E-resource ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
Water purification systems
1. Film in the standard version.

Film dostępny na portalu epodreczniki.pl
The scene takes place in an office of a company that sells and distributes devices for water purification. The owner of a detached house talks to the salesman about water purification devices. Scena rozgrywa się w biurze firmy zajmującej się sprzedażą i dystrybucją urządzeń do uzdatniania wody. Właścicielka domu jednorodzinnego rozmawia ze sprzedawcą na temat urządzeń do uzdatniania wody.
2. Film with subtitles.

Film dostępny na portalu epodreczniki.pl
The scene takes place in an office of a company that sells and distributes devices for water purification. The owner of a detached house talks to the salesman about water purification devices. Scena rozgrywa się w biurze firmy zajmującej się sprzedażą i dystrybucją urządzeń do uzdatniania wody. Właścicielka domu jednorodzinnego rozmawia ze sprzedawcą na temat urządzeń do uzdatniania wody.
3. Film with subtitles and pauses. Listen and repeat after the speaker.

Film dostępny na portalu epodreczniki.pl
The scene takes place in an office of a company that sells and distributes devices for water purification. The owner of a detached house talks to the salesman about water purification devices. Scena rozgrywa się w biurze firmy zajmującej się sprzedażą i dystrybucją urządzeń do uzdatniania wody. Właścicielka domu jednorodzinnego rozmawia ze sprzedawcą na temat urządzeń do uzdatniania wody.
4. Film with subtitles and narration.

Film dostępny na portalu epodreczniki.pl
The scene takes place in an office of a company that sells and distributes devices for water purification. The owner of a detached house talks to the salesman about water purification devices. Scena rozgrywa się w biurze firmy zajmującej się sprzedażą i dystrybucją urządzeń do uzdatniania wody. Właścicielka domu jednorodzinnego rozmawia ze sprzedawcą na temat urządzeń do uzdatniania wody.
After watching the film “Water purification systems”, match the words/phrases to form logical expressions.
Po obejrzeniu filmu “Systemy uzdatniania wody”, połącz ze sobą słowa/zwroty, aby utworzyć logiczne frazy.
compounds, removal system, demineralization, list, purity, limescale, process, osmosis
| microbiological | |
| mechanical sludge | |
| magnesium | |
| water | |
| price | |
| disinfection | |
| reverse | |
| formation of |
Household sewage

Film dostępny na portalu epodreczniki.pl
The animation presents a household and sewage management methods. Animacja przedstawia gospodarstwo domowe i metody gospodarowania ściekami.
After watching the voice-over animation “Household sewage”, complete the sentences with correct words or phrases in the correct form. Use the word bank. Po obejrzeniu animacji z lektorem „Ścieki z gospodarstwa domowego”, uzupełnij zdania odpowiednimi wyrazami lub frazami we właściwej formie. Skorzystaj z banku słów.
drainage, inspection chamber, sand filter, house drain, holding tank, soakaway, communal municipal network, sewage system, septic tank, plastic
If we live in a canalized area, we have the duty to connect our installation to the .....................................................
The .................................................... , usually called communal, can be a utility or combined sewer system.
The connection pipe of the home drainage system and the external network is called a .....................................................
The house drain runs underground and can be cleaned thanks to the .....................................................
A .................................................... is a good solution for a very small amount of sewage in a household.
We distinguish concrete holding tanks and .................................................... holding tanks.
We can drain neutralized sewage from the household sewage treatment plant into a .....................................................
Initial treatment takes place in a .................................................... From there, the sewage flows to other devices.
.................................................... enables the pre-treated sewage to flow into gravel or soil.
Drainage with a .................................................... is used on earthen or loamy soil.
Treatment of wastewater in treatment plants

Film dostępny na portalu epodreczniki.pl
The animation presents the processes occurring during wastewater treatment in a sewage treatment plant. Animacja prezentuje procesy zachodzące podczas oczyszczania ścieków w oczyszczalni.
After watching the silent animation “Treatment of wastewater in treatment plants”, decide whether the sentences are true or false.
