Rome – from settlement to empire
to describe the legendary beginnings of Rome and to explain what a founding legend is;
to characterize the Roman armyRoman army as one of the most effective in the history of Europe and indicate examples of its organization;
to distinguish the following stages in the history of Rome: the kingdom, the republic and the empire.
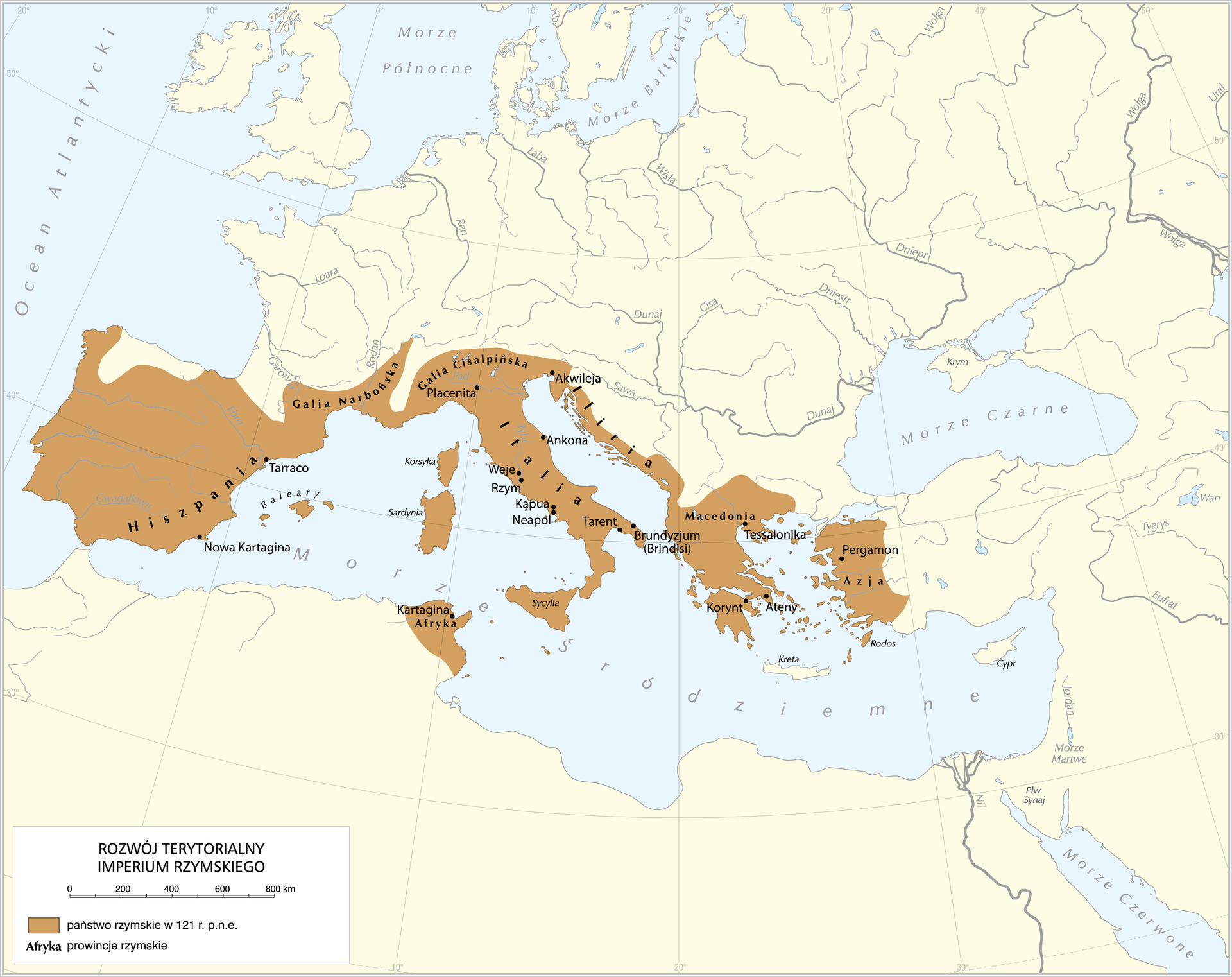
The city of RomeRome lies on the banks of the Tiber River on the Apennine (Italian) Peninsula. Legend has it that the city was founded in 753 BC by Romulus, son of Mars, the war god, and a mortal woman. At a later time, the RomansRomans expelled their kings and established a republic. Highest political authority was vested in two consulsconsuls elected for a period of one year. In the 1st century BC, the Roman Republic collapsed due to civil war. Gaius Julius Caesar, a great leader, rose to ultimate power. After Julius Caesar was murdered, leadership was passed on to his stepson, Augustus. Augustus became the first Roman emperorsemperors. EmperorsEmperors ruled RomeRome for 500 years. For centuries, Roman conquests extended their rule over not only Italy, but also the Mediterranean coast. This great state was called the Roman Empire. RomansRomans managed to conquer and secure vast swathes of land thanks to a perfectly organised army called the legionslegions. RomansRomans covered their whole empire with a network of paved roads. Roads were intended for troops, but they were also open to civilians.
