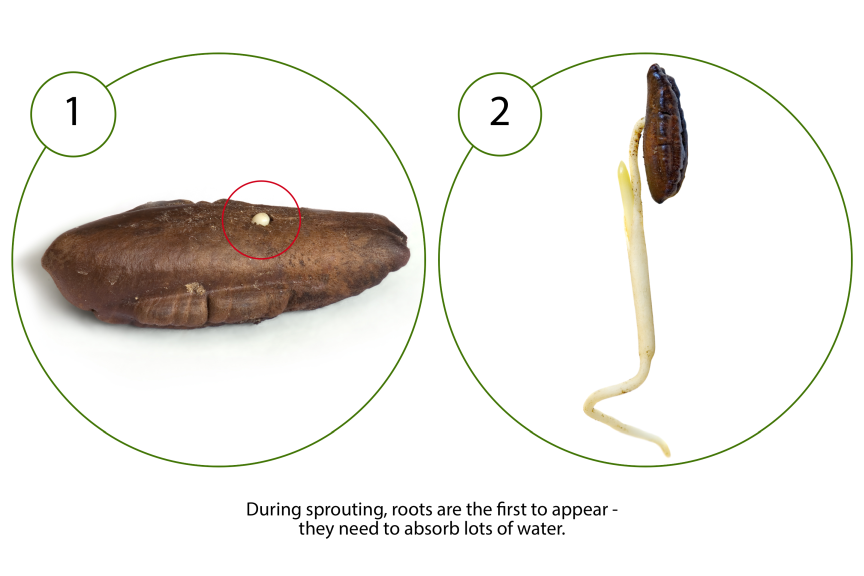
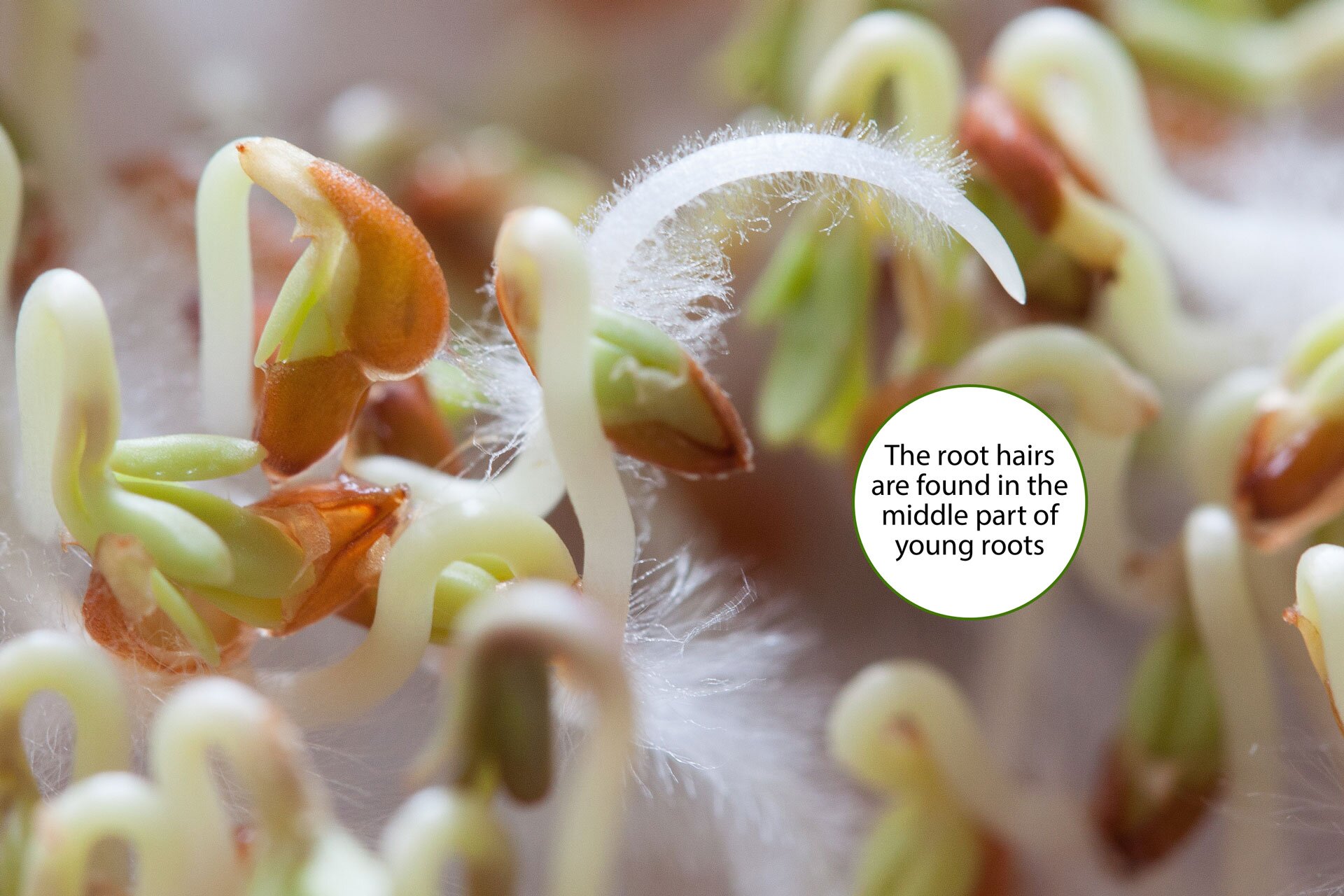