Po obejrzeniu animacji bez dźwięku „Oczyszczanie ścieków w oczyszczalni” ustosunkuj się do zdań umieszczonych w ćwiczeniu, podejmując decyzję, czy to prawda czy fałsz.
| Prawda | Fałsz | |
| The processing of sewage sludge is carried out in sewage treatment plants. | □ | □ |
| Screenings, in other words the biggest pollutants, are stopped in the primary settling tank. | □ | □ |
| The sand from the sewage is stopped in the sand separator. | □ | □ |
| In the primary settling tank, as a result of the sedimentation process, the organic suspensions that easily fall out are separated from the sewage. | □ | □ |
| The microorganisms in the bioreactors remove compounds of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus. | □ | □ |
| The sludge is concentrated in the secondary settling tank. | □ | □ |
| Anaerobic fermentation takes place in fermentation chambers and results in the decomposition of inorganic compounds. | □ | □ |
| Fermented and degassed sludge goes to the averaging tanks, where it is dewatered on belt presses in order to obtain dry mass. The mass then goes to the thermal station for sludge drying. | □ | □ |
Types of sewage
The hypertext material is a part of a guide on wastewater management.
Hipertekst stanowi fragment poradnika dotyczącego gospodarki ściekowej.
●SewageSewageis used liquids, suspensions, colloids, solutions and waste solids. They are discharged via pipelines to natural receivers, in other words watercourses, tanks, septic pits, etc. Industrial waste, food waste and faecesfaeces from urban and residential households are discharged in the form of sewage.
● Household wastewaterHousehold wastewater is created from water used in households to maintain personal hygiene, flush sanitary facilities, prepare meals, etc. This wastewater is divided into grey watergrey water, in other words a drain from all household appliances, except from toilets, with low bacteriological contamination, and black water (the outflow from toilets contaminated with a significant amount of pathogens).
● Industrial sewageIndustrial sewage usually contains various chemical compoundschemical compounds that are a by‑product of technological processes used in industrial plants.
● Agricultural wastewaterAgricultural wastewater is formed from water flowing from fields and farms, usually containing fertilizersfertilizers, pesticidespesticides and microbial contamination. SlurrySlurry is particularly dangerous. It can contain thousands of times more organic and inorganic contaminants than household sewage.
●RainwaterRainwateris wastewater that arises from atmospheric precipitation washing away built‑up areas. It contains large amounts of organic and inorganic impurities, many in the form of suspensions.
● Heated waterHeated water is created in technological processes cooled with water.
● Municipal sewageMunicipal sewageis wastewater located in the municipal sewage system, regardless of its source (household, industrial, rainwater, snowmelt or a mixture of the just mentioned).
After reading the hypertext “Types of sewage”, complete the sentences with correct words or phrases in the correct form. Use the word bank. Po przeczytaniu hipertekstu „Rodzaje ścieków”, uzupełnij zdania odpowiednimi wyrazami lub frazami we właściwej formie. Skorzystaj z banku słów.
slurry, sewage, grey water, heated water, agricultural wastewater, household wastewater, black water, municipal sewage, industrial sewage, rainwater
Used liquids, suspensions, colloids, solutions and waste solids, which are discharged via pipelines to natural receivers, in other words watercourses, tanks, septic tanks, etc. are known as ...............................................
Water used in households for personal hygiene, flushing sanitary facilities, food preparation, etc. creates ...............................................
The drain from all household appliances, except from toilets, with low bacteriological contamination is called ...............................................
The contaminated drain from toilets, with a large number of pathogens, is called ...............................................
Sewage that usually contains various chemical compounds that are a by-product of technological processes is called ...............................................
Wastewater generated from water flowing from fields and farms, usually containing fertilizers, pesticides and microbial contamination is called ...............................................
.............................................. is particularly dangerous. It can contain thousands of times more organic and inorganic contaminants than household sewage.
Wastewater that arises from atmospheric precipitation washing away built-up areas, which contains large amounts of organic and inorganic contaminants, many in the form of suspensions, is called ...............................................
Water created in technological processes cooled with its help is called ...............................................
Wastewater, industrial sewage, rainfall, snowmelt or a mixture of the just mentioned that are in the sewage system, are called ...............................................
