Properties of matter – summary
Podsumowanie wiadomości o właściwościach materii
the properties of three states of matter that explain the theory of microscopic structure of matter.
Prepare answers for the following questions.
a) What experiments confirm the theory of the atomic structure of matter?
b) What is the difference between intermolecular interactions in gases, liquids and solids.
c) What is the difference between the fourth state of matter - plasma - and gasgas?
d) Why are bodies with good electrical conductance conduct heat well?
e) How does the hydrostatic pressure depend on the liquidliquid densitydensity?
f) Present Pascal's law.
g) Present the floating conditions of the bodies.
The basic elements that mattermatter is made of are atoms. Atom is the smallest amount of a simple substance that retains its chemical and physical properties.
Atoms have a mass, volumevolume and shape. Atoms can combine with each other to form molecules that are the smallest amount of a complex substance that retains its chemical and physical properties.
Atoms are very small, but nevertheless they have a complex structure. They consist of a heavy positive nucleus in the middle of the atom and negative electrons in the outer part.
Atoms contain charges (protons, electrons). However, they are electrically neutral.
Atoms and molecules are in constant motion.
Determine if the sentences below are true or false.
a) Diffusion is the spontaneous mixing of substances, e.g. the spread of odour in still air.
b) VolumeVolume contraction phenomenon - consisting in the fact that the volume of the mixture of water and ethyl alcohol is smaller than the sum of the volume of its components, i.e. water and alcohol separately, indicates the molecular structure of the liquidliquid.
c) Atoms can be seen in a normal optical microscope.
d) Brownian motion consisting in the constant movement of fat particles in the water indicates the molecular structure of water.
Check your knowledge of phase transitions names.
The cube of butter is 10 cm x 8 cm x 2,4 cm, its mass is 200 g. Calculate the densitydensity of butter. Give the result in and in .
Determine if the sentences below are true or false.
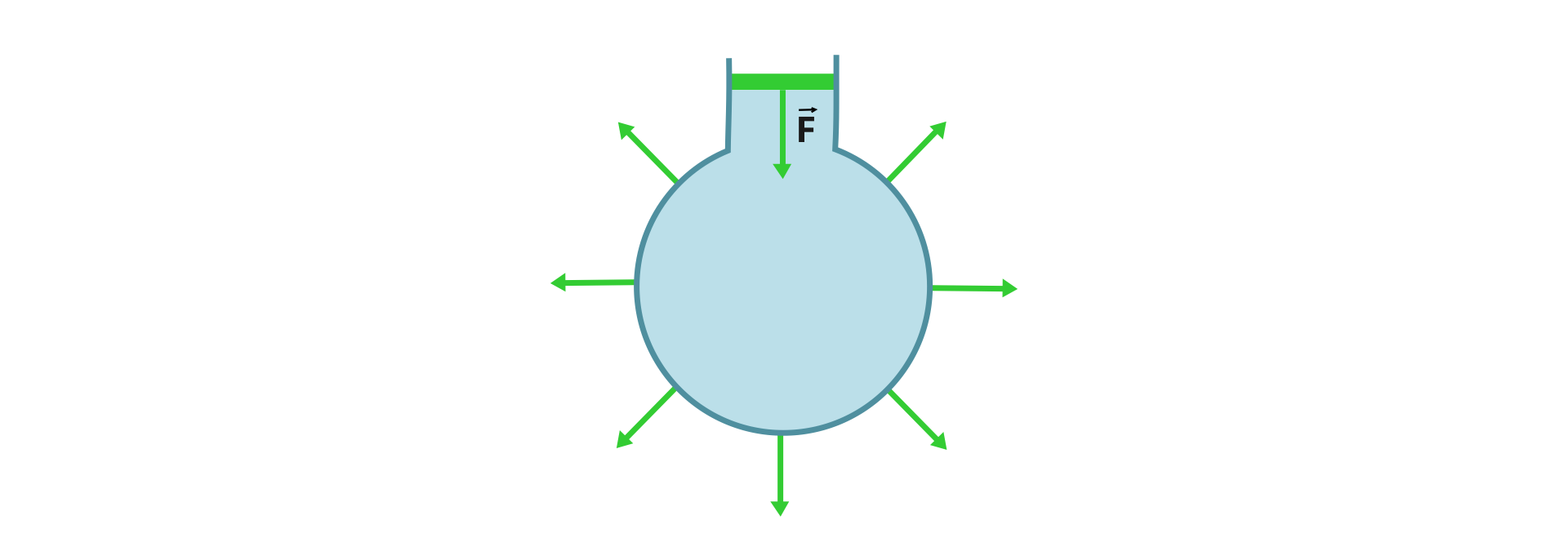
a) Pascal's law states that the external pressure exerted on the fluid depends on the distance from the plunger.