Read the text below and remember the basic information about the history of RomeRome. Who was Gaius Julius Caesar? Look for some more information about him on the Internet.
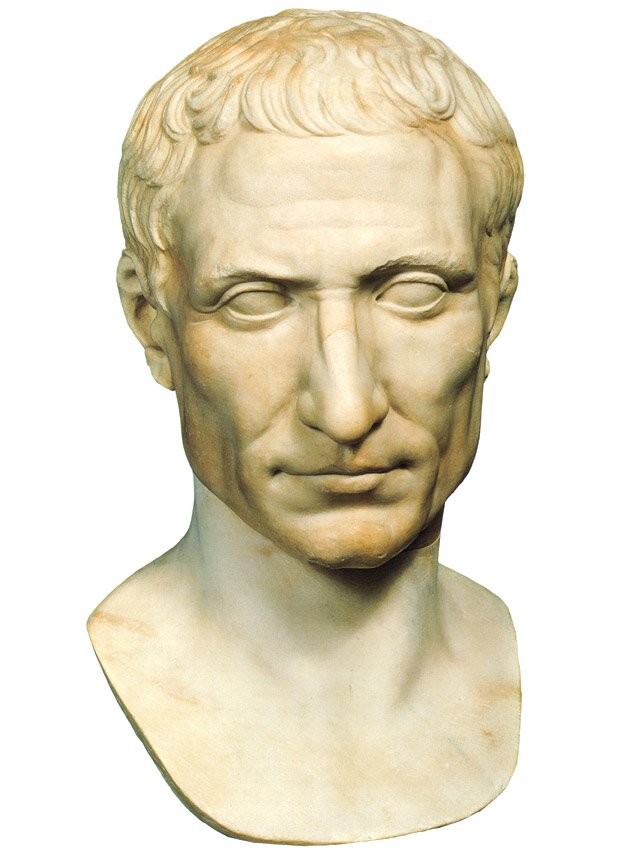

When the RomansRomans expelled their kings, RomeRome became a republic, where similar to ancient Greece, the civic community ruled. However, the Republican RomeRome never created a democracy like Athens, as the state was ruled by aristocrats – also named patricians coming from old Roman families. System of RomeRome was described as „res publica”. The expression had several meanings: „public matter”, „common good” or simply „state.” Modern terms such as „republic” and „Rzeczpospolita” originate from the mentioned name. In the Roman republic, the highest civil and military authorities were owned by two consulsconsuls elected for one year. The consulsconsuls exercised the authority in consultation with the Senate consisted of seniors and experienced citizens. The poorer citizens, named plebeians had the right to organize their own gatherings and the election of tribunes whose duty was protection plebeians' interests. The tribune was a republican official and he had the right of veto against the actions of senators and consulsconsuls. There was also existing an office of a dictator who was granted with absolute authorities for a maximum of six months to prevent extraordinary crises. Due to the fact that in the first century BC RomeRome was engaged in many wars, the permanent professional army was formed, who was blindly devoted to its commanders. At the same time the civil war was running, because capable politicians and commanders struggled for the authority. When one of them - the conqueror of Gaul, Gaius Julius Caesar took over the full authority and proclaimed himself a lifetime dictator - the Roman republic fell. Caesar was an outstanding commander and reformer (he introduced a new calendar), but the size of his authorities worried his opponents. Therefore he was murdered at their request.
