Natural environment and economy of Lithuania
the current territorial breakdown of Europe;
what the Soviet Union (USSR) was.
To discuss the location of Lithuania on the map of Europe;
To describe the natural environment of Lithuania;
To mention the main branches of industry in Lithuania.
Write down your associations with Lithuania.

Location of Lithuania
Lithuania is a small country located on the south‑eastern coast of the Baltic Sea. Its area is more than 65 thousand kmIndeks górny 22, which means that it is slightly larger than Slovakia and a bit smaller than the Czech Republic. It is almost five times smaller than Poland. Vilnius is the capital city. Lithuania borders four countries – Latvia in the north, Belarus in the east and south, Poland in the south, and the Kaliningrad Oblast, part of the Russian Federation, in the south‑west. The border with Poland is only 104 km long and it is the shortest in Lithuania. The Lithuanian part of the coastline of the Baltic Sea is even shorter – 90 km long.
Lithuania, Latvia and Estonia are the so‑called Baltic Republics. These small, now independent countries on the Baltic Sea, are former Soviet Republics. The Baltic Republics were the first to separate from the USSR, thus starting the break‑up of the Soviet empire. Lithuania proclaimed its independence already in 1990, facing strong opposition from Moscow which dispatched tanks to Vilnius. However, this did not stop the Lithuanians, and the country defended its independence.
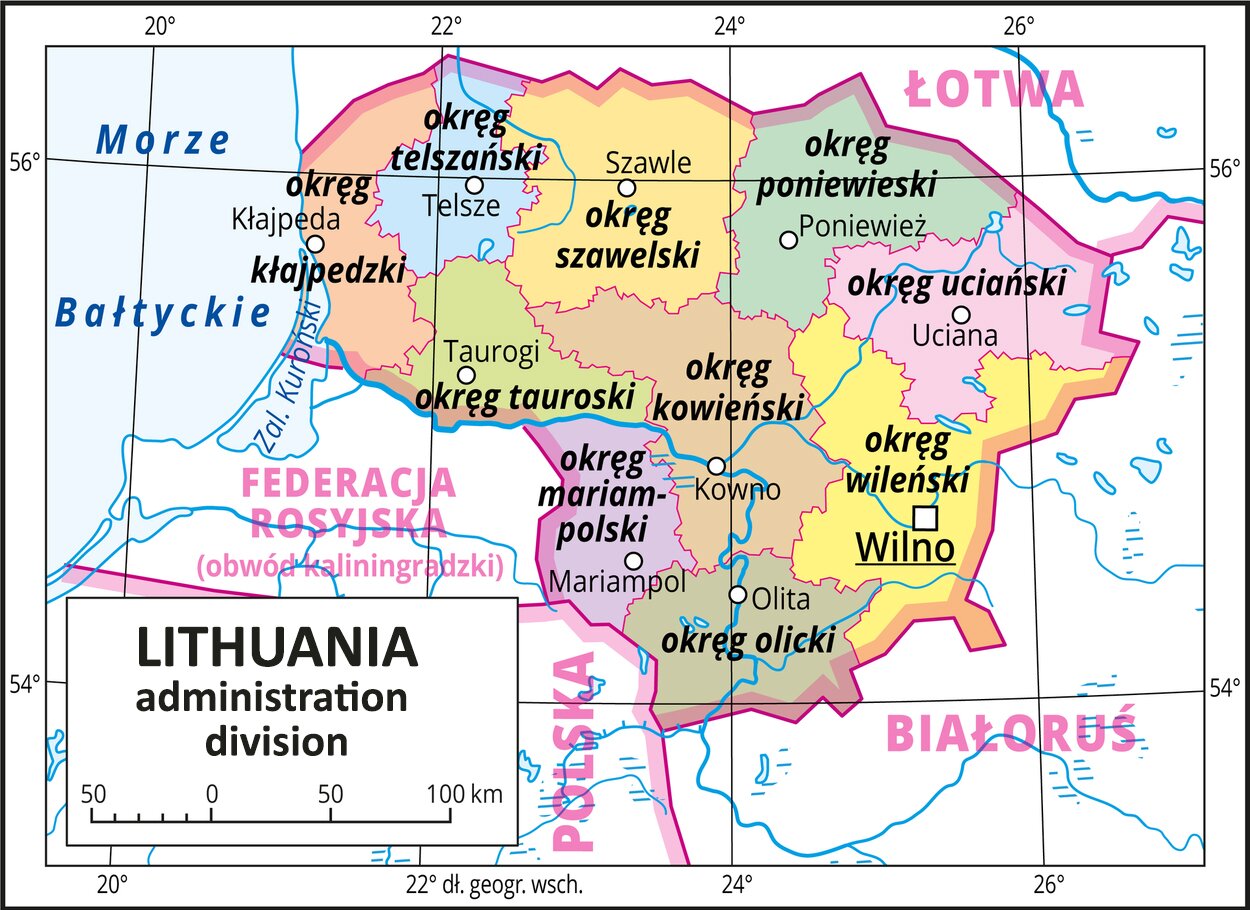
Due to the location and association with the Baltic Republics, Lithuania is sometimes considered part of Northern Europe. However, Poland has come to consider all European former Soviet Republics as part of Eastern Europe.
Natural conditions
