pH of the solutions
how to define the terms acid, hydroxide and base;
what the acid‑base indicators are and what their coloring in water, bases and acids is;
how to explain the concept of electrolytic dissociation.
to explain what the pH of the solution and the pH‑scale is;
to determine the pH values of the tested samples.
pH of the solutions – pH‑scale
See the illustration showing selected products and their pH before moving on to the experiment.

1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
What is the pH of the products in the immediate environment?
The pH of products from the immediate environment have differs.
red cabbage brew,
vinegar,
lemon juice,
toothpaste,
soap,
rust remover,
washing liquid,
aqueous solution of the pipe cleaning agent,
rock‑salt,
sugar,
distilled water,
10 Petri dishes,
Pour distilled water, vinegar and lemon juice as well as a solution of: rust remover, washing liquid and pipe cleaning agent respectively onto five Petri dishes.
Prepare toothpaste suspension in water and place it on a Petri dish.
Prepare aqueous solutions of: soap, rock salt, sugar and pour them onto Petri dishes.
Add a few drops of red cabbage brew to each sample.
Observe the changes that occur.
Universal indicators in acidic environment take red color and in alkaline - green or blue color.
The measure of acidity and alkalinity of the solution is pH‑scalepH‑scale. It takes the values 0–14.
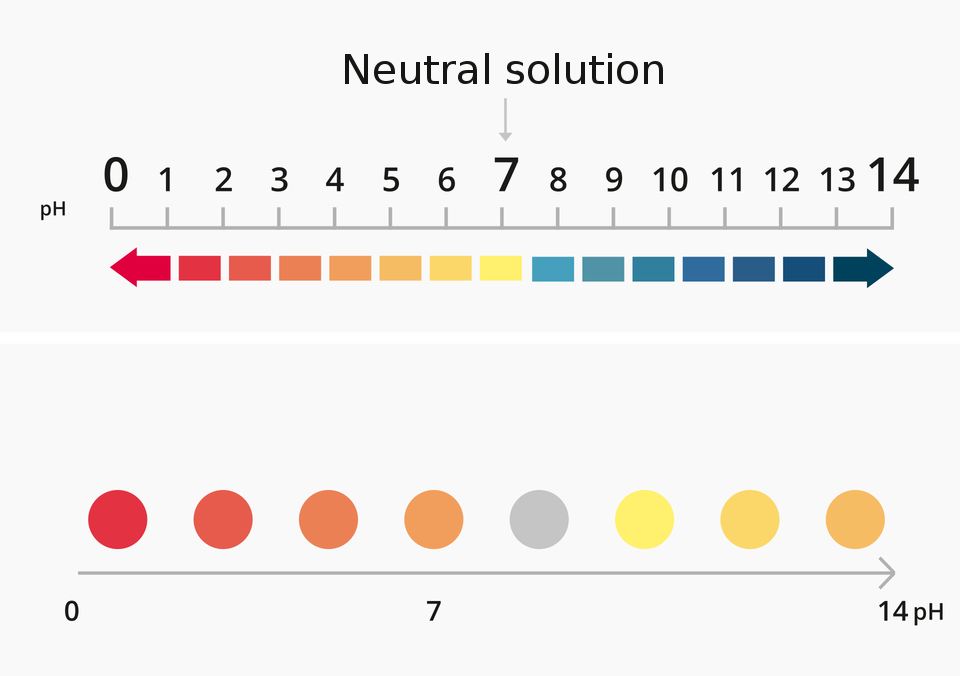
pH < 7 acidic pH, concentration HIndeks dolny 33OIndeks górny ++ > concentration OHIndeks górny --;
pH = 7 neutral pH, concentration HIndeks dolny 33OIndeks górny ++ = concentration OHIndeks górny --;
pH > 7 alkaline pH, concentration HIndeks dolny 33OIndeks górny ++ < concentration OHIndeks górny --.