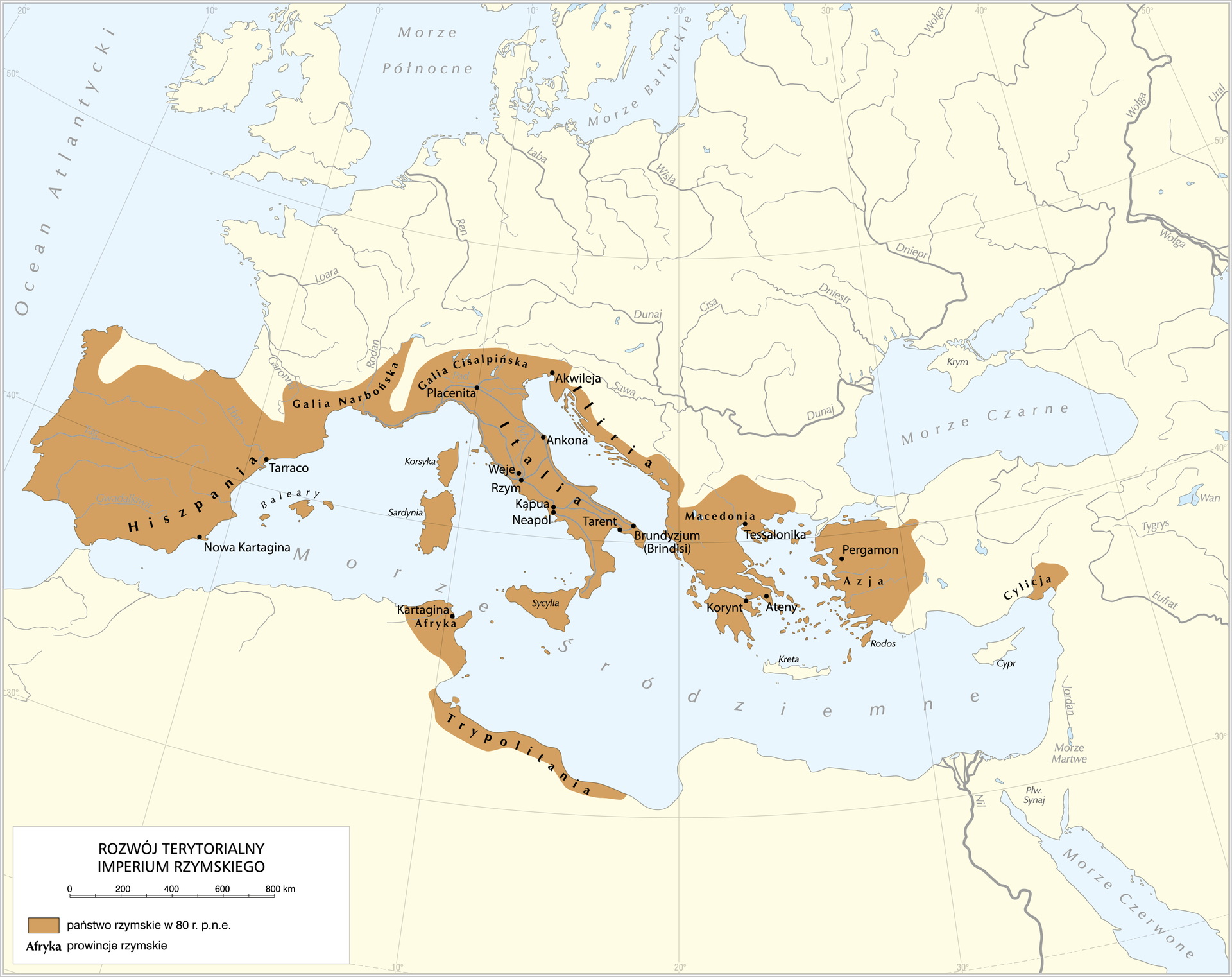
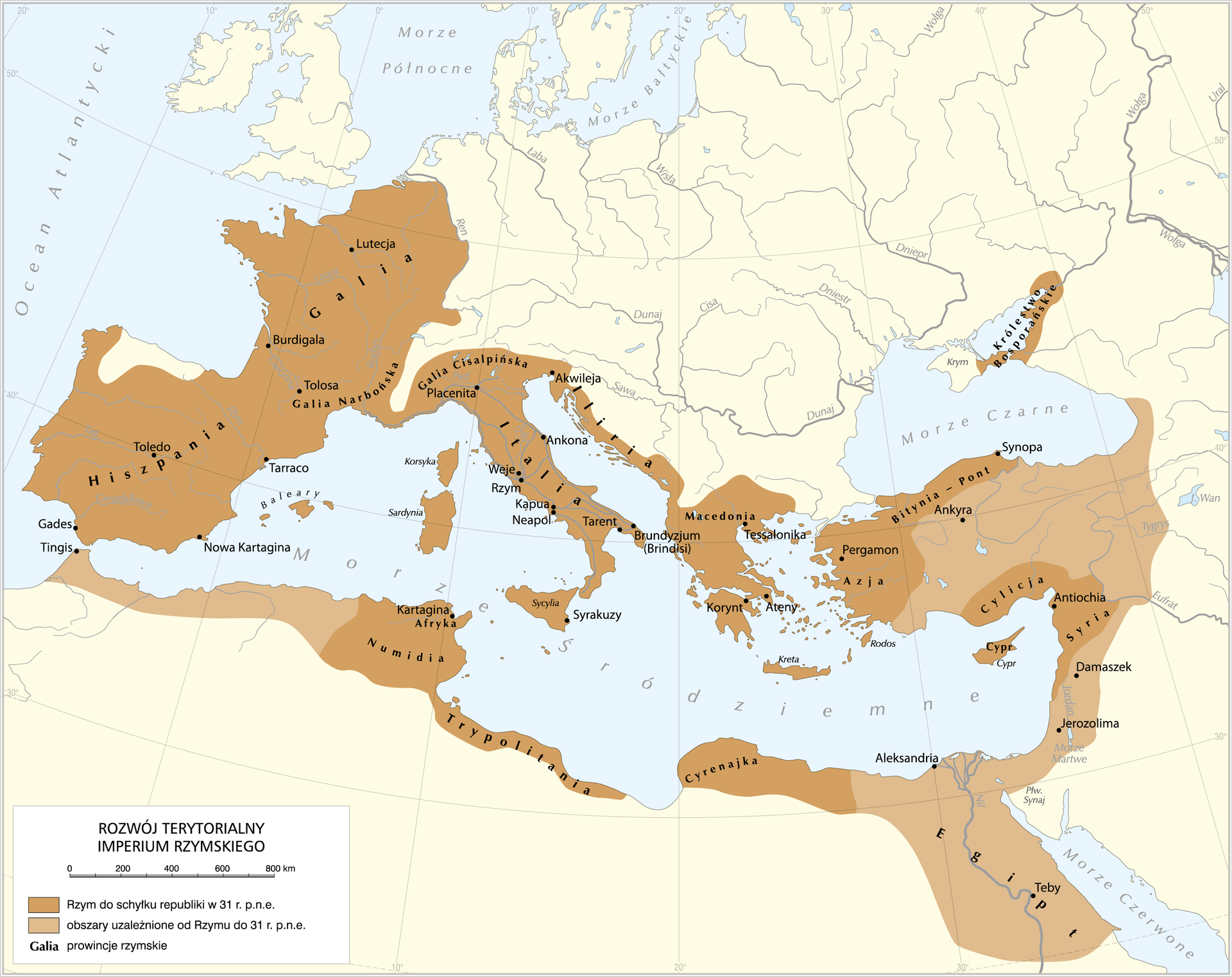
Read the text below and remember the most important information about the history of RomeRome. Why did the RomansRomans succeed in conquering vast areas of Europe?

