Proteins – properties
what the structure of proteins is;
where proteins occur;
what the functions of proteins are in the human body.
to define the terms 'denaturation' and 'salting out' of protein;
to enumerate the factors that cause the denaturation and salting out of protein;
to indicate the difference between denaturation and salting out of protein;
to design an experiment allowing to detect the presence of protein in food products.
Properties of proteins
If you direct a narrow stream of light onto a beaker with an aqueous solution of protein, you'll notice the dispersion of light. This phenomenon is called the Tyndall effect, and indicates that the egg white's protein forms a colloidal solution with water.
What are the properties of the egg white protein solution?
Before you conduct experiment, formulate research question and hypothesis.
What effect does a saturated solution of rock salt have on egg white protein?
The protein coagulates under the influence of the rock salt solution.
hen egg white,
saturated solution of rock salt,
water,
glass rod,
test tube.
Place the egg white in the test tube.
Add the saturated rock salt solution into the tube.
Observe the changes.
Add water to the mixture and stir with the glass rod.
Observe the changes again.
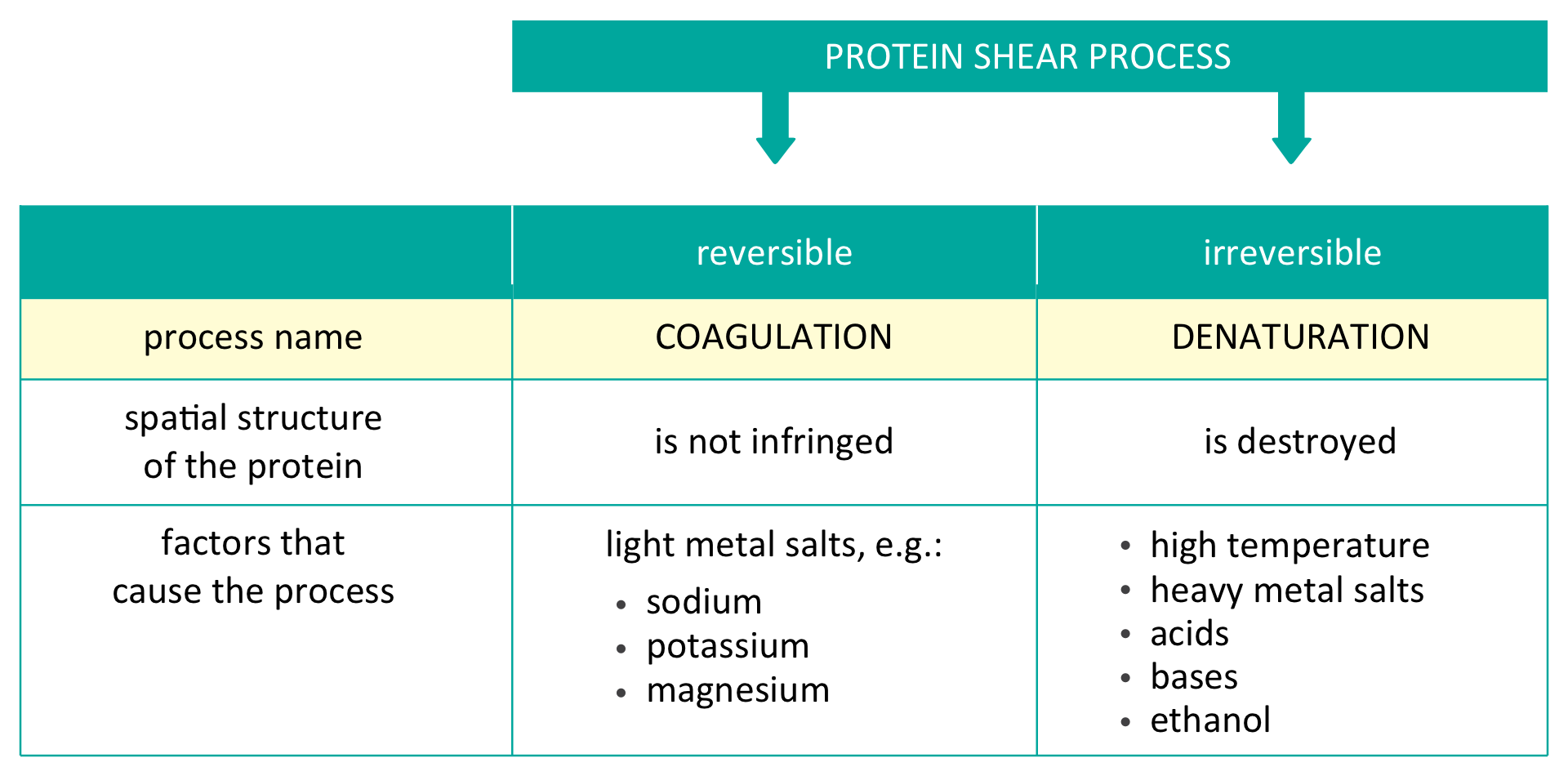
The observed process of precipitation of sediment is called coagulation. In this case, the process turned out to be reversible – after adding water, the sediment dissolved. An example of reversible coagulation is salting outsalting out. Reversible coagulation also occurs under the influence of low temperatures. Why did this happen?
When a protein is salted out, its spatial structure is not affected. Therefore, it is possible to transition back to its original form. Process of salting out proteins takes place under the influence of salts of certain metals, including sodium, magnesium and lithium.