b) Pascal's law states that the external pressure exerted on the fluid is transmitted equally in all directions.
c) Pascal's law applies to liquids and does not apply to gases.
d) Pascal's law applies to gases and liquids. Gases and liquids are called fluids.
Which of the following statements are true and which are false.
a) Liquids are compressible.
b) Gases are compressible.
c) The substance in the gaseous state, when it reaches a temperature of more than 1000 K, it will become a plasma.
Calculate the hydrostatic pressure p, at the base of the water dam at a depth of h = 10 meters underwater. Assume that the densitydensity of water is d = 1000 , and the gravitational acceleration is 9,81 , give the result in pascals.
The cube made of aluminium with side a = 10 cm has a densitydensity d = 2700 .
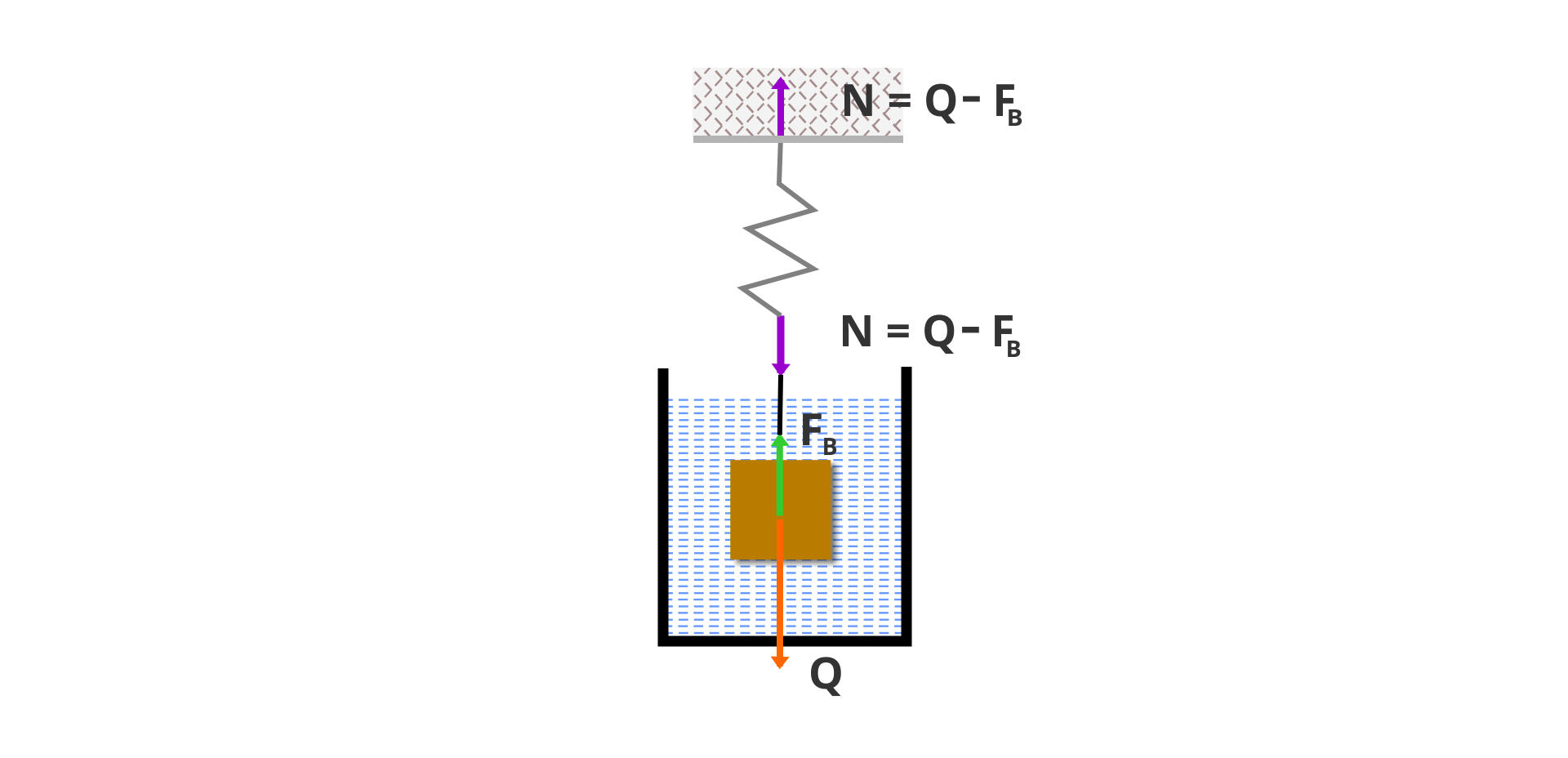
a) Prove that the dynamometer measuring with accuracy of 0,1 N on which we suspend this cube will indicate the weight of Q = 26,5 N.
