Non-renewable natural fuels – hard coal processing
the structure and properties of hydrocarbons;
the natural sources of hydrocarbons;
the difference between complete and incomplete combustion of organic compounds.
to list natural resources used to produce energy;
to explain what hard coal distillation is;
to list groups of products formed during distillation of hard coal classified by their state of aggregation;
to list and explain the use of hard coal distillation products.
Natural energy resources
The progress of humanity has always been based on natural resources. Their impact was go extensive that names of historical periods (e.g. the Stone Age, the Bronze Age, the Iron Age) are directly related to the names of these resources. Development of civilisation relies on energy‑related needs. An archaic man needed a small amount of energy to maintain proper body temperature, prepare food or scare wild animals away. Nowadays, the development of new technologies and transport, and the increase in comfort of life make energy – apart from food and air – one of the most needed recourse.

Modern energy uses mainly non‑renewable natural fuels, that is fossil carbons, crude oil, natural gas and fissile elements – uranium and thorium. Due to the declining resources of these fuels, people are searching for alternative sources of energy.
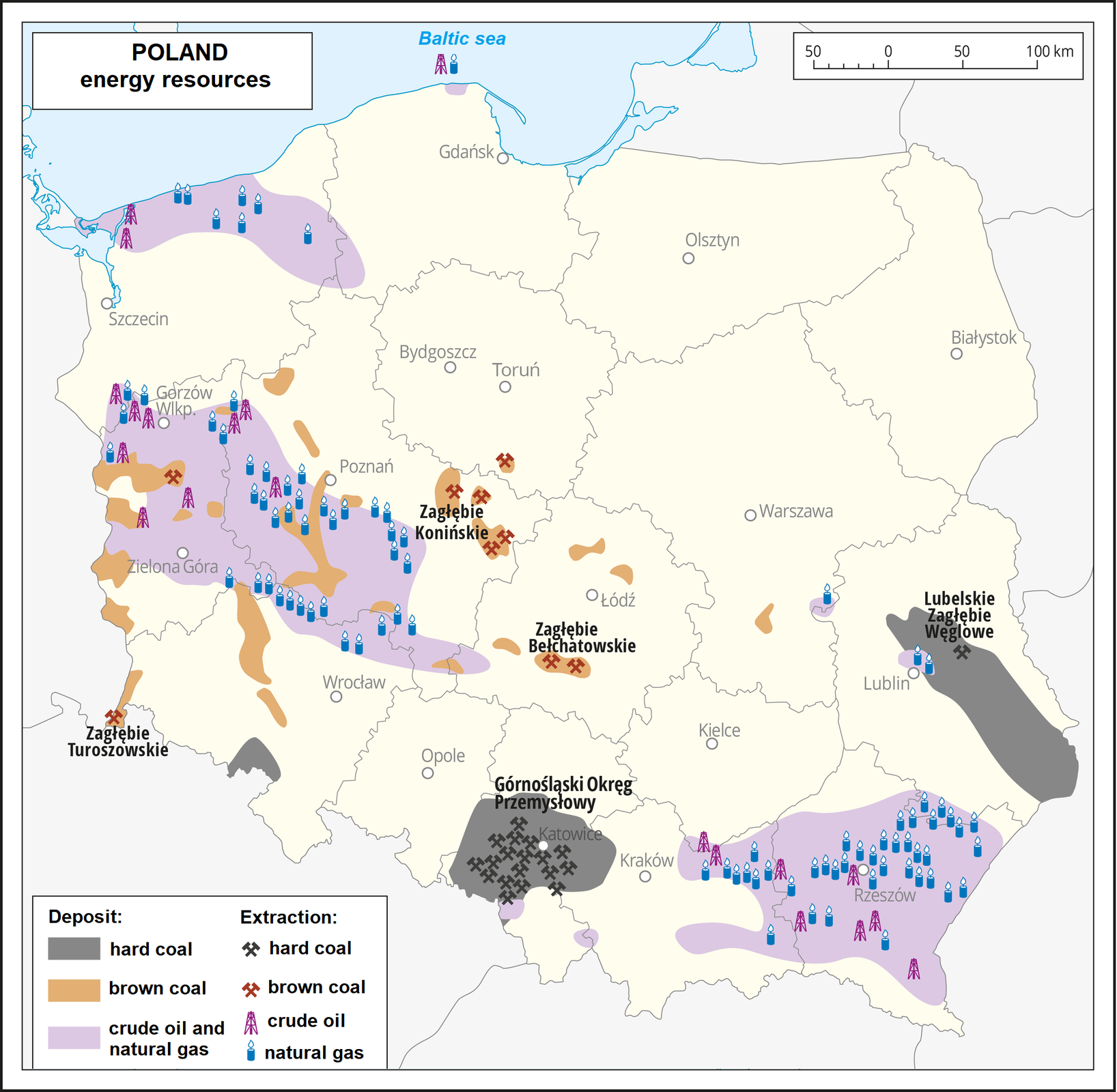
Hard and brown coal are the main energy resources of Poland. That is why electricity in our country is produced using coal. The natural gas and crude oil deposits are minor, so these raw materials are mostly imported.