Is there any permanent damage to the structure of protein, and if so, in what situation does it happen?
Before you conduct experiment, formulate research question and hypothesis.
What influence do the following factors have on egg white: temperature, ethanol, hydrochloric acid and copper(II) sulphate solution?
Protein coagulates under the influence of ethanol, hydrochloric acid, copper(II) sulphate solution, sodium hydroxide solution and high temperature.
hen egg white,
ethanol,
copper(II) sulphate solution,
hydrochloric acid,
sodium hydroxide solution,
water,
test tubes,
burner.
Place the hen egg white in five test tubes.
Heat the first tube.
Add ethanol, hydrochloric acid, sodium hydroxide solution and copper(II) sulphate solution to the other four test tubes respectively.
Observe the changes.
Add water to the obtained mixtures, shake and observe the changes.
The observed process of irreversible coagulation of protein is denaturation. During denaturationdenaturation, protein changes its structure and original properties. The factors causing denaturation of protein are as follows:
high temperature,
heavy metal salts (e.g. salts of copper, mercury, barium, cadmium, lead),
concentrated acids and bases,
ethanol.
Detection of proteins
Let's conduct experiments.
Before you conduct experiment, formulate research question and hypothesis.
Are there any peptide bonds in the hen egg white protein?
Peptide bonds are present in hen egg white.
hen egg white,
copper(II) sulphate solution,
ssodium hydroxide solution,
test tubes.
Pour a few cubic centimeters of the solution of copper(II) sulphate into one test tube and add a few cubic centimeters of the sodium hydroxide solution. In this way you will obtain copper(II) hydroxide in the form of blue sediment.
In another test tube, place the egg white and add the freshly precipitated copper(II) hydroxide.
Observe the changes.
Film dostępny na portalu epodreczniki.pl
Film pokazuje eksperyment. Problem badawczy: Czy w białku jaja kurzego znajdują się wiązania peptydowe? Hipoteza: W białku jaja kurzego występują wiązania peptydowe. Będziesz potrzebował: białko jaja kurzego, roztwór siarczanu sześć miedzi dwa, roztwór wodorotlenku sodu, probówki. Instrukcja: Do jednej probówki wlej kilka centymetrów sześciennych roztworu siarczanu sześć miedzi dwa i dodaj kilka centymetrów sześciennych roztworu wodorotlenku sodu. W ten sposób otrzymasz wodorotlenek miedzi dwa w postaci niebieskiego osadu. W drugiej próbówce umieść białko jaja kurzego i dodaj do niego świeżo strącony wodorotlenek miedzi dwa.

Film dostępny na portalu epodreczniki.pl
Film pokazuje eksperyment. Potrzebujemy: kwas azotowy pięć, różne produkty, które kładziemy na szalce Petriego: jogurt, polędwica, ziemniak, banan, chleb, twaróg, jabłko, białko jaja kurzego. Na każdy produkt kładziemy kroplę kwasu azotowego pięć. Żółto-pomarańczowa barwa na wszystkich produktach świadczy o obecności białka.
Before you conduct experiment, formulate research question and hypothesis.
What effect does concentrated nitric acid have on hen egg white protein?
Hen egg white protein coagulates under the influence of concentrated nitric acid.
hen egg white,
concentrated nitric acid,
dropper,
test tube.
Place the egg white in the test tube.
Add, in drops, the concentrated nitric acid.
Observe the changes.
Assign corresponding terms to the statements on the left:
biuret reaction, salting out, xanthoproteic reaction, factors destructive to protein, denaturation
| Protein undergoes reversible coagulation under the influence of sodium chloride, and its spatial structure is not affected. After adding water, the precipitated protein sediment dissolves. | |
| An irreversible process during which the protein spatial structure is destroyed. | |
| A characteristic reaction which allows to detect protein in food products. | |
| A reaction allowing to detect a peptide bond in proteins. | |
| Factors such as: temperature, ethanol, acid, base, heavy metal salts. |
Conclusion
Protein undergoes reversible coagulation under the influence of rock salt. The spatial structure of protein is not affected, and the precipitated protein sediment dissolves after water is added. This process is called salting out.
Protein denaturationProtein denaturation is an irreversible process during which the protein spatial structure is destroyed.
Factors causing denaturation of protein are as follows: high temperature, heavy metal salts, concentrated acids and bases as well as ethanol.
The biuret testbiuret test and xanthoproteic reactionxanthoproteic reaction are colour reactions that allow to detect the presence of protein.
Explain the differences between denaturation and the salting out of protein. List the factors causing these processes.
Keywords
protein, true solution, colloidal solution, salting out, coagulation, denaturation, sol, gel, peptide bond, xanthoproteic reaction, biuret test
Glossary
denaturacja białka – nieodwracalny proces naruszenia struktury białka; czynnikami powodującymi denaturację białka są: temperatura, sole niektórych metali, kwasy i zasady, etanol
reakcja biuretowa – reakcja wykorzystywana do wykrywania wiązań peptydowych w białkach; zachodzi pod wpływem wodorotlenku miedzi(II); w wyniku tej reakcji pojawia się fioletowe zabarwienie
reakcja ksantoproteinowa – reakcja wykorzystywana do wykrywania obecności niektórych białek; zachodzi pod wpływem kwasu azotowego(V); w wyniku tej reakcji pojawia się żółte zabarwienie
wysalanie białka – odwracalny proces koagulacji białka, zachodzi pod wpływem niektórych soli, np. chlorku sodu