Water intake protection
The hypertext presents the decision of the regional director for environmental protection regarding the establishment of sanitary protection zones for water intakes and sources to ensure the appropriate quality of water captured for water supply purposes and to ensure the protection of water resources.
Hipertekst przedstawia decyzję regionalnego dyrektora ochrony środowiska w sprawie ustanowienia stref ochrony sanitarnej ujęć i źródeł wody w celu zapewnienia odpowiedniej jakości wody ujmowanej na cele wodociągowe oraz ochrony zasobów wodnych.
Regional Director for Environmental Protection
Decision on the indirect and direct protection zone for water intake.
On the basis of the „Water Law” act, and the design documentation of the water supply network, in order to ensure the appropriate quality of water captured for water supply purposes, and due to the fact of water protectionwater protection,
I decide
to grant permission for the designation of an indirect and direct protection zone for water intake. As a result, the area will be subject to prohibitions and limitations in the use of the soil and water.
Additionally,
The areas of direct protection will include part of the water reservoirwater reservoirat the water intake point, facilities and equipment related directly to water intake, part of the area adjacent to these facilities and objects. Within the zone, the land may be used only for purposes related to the operation of water treatment equipment.
The range and boundary of the protection zone for surface water intakessurface water intakes and sourcessources should take into account the type of the water source surface, the shape, size and nature of thecatchmentcatchment, data on underground and ***surface runoff,******surface runoff,*** data on water levelswater levels and their fluctuations, physical and chemical characteristics of water, and sources of water pollution.
The range of the indirect protection zone for the need of surface water intakes is to be adapted to the hydrological characteristics of the water source, and the ability of the water to self‑purifyself‑purify.
The area of the underground waterunderground water intake zone should include devices related to water intake, and a strip of land of specific widths: 8‑10m fordrilled wellsdrilled wells, 10‑15m for dug wellsdug wells, and 10‑20 m for natural intakenatural intake of groundwater.
The abovementioned decision may be appealed against to the Local Government Appeal Court within 14 days.
After familiarizing yourself with the hypertext “Water intake protection”, match the Polish phrases with their English equivalents. Po zapoznaniu się z hipertekstem „Ochrona ujęć wody”, połącz polskie terminy z ich angielskimi odpowiednikami.
surface water intake, drilled well, water protection, surface runoff, water reservoir, underground water, catchment, water self-purification, water level, natural intake
| ochrona wód | |
| zbiornik wody | |
| powierzchniowe ujęcie wody | |
| zlewnia | |
| spływ powierzchniowy | |
| stan wody | |
| samooczyszczanie wody | |
| woda podziemna | |
| studnia wiercona | |
| ujęcie naturalne |
Water treatment
The hypertext material presents a fragment of an interview with an employee of a wastewater treatment plant. The conversation concerns the methods and technical aspects of wastewater treatment.
Hipertekst przedstawia fragment wywiadu z pracownikiem oczyszczalni ścieków. Rozmowa dotyczy sposobów i technicznych aspektów oczyszczania ścieków.
Journalist: Welcome back. Today we are visiting the local sewage treatment plant. We have already talked about removing mechanical impurities from the water, but I still have some questions. What are these flocculent depositsdeposits and layers of pure liquid above them?
Treatment plant employee: Those deposits are created in the coagulationcoagulation process. We use chemicals which are coagulantscoagulants, for example iron salts, aluminum sulfate (VI). They produce a gelatinous suspensionsuspension in the water that adheres to fine suspensions, which are easily sedimentedsedimentedas heavy flocs.
Journalist: What devices are used for this?
Treatment plant employee: DispensersDispensers, mixersmixers,reaction chambersreaction chambers, clarifiersclarifiers. They are devices used to prepare the coagulant. They constitute the technological sequence of the coagulation process.
Journalist: Is the water already purified after this process?
Treatment plant employee: No. Further purification takes place using slow, fast or super‑fast filtersfilters.
Journalist: I understand. You mentioned that over‑normative amounts of manganese and iron in purified water are a quality problem of water. How do you deal with this?
