Radioactivity (Isotopes pt 2)
that atomic nucleus consists of protons and neutrons;
that natural chemical elements are a mixture of isotopes with a constant composition;
that isotopes are atoms of the same chemical element that have the same number of protons and different number of neutrons;
that isotopes can be stable and not stable (they undergo decay which is accompanied by radiation).
to list the types of nuclear radiation and determine their hardness;
to explain the following terms: radioactive isotope (element), radioisotope;
to indicate radioactive elements in the periodic table;
to explain the origin of radioisotopes in the environment.
Radioisotopes
A significant number of elements occur in nature as a mixture of isotopes. Isotopes can be stable and unstable. The ones that are unstable decay spontaneously and transform into isotopes of other elements. They are said to be unstable and are called radioactive isotopesradioactive isotopes or radioisotopes. Elements can be a mixture of stable or unstable (radioactive) isotopes, or contain both types of isotopes. Elements that are composed of only radioactive isotopes (radioisotopes) are called radioactive elements. There are few radioactive elements in nature. For example: technetium () and promethium () and elements with atomic number greater than 82.
What is nuclear radiation?
Radiation, called nuclear or ionizing radiation, is always present when atomic nuclei are decaying. Some radioactive isotopes emit α (alpha) particles and others emit – β (beta) particles. Often radiation γ is also observed. A large amount of energy is released during decay.
Each type of radiation produced by radioactive substances has a different range and degree of penetration through the materials. α (alpha) radiation has the smallest range and can be stopped by a piece of paper. A somewhat thicker layer of another material is needed to stop β (beta) particles, for example thin lead or aluminium sheet. γ (gamma) radiation is the most penetrating – a few‑centimetre thick lead shield is needed to protect against it.
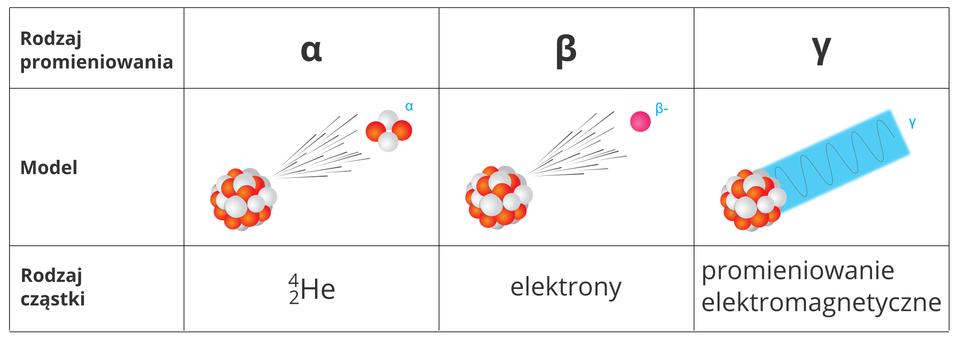
1. type of radiation
2. type of particle
3. electrons
4. electromagnetic radiation
Describe the properties of alfa and beta radiation.
Radioactive elements in our surroundings
Think of radioactive elements present in our surroundings. If there are any, where do they come from? Search the Internet, the textbook and the e‑textbook for the information on this subject. Check also the dropdown table.
- Natural occurrence of radioactive isotopes in the Earth’s crust – some of them occur in it since the beginnings of Earth, for example rubid-87, potassium-40.
- Natural occurrence of radioactive isotopes in the Earth’s crust due to decay of other radioactive isotopes, for example thorium and uranium. More radioisotopes are formed as a result of their decay, i.a. radium, polonium, radon.
- Natural occurrence of radioactive isotopes from rocks in plants and living organisms.
- Radioactive isotopes formed in the Earth’s atmosphere due to cosmic rays (neutrons) on the components of the Earth’s atmosphere, for example tritium, carbon-14.
- Emitters of alpha, beta and gamma radiation – they are derived from nuclear explosions in the atmosphere (especially in the 1960s), failure of the Chernobyl nuclear power plant in 1986 and of nuclear power plant in Japan in 2011. Most isotopes decayed short time after the failure. However some isotopes, such as cesium-137, strontium-90, plutonium-239 or plutonium-240, still occur in the environment.
- Radiation generated by various devices used in medical diagnostics, industry and scientific research.
- Radioisotopes made of natural materials or extracted from the Earth as well as burrows, smoke from coal power plants, mineral water, etc.
Expand the points below and think of radioactive elements that occur in the environment.
Natural radioactivity
- Natural occurrence of radioactive isotopes in the Earth’s crust – some of them occur in it since the beginnings of Earth, for example rubid-87, potassium-40.
