River flow sections and their characteristics
that rivers are divided into main rivers and tributaries;
that the main river flows directly into the sea, ocean or flows into the outflow area;
that the main river can not be a tributary of another river.
explain the differences between the main river and a tributary;
indicate the Vistula River and the Oder River, from the source to the mouth, on the map of Poland;
describe how a river behaves in the upper, middle and lower sections;
indicate river sections in which bottom, headward and lateral erosion types dominate;
characterize the process of formation of meanders and old river beds;
explain what contributes to the creation of a delta and an estuary, and give examples
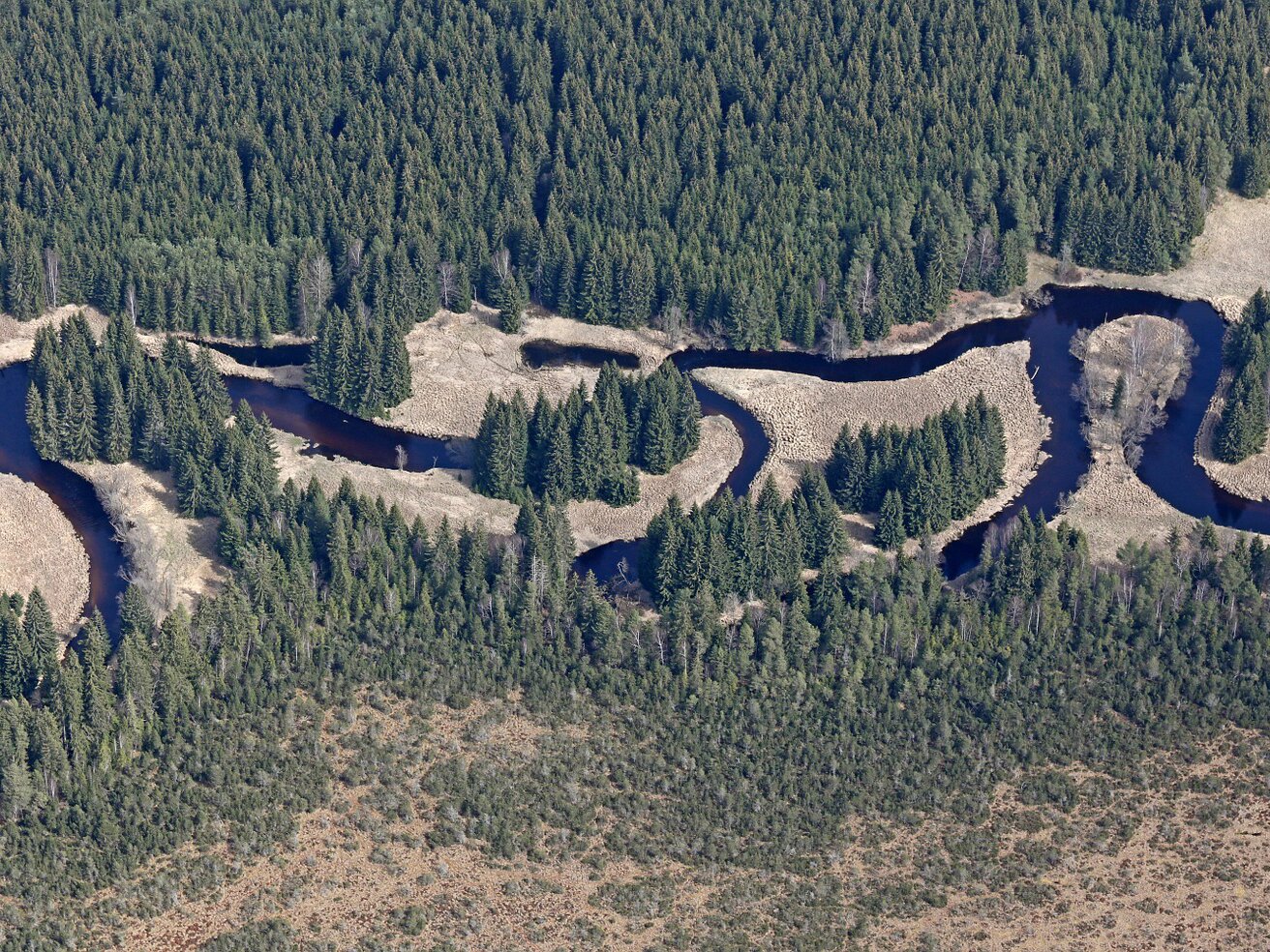
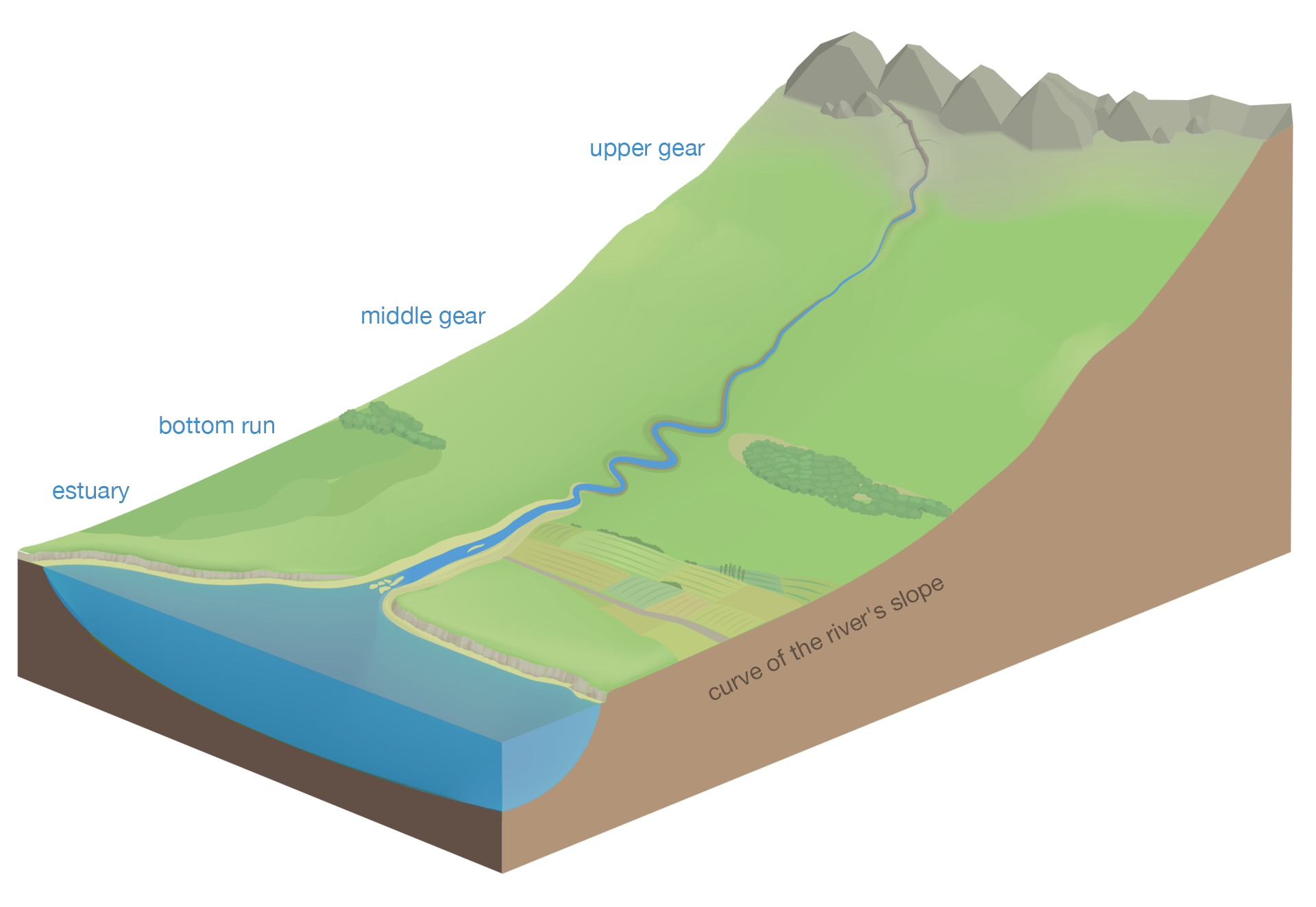
The course of most rivers is divided into three sections.
In the upper course the rivers often flow in mountainous or highland terrain. Due to large differences in altitude, the water flows at a significant speed and has a large erosive force. Deep deep erosiondeep erosion dominates there as a result of which deeper and deeper valleys are formed, and headward erosionheadward erosion causing the sources to regress and to push the hard rock of waterfalls up the river. Rock material, which is eroded by water, is worn smooth, crushed and transported.
