Pea inheritance, environment and phenotype
information about the features of an organism is stored in the DNA found in each cell;
the genetic material of the parents is passed on to the offspring via gametes.
predict the characteristics of offspring based on the characteristics of the parents by recording a genetic cross for one trait;
interpret a schematic record of inheritance (genetic cross) using the terms phenotype, genotype, gene, allele, homozygote, heterozygote, domination, recessive;
distinguish the genotype from the phenotype;
explain what determines, for example, the height of the human body and the height of a pea shoot.
Inheritance of pea traits
Genetic crossGenetic cross illustrates how genes are passed on from parents and what genotypes are created in a descendant generation. The genetic cross includes symbolically stored genotypes (in relation to the analyzed genes) of the parental generation and all possible genotypes of the generation of descendant.
How to explain the result of Mendel's experiment using a genetic cross? The tall pea has two dominant alleles responsible for tall growth (DD) and is the dominant homozygote, short pea is a recessive homozygote and has two alleles responsible for short growth (dd). After the intersection of the parental generation (tall pea x short pea), all plants in the descendant generation were heterozygotes of tall growth (Dd). Each of these plants inherited one gene after the tall ancestor and one gene after the short ancestor. The dominant allel combined with recessive pair (Dd) means that the recessive allel is not implemented and has no effect on plant height. Thus, in the first descendant generation, all plants are heterozygous with long stems.
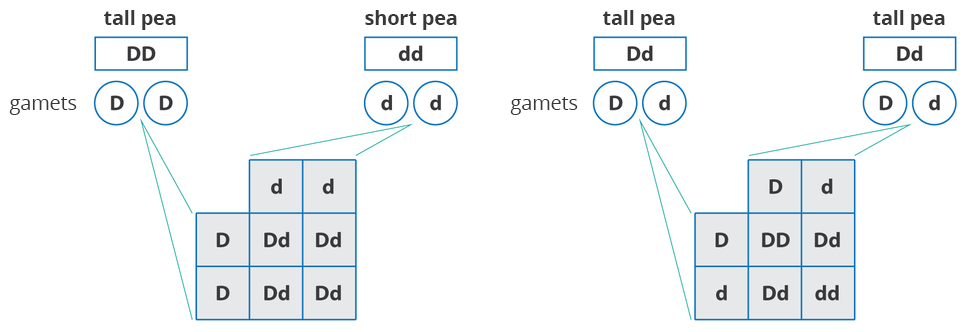
When the pea flowers from the first generation (Dd) are pollinated among themselves, we will receive a second generation of descendants. 3/4 of the plant of this generation has a tall growth, and 1/4 – a short growth. If we analyze the genotypes of individual plants of the second generation, it will turn out that 1/4 are dominant homozygotes, 2/4 (half), heterozygotes, and 1/4 are recessive homozygotes. The ratio of individual genotypes: Dd:Dd: dd is therefore 1: 2: 1, respectively.
In a similar way as the height of the shoot, the color of the pea flowers is inherited.
Make a genetic cross that depicts the inheritance of pea flowers.
Flowers of violet‑flowering pea (Ff) have been dusted with pollen from another violet‑flowering pea plant (Ff). Only 6 seeds were obtained, from which 3 plants with violet flowers and 3 with white flowers grew. Explain whether this result matches the results of Mendel's experiments.
Environmental impact on the phenotype
The environment can affect the phenotype. One of these phenotype traits is body height. If the pea on the DD or Dd genotype grew in the wrong environment, it would not reach its maximum height. In peas, height is conditioned by one pair of genes and the influence of the environment.
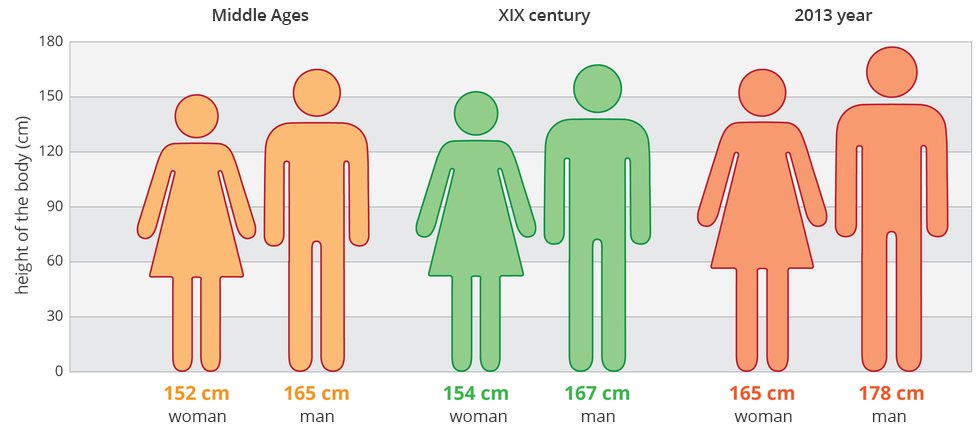
In man, body height is conditioned by many genes and the living environment. Tall parents generally have tall children. At present, because the children's living conditions are better than their parents, the descendants are growing more than their parents. However, if during development the children of tall parents lacked enough nutrients, they would not reach the genetically programmed body height.
Organisms with the same genotypes may look different if they are inhabiting different environments. If two identical grafts from one plant are planted in different soils, and the pots are set in places with different light access, after some time, although they are genetically identical, they will differ.
Which of the following characteristics of a pea plant can be modified by the influence of the environment?
- flower color
- shape of seeds
- plant height
- the color of pods
Indicate all true statements
- Two organisms with the same phenotype may differ in genotype.
- The impact of the environment can cause that two organisms with the same genotype differ in their phenotype.
- Some of the characteristics of plants or animals genetically determined reveal themselves regardless of the environmental impact.
- Conditions in which the body develops do not affect its phenotype at all.
Summary
A genotype is a set of genes of a given individual, and the phenotype is a set of its features.
Genes and the environment affect the phenotype.
In the case of crossing the dominant and recessive homozygote, we obtain heterozygotes which have phenotypic features such as the dominant homozygote.
In the case of crossing two heterozygotes, offspring are formed with a 1: 2: 1 ratio of genotypes whose phenotypes have a ratio of 3: 1.
How was this lesson? Did you like it? Finish selected sentences.

Keywords
genotype, phenotype, inheritance
Glossary
allel – jedna z dwóch lub więcej odmian danego genu, odpowiedzialnego za wytworzenie konkretnej cechy organizmu; allele danego genu są położone w określonym miejscu na chromosomie
genotyp – zespół wszystkich genów danego osobnika warunkujący jego cechy; pojęcie czasem (w krzyżówkach genetycznych) używane w odniesieniu do jednej lub kilku par alleli
heterozygota – organizm posiadający w chromosomach homologicznych dwa różne allele danego genu, np. Aa
homozygota – organizm posiadający w chromosomach homologicznych dwa identyczne allele danego genu, np. AA lub aa
fenotyp – zespół wszystkich cech budowy i fizjologii organizmu wyznaczanych przez genotyp i środowisko
krzyżówka genetyczna – graficzny sposób zapisu dziedziczenia uwzgledniający allele pokolenia rodzicielskiego i pokoleń potomnych