Treatment plant employee: There is a process associated with the removal of the excessive amount of iron from water. It includes the use of open or closed iron removersiron removers. During the softening of water, the compounds that cause water hardness are removed. We use devices for chemical water softening and exchanger systems for the exchange of ionsexchange of ions which cause water hardness.
Journalist: Is this water that you can drink?
Treatment plant employee: Treated water isn’t free of bacteria. We subject such water to disinfectiondisinfection processes. Most often, disinfection is carried out by chemical methods involving the addition of strong oxidants to the water.
Journalist: Thank you for the information. Time for a short break now, and after the break, we will have the third, and last part of our conversation.
After familiarizing yourself with the hypertext “Water treatment”, select the phrase that is concerned with freeing water from bacteria by adding strong oxidizers. Po zapoznaniu się z hipertekstem „Uzdatnianie wody”, wskaż, który termin związany jest z uwolnieniem wody od bakterii przez dodanie do wody silnych utleniaczy.
- coagulation
- sedimentation
- clarifier
- disinfection
- exchange of ions
- filter
- iron remover
- dispenser
Gallery
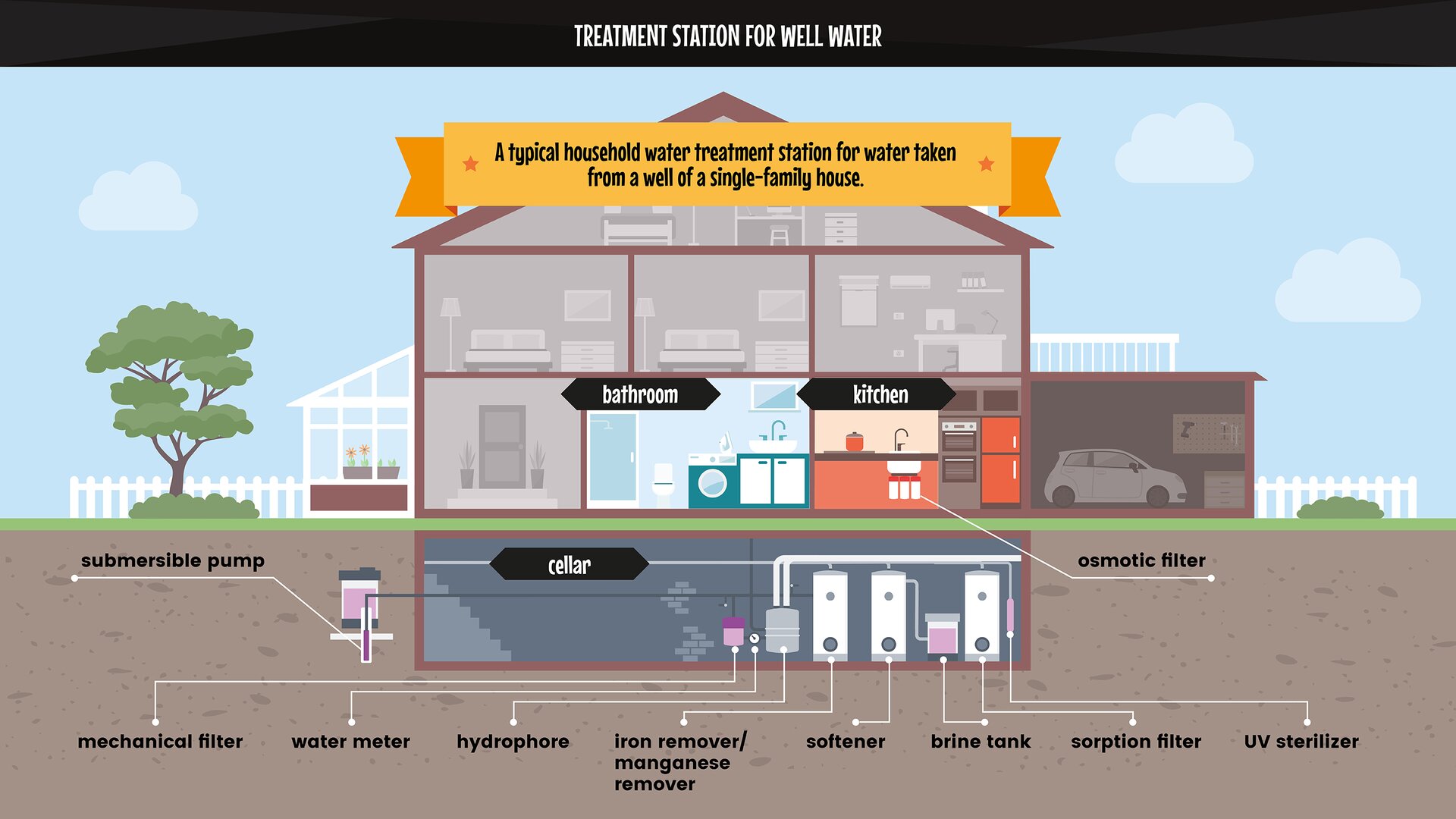
From the word bank, choose the words and phrases that are needed to describe photo no. 1 “Treatment station for well water”. Z banku słów wybierz słowa i zwroty, które są potrzebne do opisania rysunku nr 1 „Stacja uzdatniania wody ze studni”.