- Natural occurrence of radioactive isotopes in the Earth’s crust due to decay of other radioactive isotopes, for example thorium and uranium. More radioisotopes are formed as a result of their decay, i.a. radium, polonium, radon.
- Natural occurrence of radioactive isotopes from rocks in plants and living organisms.
- Radioactive isotopes formed in the Earth’s atmosphere due to cosmic rays (neutrons) on the components of the Earth’s atmosphere, for example tritium, carbon-14.
Artificial radioactivity
- Emitters of alpha, beta and gamma radiation – they are derived from nuclear explosions in the atmosphere (especially in the 1960s), failure of the Chernobyl nuclear power plant in 1986 and of nuclear power plant in Japan in 2011. Most isotopes decayed short time after the failure. However some isotopes, such as cesium-137, strontium-90, plutonium-239 or plutonium-240, still occur in the environment.
- Radiation generated by various devices used in medical diagnostics, industry and scientific research.
- Radioisotopes made of natural materials or extracted from the Earth as well as burrows, smoke from coal power plants, mineral water, etc.
Is it possible to measure nuclear radiation?
Most radiation absorbed by the matter, including its effect on living organisms, is described by means of the unit called sievertsievert (Sv). In Poland, radiation dose, both from natural and artificial sources, amounts to approx. 3.3 mSv (millisieverts) during the year.
Radiation originating from natural radioisotopes is often referred to as the radiation background. Natural radiation background usually differs in various places throughout the world. It depends mainly on the local geological structure of the ground and the average concentration of noble gas – radioactive radon – in the atmosphere.
- paramecium (protozoan) – 3000 Sv
- snail – 80–200 Sv
- fly – 800 Sv
- bat – 150 Sv
- turtle – 15 Sv
- rat – 6–10 Sv
- pig – 3.5–4.5 Sv
- monkey – 5–6 Sv
- man – 3–4 Sv
Expand the points below and read information on the effects of radiation on living organisms.
Harmfulness of radiation
depends on its type, intensity (power) and duration. Too high doses of radiation can overcome defence mechanisms of the organism and lead to severe diseases, or even death. This property of radiation is used to destroy cancer cells.
Advantages of radiation
Small doses of radiation stimulate the immune system and reduce the incidence of cancer.
Radiation resistance – human body
a single dose lethal to a human being is a thousand times higher than the average annual background dose and amounts to 3–4 Sv (3000–4000 mSv).
Radiation resistance – other living organisms
single lethal dose – half of the population dies
after 30 days from being exposed:
- paramecium (protozoan) – 3000 Sv
- snail – 80–200 Sv
- fly – 800 Sv
- bat – 150 Sv
- turtle – 15 Sv
- rat – 6–10 Sv
- pig – 3.5–4.5 Sv
- monkey – 5–6 Sv
- man – 3–4 Sv
Application of nuclear energy
Find information on the application of radioactive elements in various areas of life in different sources and then do the exercises.
The amount of radiation absorbed by the matter is reflected by the unit called:
- radian
- sivert
- rontgen
- centile
α (alpha) radiation is blocked by:
- piece of paper
- aluminium plate with a thickness of approx. 3 mm
- lead shield which is few centimetres thick
- concrete wall with a thickness of several dozen centimetres
Summary
Radioactive isotopes are mixtures of unstable isotopes; these are elements of atomic number greater than 82, technetium () and promethium ().
Unstable (radioactive) isotopes undergo spontaneous decay and transform into isotopes of other elements with different decay rate, typical of given isotope.
Radioactive isotopes can emit three types of radiation: α (alpha) (, nuclei of the helium atom), β (beta) (rapidly moving electrons) and γ (gamma) (electromagnetic radiation).
In nature there are many radioisotopes that are fixed components of water, air and soil. They are a source of radiation called natural radioactivity.
Harmfulness of radiation depends on its type, intensity (power) and duration.
Check how far the nearest nuclear power plant is from your place of residence.
Keywords
radioactive isotopes, radioactivity
Glossary
izotopy promieniotwórcze – radionuklidy; izotopy, których jądra samorzutnie zmieniają swą strukturę i emitują promieniowanie
promieniotwórczość – radioaktywność, zdolność do spontanicznej emisji promieniowania przez jądro atomowe
siwert [Sv] – jednostka tzw. dawki efektywnej promieniowania jonizującego; obrazuje całkowite narażenie organizmu zarówno przy równomiernym, jak i nierównomiernym napromienieniu narządów i tkanek