copying of the strand, but as a result of external factors, called mutagensmutagens. They can not only cause changes in the sequence of nucleotides (gene mutations), but also in the build and number of chromosomes (chromosome and genome mutations(chromosome and genome mutations. Mutagens are physical factors, e.g. UV radiation; chemical factors, e.g. some chemical compounds in exhaust fumes (dioxinesdioxines) and cigarette smoke; and biological factors, such as some viruses and products of the metabolism of mould.
Mutations that take place in individual genes are called gene mutationgene mutation. Those are the changes in the sequence of individual nucleotides in the DNA. Those can appear in any given DNA section.
Other types of mutations are chromosome and mutations which are based on the change of the structure of chromosomes, caused mainly by mutagenic agents. As a result of e.g. ionizing radiation, chromosomes can break into pieces, which can rearrange themselves in a different configuration. Changes in number of chromosomes (genome mutations) occurs when an individual either is missing a chromosome from a pair or has more than two chromosomes of a pair (e.g. Down syndrome).
Majority of small changes in the genetic material is neutral. Some of them are beneficial and give the organisms an upper hand over those, which did not undergo that particular mutation. Very few mutations are dangerous. Sometimes a change in one nucleotide in the DNA sequence can cause an incorrect function of an entire gene, and, as a result, the creation of an incorrect protein (or lack of a protein) and, in consequence, a genetic disease.
Organism has many ways of protecting itself from DNA damage. However, sometimes those mechanisms fail. Mutations can spread to offspring cells during the next reproduction. Mutagens appearing in somatic cells are not inherited by the offspring that is created as a result of sexual reproduction, but they can e.g. cause cancer in organisms where they took place. If a mutation is in the DNA of reproductive cells, it will be transferred to the offspring.
Explain why during teeth x‑ray your torso is covered by a special apron that stops the radiation.
Are mutations dangerous for the life on Earth? Select the correct answer.
- Majority of mutations is not dangerous. It is proved by the current biodiversity.
- All mutations are dangerous. The effect of every mutation is a disease of the organism that underwent the mutation.
- All mutations are beneficial. This is proved by lack of diseases caused by mutations.
- It is unknown whether mutations are dangerous or beneficial. There hasn’t been any research done yet.
Match definitions to the notions below.
chemical compounds that are the result of burning organic substances and are mutagenic, factors that cause mutations, sudden permanent changes in genetic information of organism
| mutation | |
| mutagens | |
| dioxin |
Select mutagenic factors on the following list.
- some viruses
- high temperature
- high humidity of air
- nuclear radiation, x-rays, UV radiation
- sugar present in food
- certain heavy metals
Move the effect of the DNA mutation to the correct group.
The emergence of allele that conditions pink colour of flowers, the emergence of people with incorrect number of sex chromosomes in human population, the emergence of people suffering from Down syndrome in human population, the emergence of alleles that condition light coloured eyes in human population, the emergence of allele that conditions blue colour of fur in the population of domestic cat
| gene mutations | |
|---|---|
| chromosome and genome mutations |
Summary
Mutations change the genetic information; they can happen spontaneously, as a result of an error in the process of copying DNA, or can be caused by mutagenic agents.
Gene mutations take place in individual genes and are based on changes in the sequence of nucleotides in the DNA.
Chromosome and genome mutations are based on changes in the build and number of chromosomes, respectively.
Keywords
mutations, mutagens, gene mutations, chromosome and genome mutations
Glossary
dioksyny – związki chemiczne o działaniu mutagennymi i rakotwórczym; powstają głównie podczas spalania drewna, węgla, benzyny i innych substancji organicznych, w tym także odpadów komunalnych i przemysłowych, oraz podczas produkcji i przetwarzania metali
mutacja – nagła, trwała zmiana w informacji genetycznej organizmu, polegająca na zmianie struktury lub ilości materiału genetycznego
mutacja chromosomowa i genomowa – rodzaje mutacji polegające odpowiednio na zmienie struktury i liczby chromosomów
mutacja genowa – jeden z typów mutacji; polega na zmianie sekwencji nukleotydów w DNA, co może powodować powstanie nowych alleli genów
mutageny – czynniki powodujące mutacje, czyli zmiany w informacji genetycznej
zmienność genetyczna – naturalne różnice w sekwencji DNA, występujące u osobników danego gatunku, będące wynikiem rozmnażania płciowego i mutacji
zmienność niedziedziczna – zróżnicowanie cech osobników jednej populacji zachodzące pod wpływem środowiska; nie jest dziedziczona