In terms of terrain, Lithuania is very similar to Belarus – mostly with flat lowlands intersected by small hills. Both countries are located within the great East European Plain. The central part of Lithuania lies within the Middle Lithuanian Lowland. The Lithuanian Lakeland spreads in the east, with the highest landmark of the country - the Aukštaitija Mountain with a height of 294 m asl. Across the state border, the Lithuanian Lakeland neighbours the Belarusian Lakeland. In the west of Lithuania lies the Samogitia Highland which comprises the area of the historical region called Samogitia. The Baltic is bordered by a narrow strip of lowland coast.
The Lithuanian coastline is rather plain. Its only variation is the final fragment of the Curonian Spit which separates the Curonian Lagoon from open sea. The state border between Lithuania and Russia separates the Curonian Spit and Lagoon into two parts.
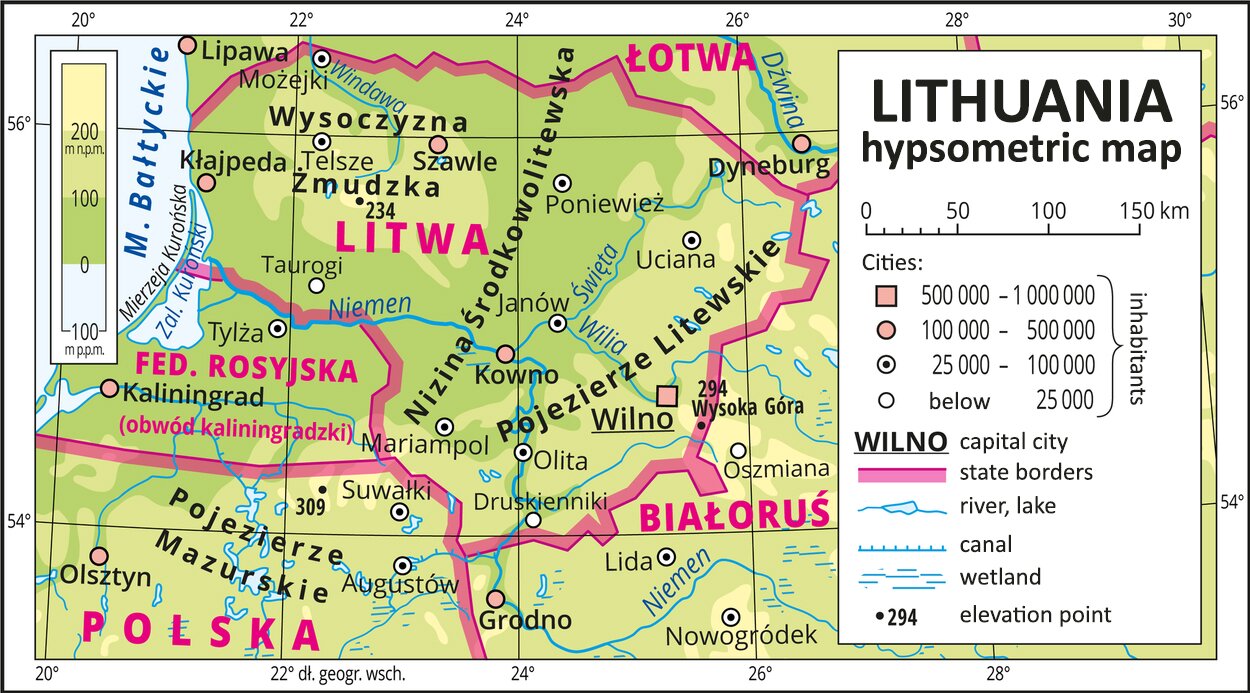
The entire area of Lithuania lies within the catchment area of the Baltic Sea. The main river, Nemen, is 475 km long. Its lower section, down to its mouth, is a natural state border with the Russian Federation. Nemen flows into the Curonian Lagoon, where it forms a delta which lies entirely on the Lithuanian side. The largest Nemen tributary in Lithuania is the Viliya River on which the capital of the country is situated.
Although Lithuania is a coastal country, its climate is temperate warm transitional. The impact of the marine air masses is often restricted to the coast, as on the other side there is the vast land territory of Eurasia from where continental air masses flow. Thus, two types of air masses clash above Lithuania and it cannot be said that either of them – marine or land – is dominant over the year.
Like in Belarus, the potential natural flora in Lithuania is represented by mixed forests. However, Lithuania has more lakeland and glacial areas with sand sediments, where podsolic soils characteristic of coniferous forests were formed. Nowadays, 1/3 of Lithuania’s area is covered by forests, and this is an average level – a bit higher than in Poland, and a bit lower than in Belarus.