During the time of the republic, the unification of RomansRomans by Italia became the starting point for further expansion. Initially west against Carthage, and later to the east. Octavian Augustus, the adoptive son of the famous leader Julius Caesar, after his death, became the first Roman emperoremperor. The epoch of the empire is divided into two periods: the early and late empires. The successive emperorsemperors ruled RomeRome for the next 500 years. Their authorities extended far beyond Italy, to all areas surrounding the Mediterranean Sea. Through military conquests, the RomansRomans for the first time in history have adjoined significant areas of Europe into the Mediterranean culture, which meant the start for their subsequent civilization development. Only in the early period of the Empire the inhabitants of the Roman Empire, did enjoy peace. Later, their most important task was to defend the state borders. Both the conquest and maintenance of vast areas was possible due to a perfectly organized army, known as legionslegions. The RomansRomans throughout the empire built a network of beaten roads. They were created for the needs of the army, but civilians also used them. The fall of the Roman Empire took place as a result of the expansion of Germans and Slavs. Almost exactly half of the existence of the Roman state - counting from the birth of the republic to the fall of the empire - is the birth of Christianity. It survived despite the political fall of RomeRome.
Select the correct answer from the following.
- The Roman Empire developed only northward.
- The Roman Empire gradually took over more and more areas around the Mediterranean Sea.
- The Roman Empire gradually took over areas around the Baltic Sea.
Learn about the battle of the Teutoburg Forest. What was the effect of this defeat on further expansion of Rome?
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
Wersja alternatywna: Wysłuchaj poniższego nagrania i przygotuj związane z nim pytania, które zadasz koledze lub koleżance.
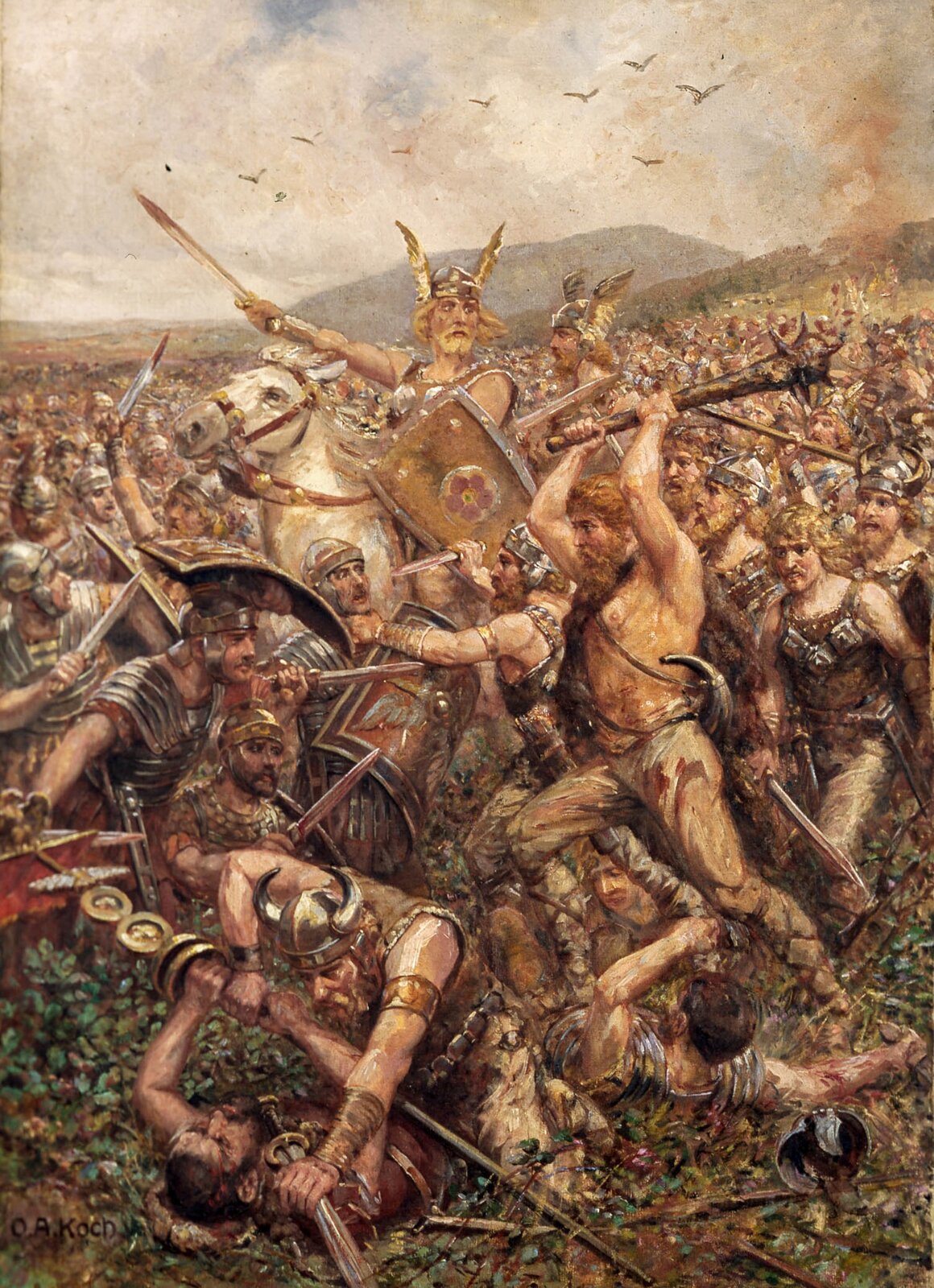

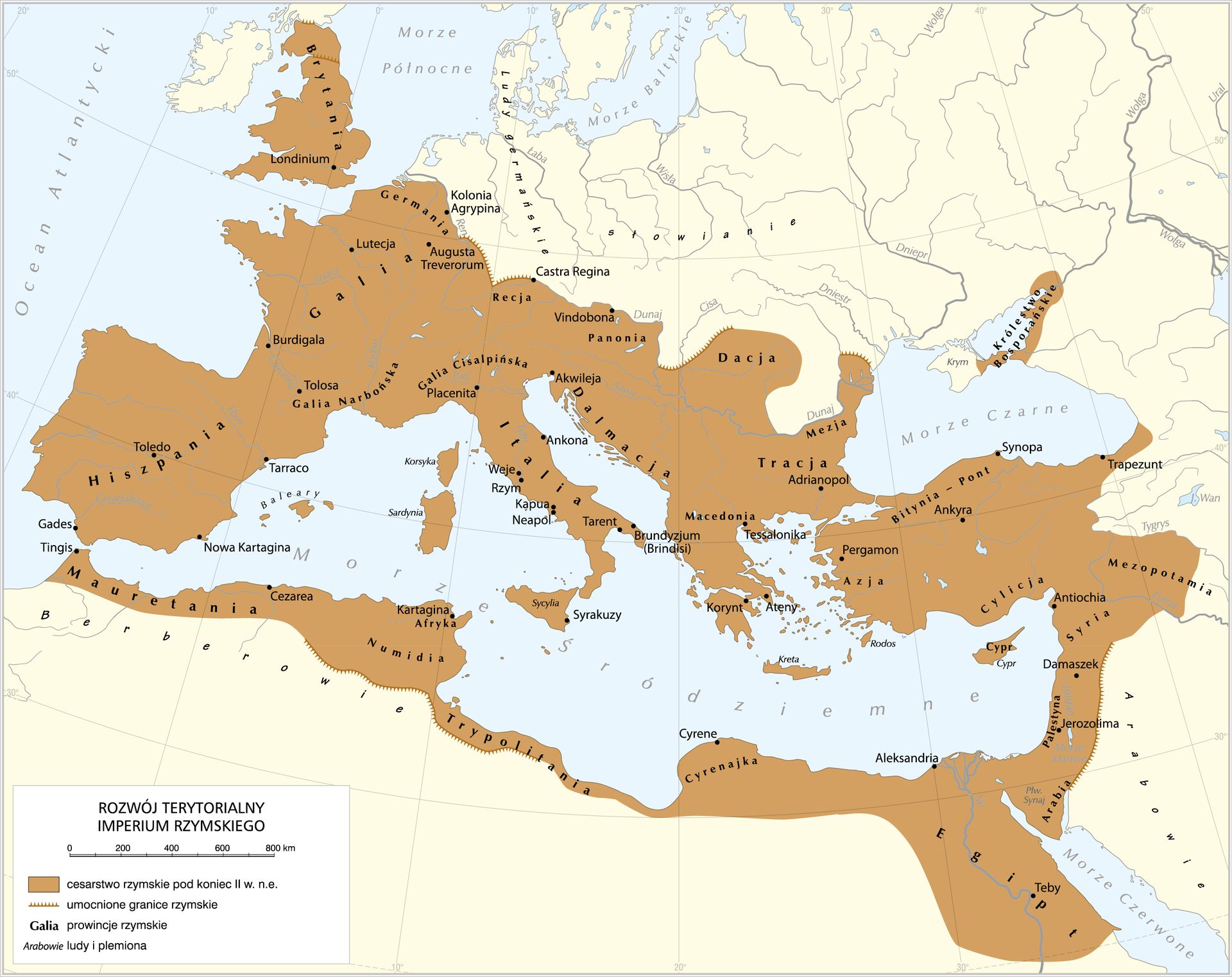
At the beginning of our era, in 9 AD, the RomansRomans in their conquests stopped on the Rhine. The reason was their defeat in the battle with the Germans, in the Teutoburg Forest, east of the Rhine.