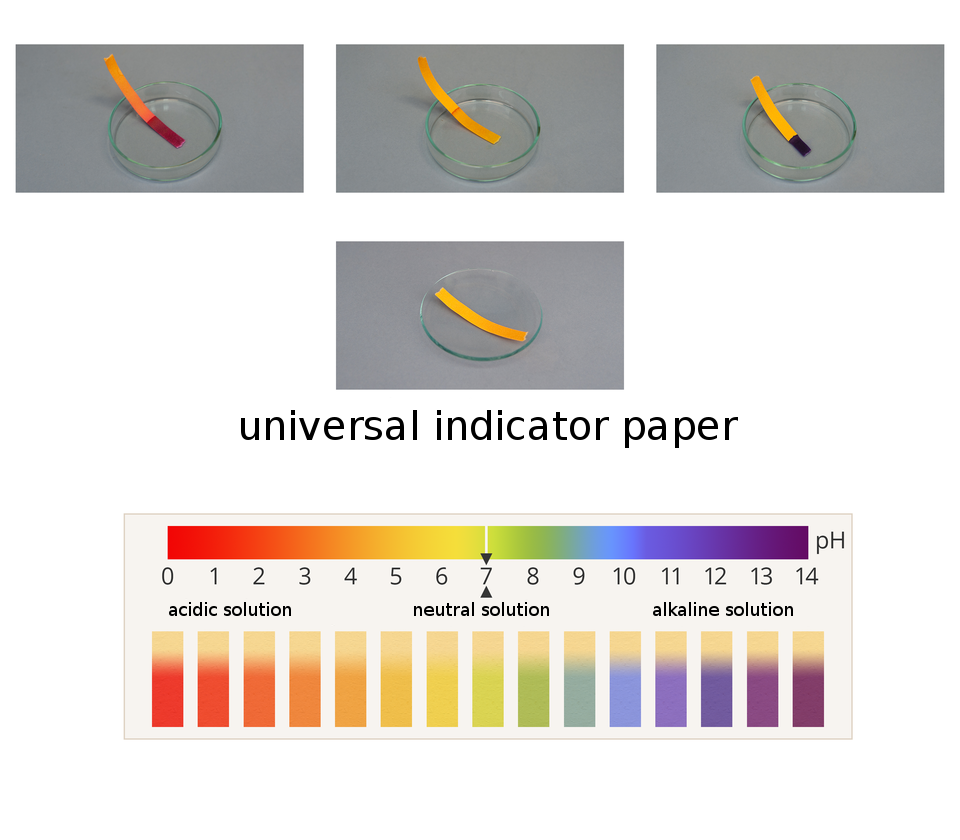
A visual comparison of the color of the indicators with a standard, e. g. a color pH scale on the packaging, only allows for an approximate determination of the solution's acidity. The pH value of the solution can be determined precisely by, among others, a device called a pH meter. It is used in chemical, medical, agricultural and cosmetic laboratories.
The pH meter consists of a sensor called an electrode, which is immersed in the tested solution, and a display from which the pH value is read out. Some pH meters are equipped with thermometers because the temperature influences the measurement.
The so‑called universal indicatoruniversal indicator, which is a mixture of several indicators, can also be used for pH‑testing. It changes its color at different pH values. It takes on a red color in acids and in bases – green to blue color.
Solution pH in everyday life
Knowing the pH value is of great practical importance, e. g. in the production of medicines (apart from the active substance, drugs contain a protective layer that protects e.g. the esophagus against unfavorable pH) or cosmetics (e.g. nowadays there are liquid soaps with a pH similar to natural pH of human skin – a slightly acidic pH, which has a bactericidal effect).
The pH value of the soil determines its suitability for growing certain types of plants. The quality and height of the yield depend on the soil pH. For most plants pH is optimal in the range of 5.6–7.8, but it is an individual value for each of the species.
Plant | Optimal pH |
potatoes | 4.5–6.0 |
rye, flax | 5.0–6.5 |
cucumber, carrot | 5.5–6.5 |
tomato, garlic | 5.5–7.5 |
wheat, barley, rape | 6.0–6.5 |
sugar beet, peas, maize | 6.5–7.0 |
fruit trees | 6.5–7.5 |
Organic fluids in the human body have different pH values, e.g. gastric juice has pH = 1.0–1.5, pancreatic secretion – 7.5–8.8, and the pH of the blood remains within the range 7.35–7.45. Both too low and too high a pH is the cause of many diseases. The decrease of the pH value below 6.8 results in so called acidosis, and the increase above pH 7.45 – alkalosis. This problem may occur during damage to any of the organs responsible for the excretion of toxins, e. g. kidneys or lungs, which makes them work less well.