b) After immersing the cube in water, the dynamometer indication decreased to QIndeks dolny 11 = 16,7 N. Calculate the buoyant forcebuoyant force, FIndeks dolny BB, acting on aluminium. Can aluminium in the form of a cube float on the surface of water?
c) Explain why a tourist boat made of aluminium does not sink in water, although the density of aluminium is almost three times higher than the density of water. What condition must be fulfilled by a boat so that it can float on the surface of water.
Summary
The theory of atomic structure of mattermatter is confirmed by the phenomenon of diffusion and the phenomenon of Brownian motion. Matter is made up of atoms that can combine into molecules. Atoms and molecules are in constant motion. In solids, molecules vibrate around their equilibrium positions, in liquids, molecules can move relative to each other, in gases, molecules move freely relative to each other. Gases fill freely the entire volume of the vessel and are compressible. Liquids take the shape of the vessel and create a free surface at the boundary with solids and gases. The change in temperature can cause phase transitions of solids, liquids and gases. Above 1000 K gases transforms into the fourth state of matter - plasma.
DensityDensity is the quantity that characterizes the body, calculated as the ratio of the mass to the volume:
According to Archimedes' principle, on the body immersed in liquidliquid or gasgas acts the buoyant forcebuoyant force equal to the weight of displaced liquid or displaced gas.
If the density of the body is greater than the density of liquid or gas, the body sinks. If the density of the body is smaller than the density of liquid or gas, the body floats on the surface of the liquid, or rises in the gas.
Within gas or liquid there is a hydrostatic pressure p, depending on the depth of the body immersion h, and the density of liquid or gas d:
The normal force acting on liquid or gas in a closed tank, according to Pascal's law, creates additional pressure, which is the same in the entire volumevolume of the gas or liquid under consideration.
Exercises
Determine which sentences are true.
- The steel ball will be drowned in mercury.
- The buoyant force acting on a ship sailing on a lake is greater than its weight.
- The balloon floats in the air and remains motionless at one height where the average balloon density is equal to the air density at this height.
- Water vapour is denser than water.
- The diffusion explains the phenomenon that the drop of ink entering motionless water after a certain time colours the entire volume of water.
The submarine is submerged at a depth of 100 meters. What is the magnitude of the normal force with which the water acts on the surface of the boat? The surface area of the submarine is , and the density of seawater , assume that the gravitational acceleration .
Write in English about construction of which machines and devices Pascal's law has been applied.
Indicate which pairs of expressions or words are translated correctly.
- materia - matter
- ciecz - liquid
- gaz - gas
- ciało stałe - solid
- gęstość - volume
- objętość - density
- volume
- liquid
- gęstość
- matter
- objętość
- density
- materia
- solid
- ciało stałe
- ciecz
Glossary
prawo Archimedesa
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: Archimedes’ principle
siła wyporu
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: buoyant force
gęstość
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: density
gaz
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: gas
ciecz
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: liquid
materia
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: matter
cząsteczka
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: molecule
prawo Paskala
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: Pascal’s law
ciało stałe
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: solid
objętość
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: volume
Keywords
gasgas
liquidliquid
mattermatter
solidsolid