During the 3 days and 2 nights of fighting, all 3 Roman legionslegions stationed there and all other divisions fell. Approximately 20,000 to 25,000 soldiers were killed along with the highest command. Right at the beginning of the battle, the RomansRomans’ leader, Varus, was wounded when trying to break into the Rhine. Seeing no chance of survival and afraid of being captured alive, he committed suicide. He was followed by the highest‑ranking officers, three legates of the legionlegion. As a result of the defeat, the Roman armyRoman army was reduced to 25 legionslegions for some time, and the unlucky numbers XVII, XVIII and XIX were never used again.

Ancient sources say that on sleepless nights, EmperorEmperor Augustus walked the corridors of his palace, crying „Varus, return my legionslegions to me!”. As a sign of mourning, he did not cut his hair for months and he tore his robes apart in desperation.
The leader of the Germanic peoples, Arminius, cut off Varus' head, as a gift to his ally - the Germanic king of the Marcomanni, Maroboduus. However, he sent it to RomeRome, where the emperoremperor buried it in a family mausoleum.

EmperorEmperor Augustus decided that the further expansion of RomeRome in Europe is pointless. From then on, the empire defended its borders on the lines of the great rivers of the Rhine and the Danube, where in total, more than half of the Roman legionslegions were stationed.
The Roman soldiers went to the Teutoburg Forest two more times, seven years after the defeat. The first time they buried the bones of Varus’ legionaries; the second time they even managed to beat Arminius, but these actions did not bring them anything - they did not ensure the recovery of the lost Germanic lands. They only managed to recover the eagle of the 19th legionlegion.
Read the text below and check the position occupied by the scouts, armoured cavalryarmoured cavalry, siege equipment, legionnaire cohorts, and rolling stock in the Roman armyRoman army.