Fossil carbon
Anthracite, hard coal, brown coal and peat are different types of fossil carbon. Their deposits were formed millions of years ago in a hot, humid climate, under anaerobic conditions. Various types of fossil carbons differ in colour (from light brown to intense black), hardness, sheen, percentage content of carbon, which results from the degree of carbonisation of organic matter.
Each variety of fossil carbon is applied in practice. Due to humus content, peat is used mainly in agriculture and horticulture to fertilize soils. On the other hand, for example in Ireland and Finland it is still used as fuel. In medicine it is applied to treat for example rheumatic diseases and some diseases of internal organs (for example in peat baths). Brown coal is used as an energy source – mainly in heat and power generating plants. Its loose and porous structure makes it possible to retain water, that is why it may be successfully used also to garden lawns and ornamental plants or to grown mushrooms, such as oyster mushrooms. Anthracite is used on a small scale, mainly to treat water and waste, produce electrodes and as a fuel for fireplace.
Hard coal processing
Hard coal may be used as an energy source in an unprocessed form. Complete carbon combustion is an exogenous process. That is why coal can be used as fuel and in industry:
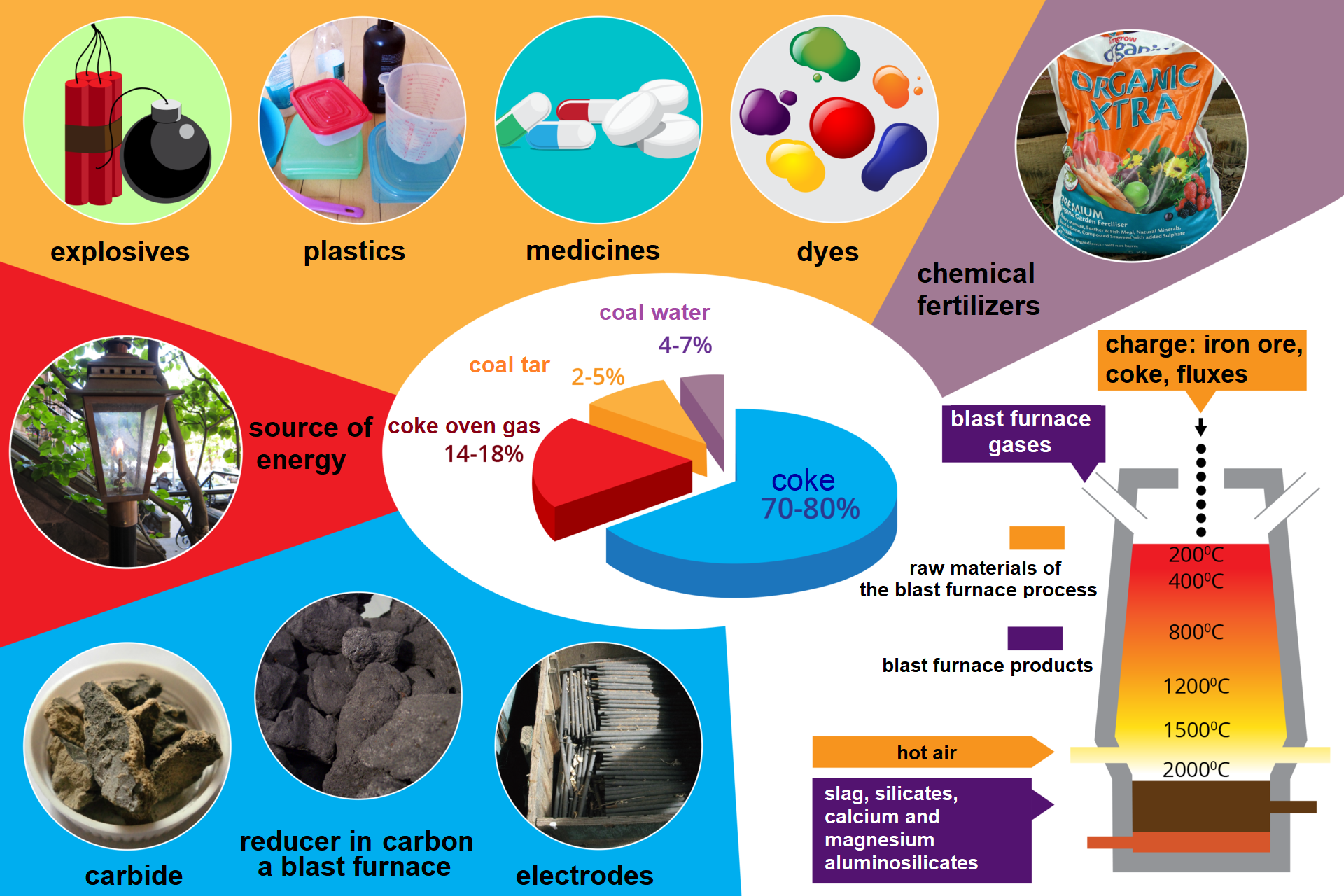
A substantial part of this raw material undergoes processing as a result of which numerous valuable substances are obtained. High temperature carbonization, also referred to as pyrolysis, coking, degassing or dry distillation of hard coal, is one of such processed carried out in coking plants. Coal is heated to a temperature of up to 1000°C without air supply. Its decomposition takes place under such conditions.
