Parenchymal tissues
all organisms are made of cells;
basic life processes occur in cells;
plant cells have chloroplasts, cell walls and vacuoles.
recognize plant tissues;
discuss the basic functions of individual plant tissues;
show the relationship between the structure of tissues and the function they perform;
microscopic observation of plant tissues.
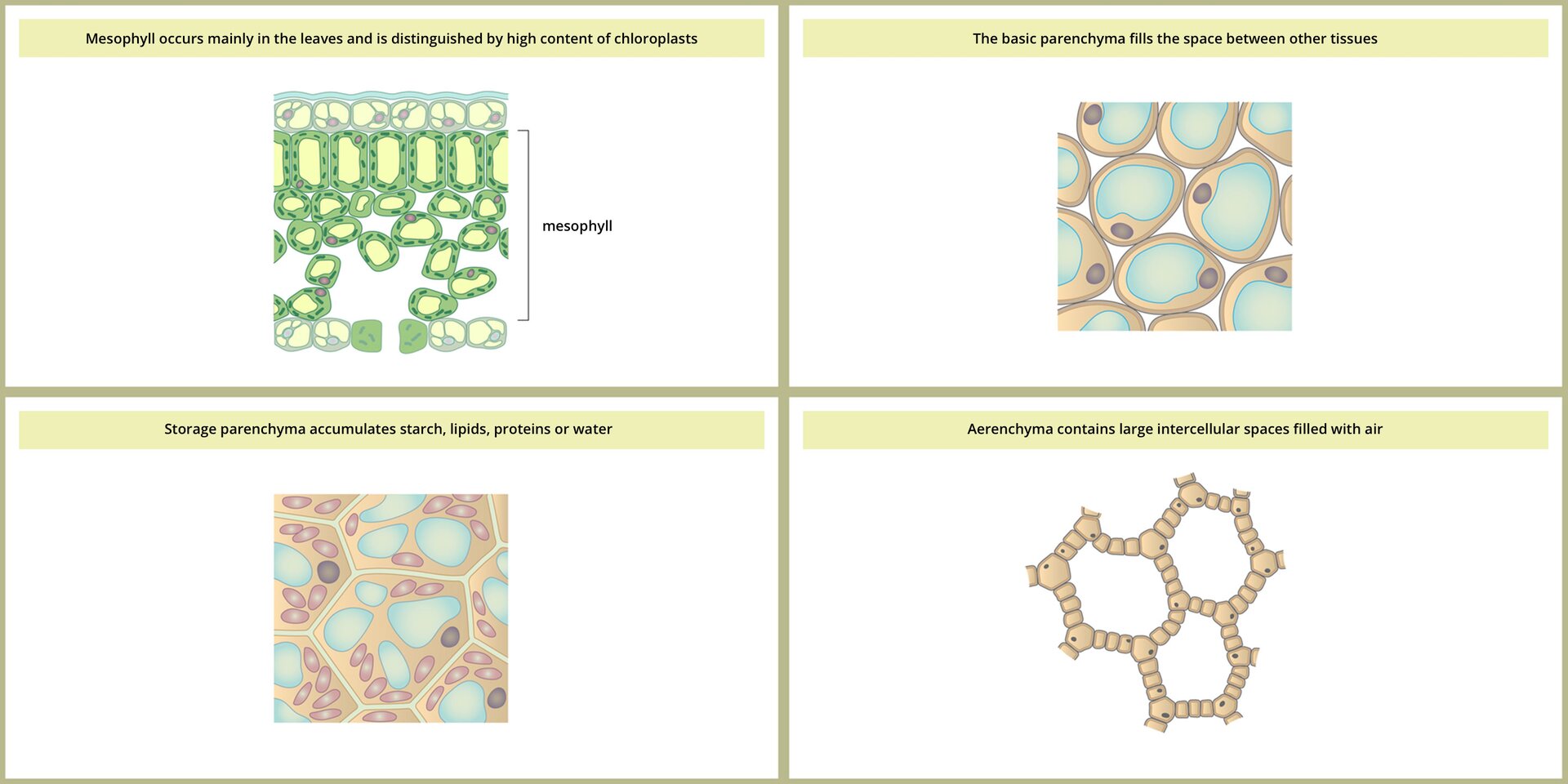
The main body mass of the plant is parenchymal tissuesparenchymal tissues. The cells of these tissues are usually large, thin‑walled and loosely arranged. Between them there are free spaces called intercellular spaces. Depending on the function, four types of parenchyma are distinguished:
chlorenchyma occurring in all green parts of the plant, mainly in the leaves; its cells contain a lot of chloroplasts, which makes it possible to carry out photosynthesis;
basic parenchyma filling the entire interior of the plant; its living cells are loosely arranged and contain large vacuoles; occur in stems, roots, fleshy fruits;
storage parenchyma storing food substances and water; is found in stems, roots and in plant seeds;
aerenchyma characteristic for aquatic and marshy plants; its cells are separated by spaces filled with air, which facilitates the raising of leaves and stalks on the surface of water, and enables the storage of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Describing the characteristics of the cells of the potato bulb and storage parenchyma.
cross‑section of a potato bulb,
microscope,
equipment for microscopy,
Lugol's solution.
Apply a drop of water to the base slide.
Scrape the razor with a little crumb of potato bulb.
Using a preparation needle, place a little bit of pulp in the drop of water.
Add a drop of Lugol's liquid.
Cover the preparation with a cover slip and observe it under 40x magnification.
Observe the stained starch grains, shape and arrangement of the storage cells.
Make a schematic drawing and describe it.
The potato bulb’s storage parenchyma contains many starch granules, which are the reserve material for plants.
Indicate true sentences.
- The storage tissue cells are thin-walled.
- Air accumulates in the cells of aerenchyma.
- The storage parenchyma of potato bulb gathers potato starch.
- Aerenchyma occurs in plants which occur in a water rich environment.
Summary
The body of plants is filled with tissues, i.e. assemblies of cells with a similar structure specialized to perform specific functions.
The parenchyma fills the spaces among other tissues, stores the substances produced by the plant, and when it has chloroplasts – conducts photosynthesis.
Keywords
tissue, plant tissue, cross‑section, longitudinal section, absorption
Glossary
tkanka miękiszowa – tkanka roślinna, która wypełnia ciała roślin, luźno ułożona między innymi tkankami; może przeprowadzać fotosyntezę (chlorenchyma), gromadzić materiały zapasowe i wodę (miekisz zapasowy); miekisz powietrzny (aerenchyma) ułatwia wymianę gazową i unoszenie się w wodzie roślinom wodnym