My place of residence and its location on the administrative map of Poland
how to locate Poland on the map of Europe;
how to describe Poland’s location;
what are geographical and mathematical locations;
how to describe location of an object on the map;
how to read geographical coordinates on the map;
what geographical macroregions are located in Poland.
explain what the administrative division is;
determine which province you live in;
provide, and indicate on a map, all provinces and their capitals;
describe three level administrative division of Poland.
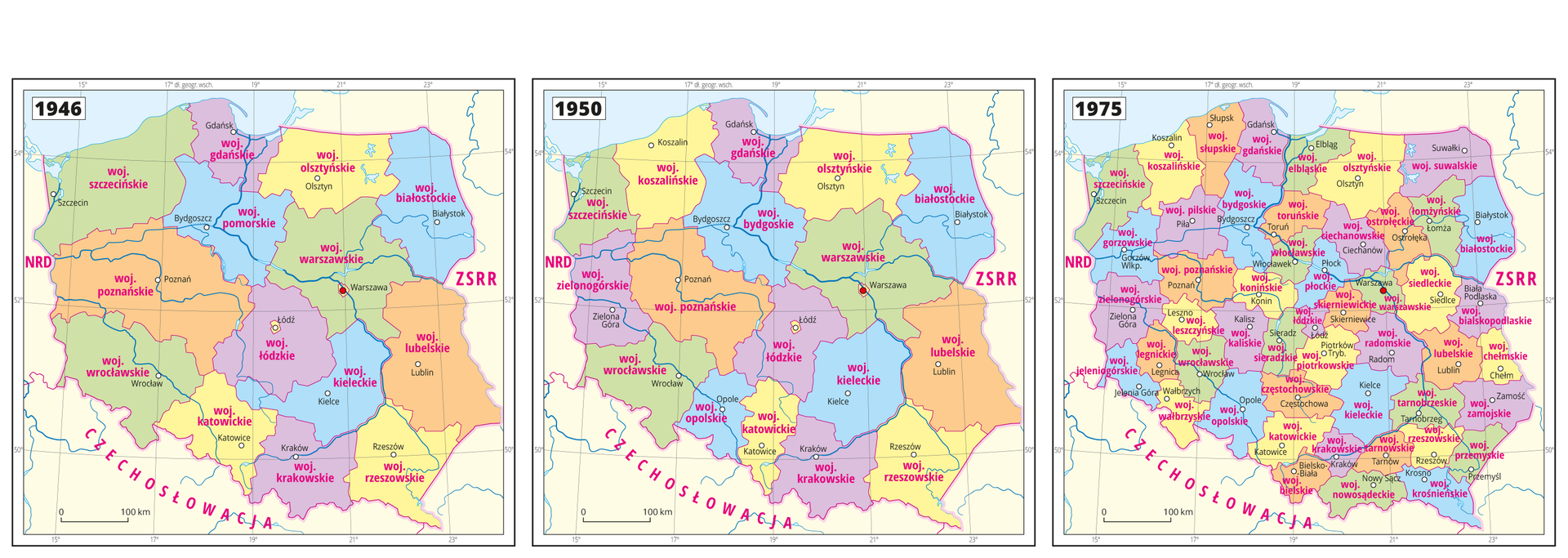
Former administrative divisions of Poland
Almost every country in the world manages its own, internal administrative divisionadministrative division. Its purpose is to make country‑level management easier. Currently, Poland is divided to 16 provinces (voivodeships). Each provinceprovince is divided to counties (poviats), and each county is divided to communes/municipalities. This administrative division was introduced in 1999. But, previous administrative division was different.
After the Second World War, in June 1946, 14 provinces were established. Another level of administrative division included counties (poviats), and the lowest one included communes and cities. In 1950, the number of provinces was increased to 17 as some large provinces in the West Lands were divided.
In 1955, communes were abandoned, and subsequently replaced by gatherings. In 1973, this process was reversed – gathering were replaced by communes. In 1975, 49 provinces were established with simultaneous dissolution of counties (poviats).
Modern administrative division of Poland
Currently, a three level administrative division (territorial division) is used.
On the 1st of January 1999, 16 provincesprovinces (first level) were established. Each province was divided to countiescounties (second level) which in turn were divided to communescommunes/municipalities (third level).