Which of those cities are located in Lithuania?
- Kaunas
- Klaipėda
- Grodno
- Brest
- Vilnius
Choose the correct answer.
30, most densely, Baltic, Vistula, 20, lowland, Curonian, Vilnius, Kaunas, Narew, elevated, White, 200, Vistula, 3, Nemen, flat, most scarcely, highland
Lithuania is a small country bordering the .......................... Sea.
Lithuania is a .......................... country, with post-glacial lake districts and lightly undulating land.
The coast of Lithuania is .......................... and level. In the south, the Curonian Spit separates the .......................... Lagoon from open sea. The border between Lithuania and Russia lies across the Spit and the Lagoon.
The major rivers of Lithuania are: .......................... and its right tributary Viliya on which the capital of the country, Vilnius, is situated.
1/3 of Lithuania’s area is covered by forest – mainly mixed and coniferous forests on poor podsolic soils.
Lithuania is Poland’s .......................... populated neighbour – with approx. .......................... million people.
In Lithuania, there are more than .......................... thousand Poles living mostly in the .......................... region.
Mark in blue the cities located within the Samogitia Highland, in green – the cities within the Middle Lithuanian Lowland, and in red – those within the Lithuanian Lake District.
{blue}Šiauliai{/blue}
{blue}Telšiai{/blue}
{red}Vilnius{/red}
{green}Jonava{/green}
{green}Kaunas{/green}
{red}Druskininkai{/red}
{red}Alytus{/red}
Plan a crossword puzzle with the keyword ‘Vilnius,’ and with other words related to Lithuania.
Keywords
Lithuania, Baltic Republic, Vilnius
Glossary
Republiki bałtyckie - to małe, niepodległe dziś państwa leżące nad Morzem Bałtyckim, będące dawniej republikami Związku Radzieckiego, jako pierwsze odłączyły się od ZSRR, czym zapoczątkowały rozpad radzieckiego imperium. Zalicza się do nich Litwę, Łotwę i Estonię.