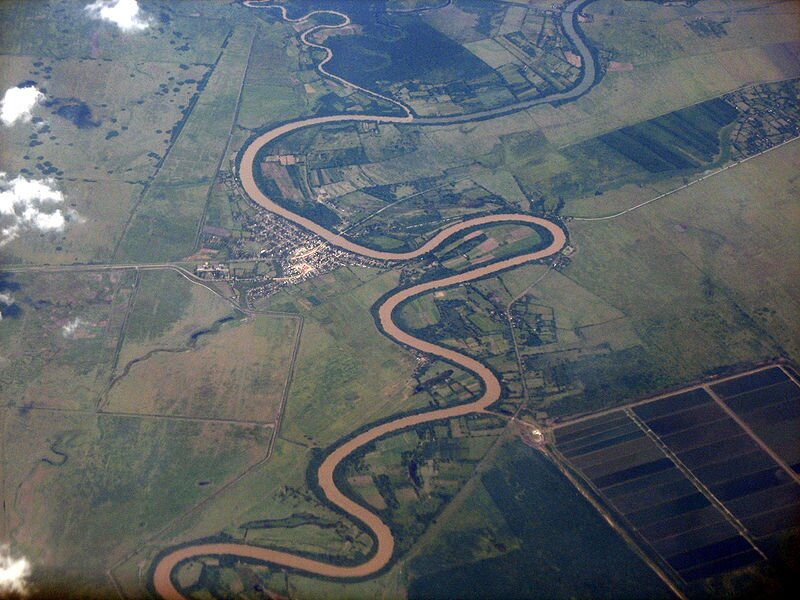
In the middle course the river usually flows slower and thanks to inflows it has more water. Now it destroys the channel differently and changes its character to lateral erosionlateral erosion, causing the river to significantly widen its valley and transport finer material. This process consists in undercutting or undermining the banks, which is caused by an uneven river current. The water undermines concave edges, and it deposits segregated material on convex edges: gravel and coarse sand, forming outwash. The effects of this process include breaking down of rock and earth material, shifting of the edge wall and supplying of new rubble to the riverbed. This process creates meandersmeanders. After some time, meanders cut themselves off from the river, which at high levels of waters straightens its course, and small, shallow, fast‑growing lakes are formed and they are called oxbow lakesoxbow lakes.
In the lower course, especially at the mouths of the sea or the lake, the river no longer has its erosive force, gradually loses its ability to transport material and accumulates it in its own bed, at the mouth or at the bottom of the reservoir to which it falls. Therefore, characteristic elements of riverbeds in their lower courses are sandbanks (river banks).
How the river finds its way to the estuary?

Film dostępny na portalu epodreczniki.pl
Film przedstawiający, jak w domowych warunkach można nauczyć się formowania biegu rzeki (meandering river). Należy skorzystać z piasku, wody, miski, lejka oraz deski. Wlewamy przez lejek wodę na piasek. Woda, która wylewa się z lejka pokazuje w jaki sposób rzeka meandruje i w jaki sposób tworzy się koryto rzeki.
Based on the information obtained during classes, do the following exercises.
Match the rivers to the appropriate group according to their mouth types.
Garonne, Tagus River, Saint Lawrence River, Mississippi River, Loire River, Danube, Elbe, Niger River, Amazon River, Nile, Vistula River, River Thames, Huang He
| Estuary | |
|---|---|
| Delta |
From the word spread, match with the red color the characteristics of the upper river, the blue central and the purple lower section.
{red}groan narrow valleys{/red}{blue}formation of oxbow lakes{/blue}{red}strong current of the river{/red}{red}deep erosion{/red}{purple}formations of shoals{/purple}{purple}accumulation{/purple}{purple}small drop {/purple}{red}formation of waterfalls{/red}{red}it flows on steep slopes{/red}{blue}lateral erosion{/blue}{blue}formation of meanders{/blue}{purple}creation of a delta or estuary{/purple}{red}source{/red}{blue}the water speed is much lower{/blue}
Keywords
river, river sections, erosion
Glossary
akumulacja – proces gromadzenia osadów w wyniku działalności wody, wiatru lub lodowca
delta – ujście rzeki w postaci dwóch lub więcej odnóg na obszarze usypanym z osadów przyniesionych przez rzekę
erozja – procesy niszczenia skorupy ziemskiej, polegające na żłobieniu i rozcinaniu powierzchni przez wody, lodowce i wiatr, połączone z usuwaniem powstających produktów niszczenia
erozja boczna – niszczenie brzegów rzek w wyniku nierównomiernej prędkości przepływu wody
erozja wgłębna – wcinanie się rzek w podłoże na skutek niszczenia dna za pomocą niesionego materiału skalnego; doliny rzeczne tego typu mają w przekroju poprzecznym kształt litery „V”
erozja wsteczna – przesuwanie się źródeł rzeki oraz progów i załomów skalnych w kierunku przeciwnym niż kierunek biegu rzeki; erozja wsteczna powoduje wydłużanie się doliny w górę rzeki
estuarium (ujście lejkowate) – poszerzone przez pływy morskie ujście rzeki uchodzącej do głębokiego morza
meander – fragment koryta rzeki o kształcie przypominającym zakole, łuk lub pętlę, utworzony w wyniku erozji bocznej
starorzecze – jezioro leżące w dolinie rzecznej, powstałe w wyniku odcięcia pętli meandrameandra