The current administrative division has been presented on e‑books.
Province maps displaying division to counties and communes/municipalities
The names of provinces often originate from historical or geographical macroregionsgeographical macroregions. Despite being proper names, in Polish these are written with no capital letter, e.g. “województwo mazowieckie” meaning the Masovian Province. The names of counties and communes usually originate from their capitals (major cities/towns), however, the name of any county is an adjective (e.g. “powiat oleśnicki” meaning the Oleśnica County), and the name of a commune/municipality is a noun (e.g. “gmina Dobroszyce” meaning the Dobroszyce Commune). Therefore, in Polish names of counties contain no capital letter, yet names of communes do.
In the nomenclature of counties one may found some exceptions, such as “powiat tatrzański” (Tatra County) with its capital in Zakopane or “powiat bieszczadzki” (Bieszczady County) with its capital in Ustrzyki Górne. There are also names originating from a pair of towns, such as “powiat strzelecko‑drezdenecki” (the Strzelece‑Drezdenko County) or “powiat ropczycko‑sędziszowski” (the Ropczyce‑Sędziszów County). There are also names of county capitals which make it quite hard to form a suitable name in adjective form — this is why there is “powiat suski” (the Sucha Beskidzka County) or “powiat niżański” (the Nisko County).
Geographical location of my city/town and my region
As you might remember from the primary school, Poland is divided into following geographical macroregions: the mountains (e.g. Sudetes), highlands (e.g. the Lublin Highlands), lowlands (e.g. the Silesian Lowlands), lakelands (e.g. the Masurian Lakeland) etc. During geography lessons, we will often determine location of a certain object in relation to these macroregions as well as in relation to other geographical objects, such as rivers, lakes or cities/towns. Describing geographical location of the object, we will also use primary and secondary directions as well as geographical coordinates.
Hypsometric maps of provinces have been presented on e‑books.
Observe the material. It presents three level administrative division.
Using the knowledge gained during the lesson, do the following exercises.
Match a city or a town with the correct province (voivodeship).
Biała Podlaska, Zielona Góra, Ełk, Przemyśl, Kędzierzyn-Koźle, Tarnów, Słupsk, Suwałki, Płock
| Warmian-Masurian province | |
| Podlaskie province | |
| Lublin province | |
| Lubusz province | |
| Masovian province | |
| Lesser Poland province | |
| Opole province | |
| Subcarpathian province | |
| Pomeranian province |
Indicate the coreect answer. In the West Pomerania province, the following cities and towns are located:
- Szczecin, Koszalin, Pyrzyce, Gryfice
- Szczecinek, Ustka, Starogard Szczeciński
- Kostrzyn, Police, Darłowo, Koszalin
- Kołobrzeg, Lębork, Wałcz, Szczecin
Summary
In Poland, a three level administrative division is used.
Division of Poland into smaller territorial units allows for better administrative management of the country and more efficient operation of public services.
Keywords
administrative division, province, voivodeships, communes, municipalities, counties
Glossary
gmina - jednostka podziału terytorialnego III stopnia
kraina geograficzna - jednostka ukształtowania terenu o krajobrazie odmiennym niż w sąsiednich jednostkach; różnice mogą występować w pokryciu terenu roślinnością czy zabudowaniami, a także w zaludnieniu, klimacie, budowie geologicznej
podział administracyjny - podział obszaru całego państwa na mniejsze jednostki terytorialne służący usprawnieniu życia i działalności jego mieszkańców, np. zarządzania krajem przez administrację państwową i samorządową (lokalną), funkcjonowania służby zdrowia, szkolnictwa, wymiaru sprawiedliwości itp.
powiat - jednostka podziału terytorialnego II stopnia (po raz pierwszy powiaty w Polsce wprowadzono w drugiej połowie XIV wieku)
powiat grodzki - obejmują obszary większych miast (jednej gminy miejskiej), które liczą ponad 100 tys. mieszkańców lub do końca 1998 roku były stolicami dawnych województw (poza Ciechanowem, Piłą i Sieradzem)
powiat ziemski - obejmują obszary kilku leżących obok siebie gmin zarówno miejskich, jak i wiejskich
województwo – jednostka podziału terytorialnego I stopnia