brine tank, hydrophore, submersible pump, manganese remover, mechanical filter, septic tank, connection chamber, drainage with a sand filter, house drain, drainage
| TRUE | |
|---|---|
| FALSE |
Scrabble

Zasób interaktywny dostępny pod adresem https://zpe.gov.pl/a/D5tNupwaP
Dictionary
ścieki rolnicze
nawóz sztuczny
sztuczny zbiornik wodny
ciek sztuczny
woda stojąca
hala krat
prasa taśmowa
biogaz
bioreaktor
zbiornik solanki
potok
związek wapnia
jon wapniowy
teren skanalizowany
zlewnia
związek chemiczny
metoda chlorowania
chlor
klarownik
koagulant
koagulacja
kanalizacja ogólnospławna
sieć zbiorcza komunalna
zagęszczanie
zbiornik bezodpływowy betonowy
woda wgłębna
zwierciadło napięte
studzienka przyłączeniowa
odtłuszczanie
woda odżelaziona
woda odmanganiona
detergent
dezynfekcja
dozownik
drenaż rozsączający
system drenująco‑rozsączający
drenaż z filtrem piaskowym
studnia wiercona
studnia kopana
barwnik
wymiana jonów
fekalia
fermentacja
nawóz
filtr
woda płynająca
woda słodka
szara woda
woda gruntowa
woda podgrzana
metal ciężki
zbiornik bezodpływowy
przykanalik
ścieki bytowo‑gospodarcze
hydrofor
oczyszczalnia hydroponiczna
ścieki przemysłowe
studzienka rewizyjna
proces wymiany jonów
odżelaziacz
jezioro
wysypisko śmieci
ołów
związek magnezu
jon magnezowy
odmanganiacz
filtr mechaniczny
rtęć
czystość mikrobiologiczna
mieszalnik
ścieki komunalne
ujęcie naturalne
ciek naturalny
azotan
filtr osmotyczny
metoda ozonowania
ozonator
pestycyd
benzyna
fosfor
zbiornik bezodpływowy z tworzyw sztucznych
staw
osadnik wstępny
radioaktywność
woda opadowa
komora reakcji
odwrócona osmoza
rzeka
piaskownik
skratki
osadnik wtórny
sedymentacja
proces sedymentacji
osadnik gnilny
ścieki
osad pościekowy
kanalizacja
oczyszczalnia ścieków
osad
gnojowica
studia chłonna
jon sodu
zmiękczacz
rozpuszczalnik
filtr sorpcyjny
woda głębinowa
struga
strumień
pompa głębinowa
spływ powierzchniowy
woda powierzchniowa
powierzchniowe ujęcie wody
powierzchniowe źródło wody
zawiesina
woda uzdatniona
metoda ultrafiltracji
zwierciadło swobodne
woda podziemna
kanalizacja bytowa
sterylizator UV
kanał wodny
demineralizacja wody
rów wodny
twardość wody
metoda naświetlania wody przy użyciu promieni ultrafioletowych
stan wody
licznik wody
ochrona wód
zbiornik wody
samooczyszczanie wody