Dry distillation of hard coal results in the following solids: coke; liquids: coal tar and gas liquor (ammonia liquor); and gases: coke‑oven gas. Coke is practically pure carbon with a small admixture of inorganic compounds. It has porous structure and high calorific value. Coal tar is a mixture of numerous chemical compounds, mainly organic ones. It looks like a black, dense liquid with typical odour. Fractional distillation of coal tar leads to a number of organic compounds that are valuable raw materials for chemical industry. The so‑called coal‑tar pitch is a residue from distillation of coal tar. It is used to produce tar and roofing pitch, and to briquette coal dust. Gas liquor is an aqueous solution of ammonia and ammonium salts. Coke‑oven gas is a mixture of hydrogen, methane and carbon monoxide. All products of dry hard coal distillation are widely used.
Formulate a research question and hypothesis before doing the experiment “Hard coal distillation”. Write down your observations and conclusions.
test tube,
test tube rack,
test tube clamp,
gas burner,
lighter,
stopper with a drain tube,
glass tube,
hard coal.
Place the coal lumps in a test tube.
Close the tube with a stopper with the drain tube. Place the other end of a drain tube in the receiver.
Heat the tube in the flame of the burner.
Observe changes.
If the carbon inside the tube begins to decompose, apply the flame from the lighter to the tube outlet.
Observe the changes.

Film dostępny na portalu epodreczniki.pl
Film przedstawia labolatorium, gdzie przeprowadzany jest eksperyment destylacji węgla kamiennego, w wyniku którego powstają nastepujące substancje: koks, smoła węglowa, ciecz gazowa oraz gaz koksowniczy. Gaz w czasie spalania wydziela nieprzyjemny, ostry zapach oraz jest łatwopalny
Application:
Answer the questions based on knowledge you acquired during the lesson.
Mark true statements.
- Peat, brown coal, hard coal and anthracite are varieties of fossil coal.
- Gassing is a process of cooling coal with oxygen and superheated steam.
- Anthracite is a type of fossil coal with the greatest content of elemental carbon.
- Peat is a fossil fuel which contains up to 60% of elemental carbon.
- Still water is one of liquids obtained during distillation of hard coal.
Create a multiple-choice test based on today's lesson. Then exchange your questions with a friend or classmate.
Question: ...
- ...
- ...
- ...
- ...
Summary
The following natural mineral fuels can be distinguished: hard coal, brown coal, peat.
The following products are obtained as a result of heating of hard coal at a temperature of approx. 1000°C without air (high temperature carbonization): coke, coal tar, gas liquor and coke‑oven gas.
Keywords
distillation, fractional distillation
Glossary
destylacja – metoda rozdzielania składników ciekłej mieszaniny, wykorzystująca różnice w ich temperaturach wrzenia; proces destylacji polega na odparowywaniu kolejnych składników mieszaniny, a następnie skraplaniu ich par w wyniku oziębienia
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
Nagranie dźwiękowe słówka: fractional distillation rectification
destylacja frakcyjna (destylacja frakcjonowana, rektyfikacja) – metoda rozdzielania składników mieszaniny wieloskładnikowej na frakcje
frakcja – mieszanina substancji o zbliżonych temperaturach wrzenia, mieszczących się w określonym przedziale wartości
sucha destylacja – proces polegający na termicznym odgazowaniu paliw stałych bez dostępu powietrza