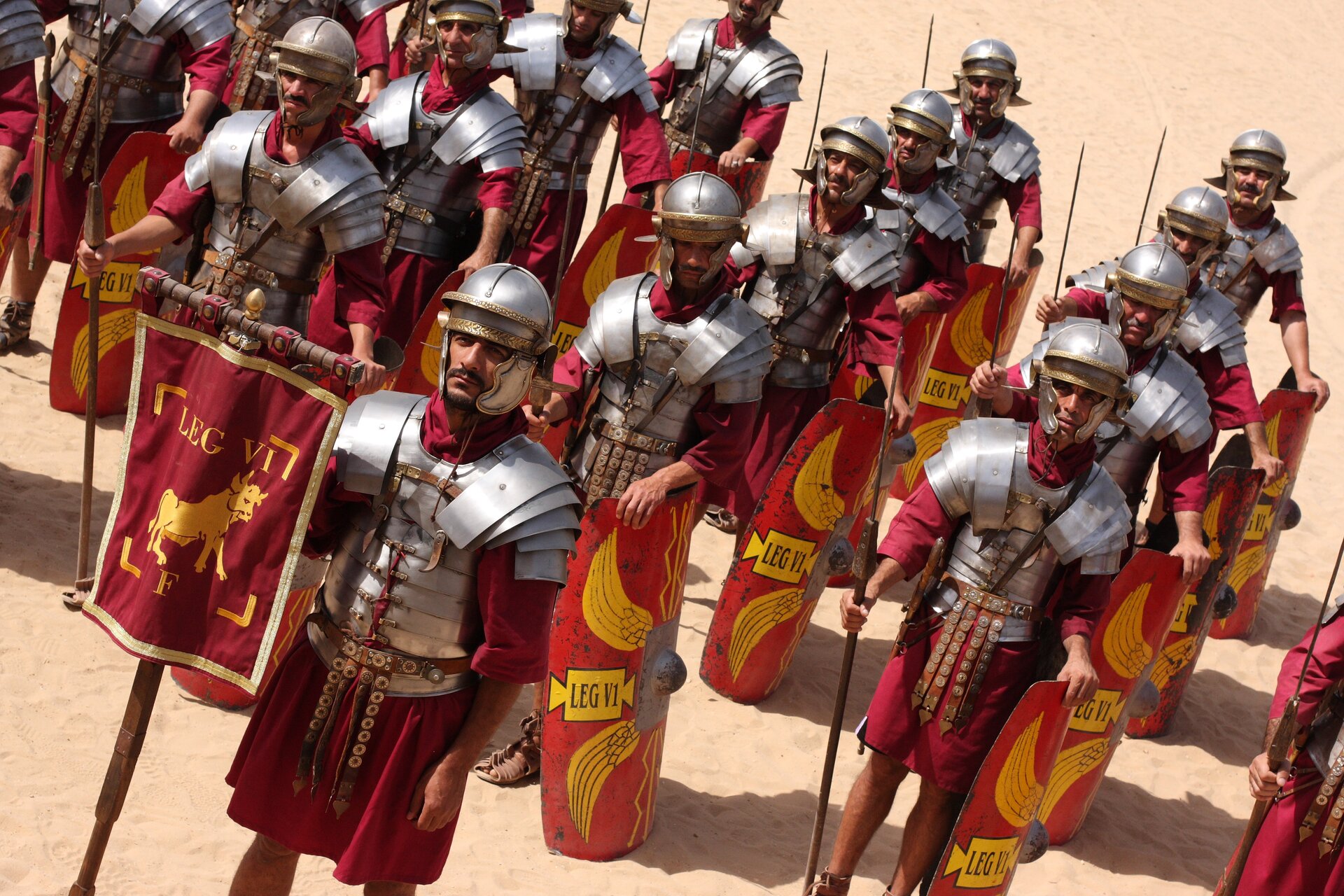

The linear formation was the most popular in the Roman armyRoman army. It consisted of all the units moving in a long column, and each of them had a specific place and task in it. Scouts were marching first. The task of the subsequent units was to prepare the way for the main forces to march and find the right place for the camp. They were followed by pack animals carrying the luggage of soldiers and officers. Next, commanding officer together with the senior officers and the collateral procession were moving. Behind them the proper armoured horse‑mounted troops were marching, where the riders were positioned so that they could quickly move to any place of the marching column at any time. They were followed by siege equipment and war machines, and in this part of the army also legionary signs and emblems and trumpets were carried. The main forces of the army followed the signs. These were legionary cohorts arranged in a fixed order, six soldiers each in a row. They were followed by rolling stock, carrying food, tools, and finally a pedestrian and a horse rearguard.
Language practice. Match pairs: English and Polish.
Rome, legions, Roman army, camp, armoured cavalry, consul, emperor, republic
| Rzym | |
| konsul | |
| republika | |
| cesarz | |
| armia rzymska | |
| legiony | |
| jazda pancerna | |
| tabory |
Keywords
Rome, empire, legions, emperor
Glossary
ciężka kawaleria, kawaleria opancerzona
konsul – jeden z dwóch najwyższych urzędników republiki sprawujących władzę cywilną i wojskową.
cesarz – władca sprawujący samodzielnie dożywotnią władzę w swoim imperium.
legiony – oddziały, z których zbudowana była armia rzymska.
Rzymianie
Rzym
armia rzymska