Most fish species live in water with pH value = 6–8. Lowering the pH of the water to a level below 5 causes an abnormal behavior of the fish, consisting in rapid movements and the appearance of a blue color on the skin. At a pH higher than 8, the skin of the fish is covered with mucus, the scales become turbid and the fins become frayed and fall off.
Red geranium flake indicator
Red geranium, like red cabbage, can be a convenient indicator to use. To this end, pour hot water over the chopped petals and wait 20 minutes. Then filter the decoction through e.g. a coffee filter, and retain for testing.
A good indicator is red onion, which is pale red in the acidic environment and in alkaline environment – green.
Onion and vanillin oil, which do not emit characteristic odors in a strongly alkaline environment, are oflactory indicators.
Place the products in the correct places on the pH scale.
soap, tomato, banana, distilled water, washing liquid, lemon juice, pipe cleaning agent
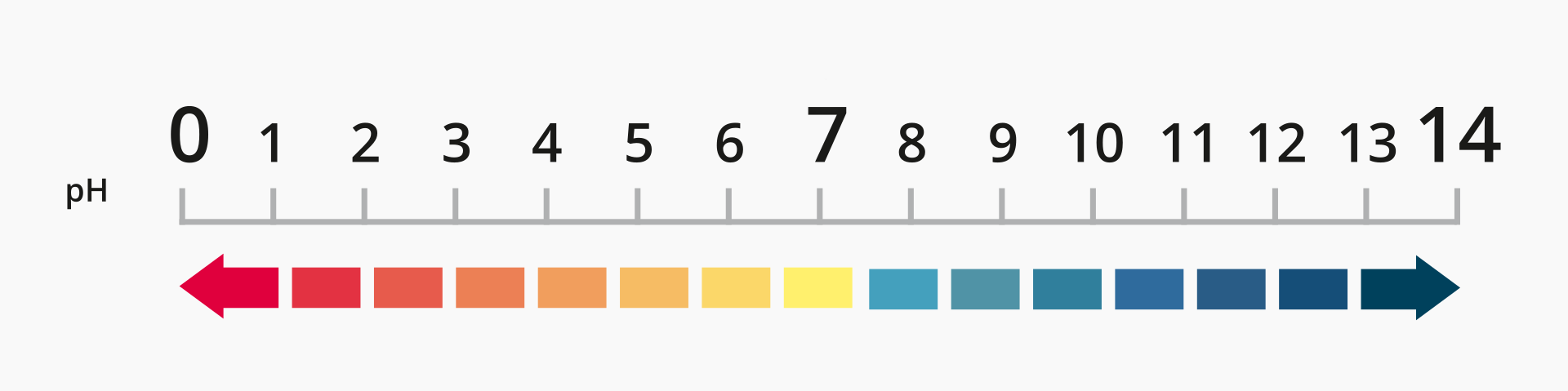
Place the samples tested using red cabbage brew in the order from those with the lowest pH to those with the highest pH.
What determines the alkaline reaction?
- Hydrogen cations
- Metal cations
- Hydroxide anions
- Anions of acid radicals
Conclusion
The measure of the acidity and alkalinity of the solution is the pH value, which is quantified in numbers 0–14.
The solution is acidic at pH
The solution is neutral at pH = 7.
The solution is alkaline at pH > 7.
The higher the concentration of hydrogen ions, HIndeks dolny 33OIndeks górny ++ (or simplified notation: HIndeks górny ++), the lower the pH‑value of the solution.
The higher the concentration of hydroxide ions, OHIndeks górny --, the higher the pH‑value of the solution.
Keywords
pH, acidic, alkaline, neutral, pH, indicator
Glossary
odczyn roztworu – właściwość roztworu wynikająca ze stężenia jonów HIndeks dolny 33OIndeks górny ++ (uproszczony HIndeks górny ++) i w roztworze
skala pH – ilościowa miara kwasowości i zasadowości roztworu
wskaźnik uniwersalny – mieszanina kilku wskaźników, która zmienia barwę przy różnych wartościach pH; w kwasach przyjmuje barwę czerwoną, a w zasadach – od zielonej do niebieskiej
wskaźniki kwasowo‑zasadowe (indykatory) – substancje, które zmieniają barwę w roztworach o różnym odczynie