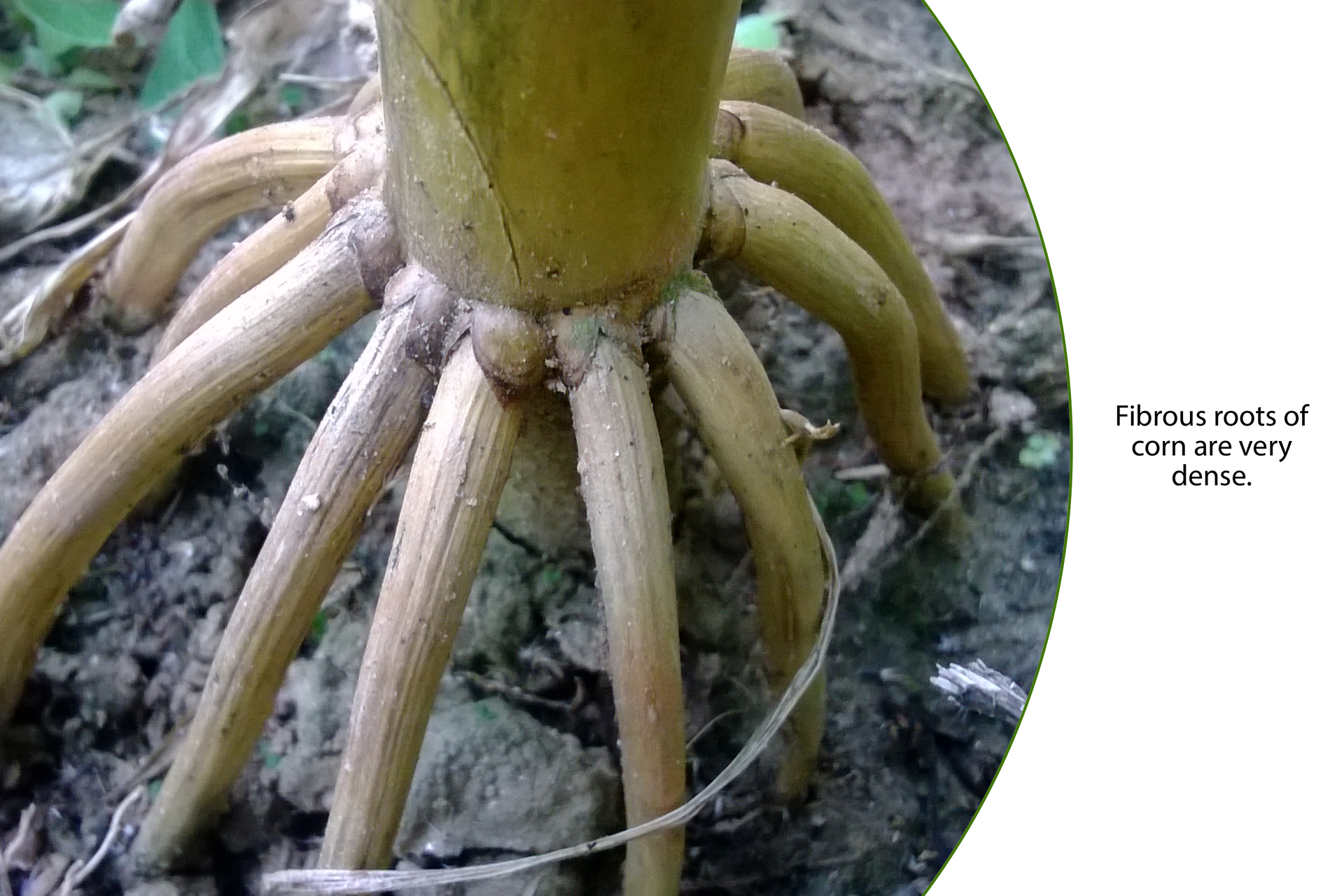
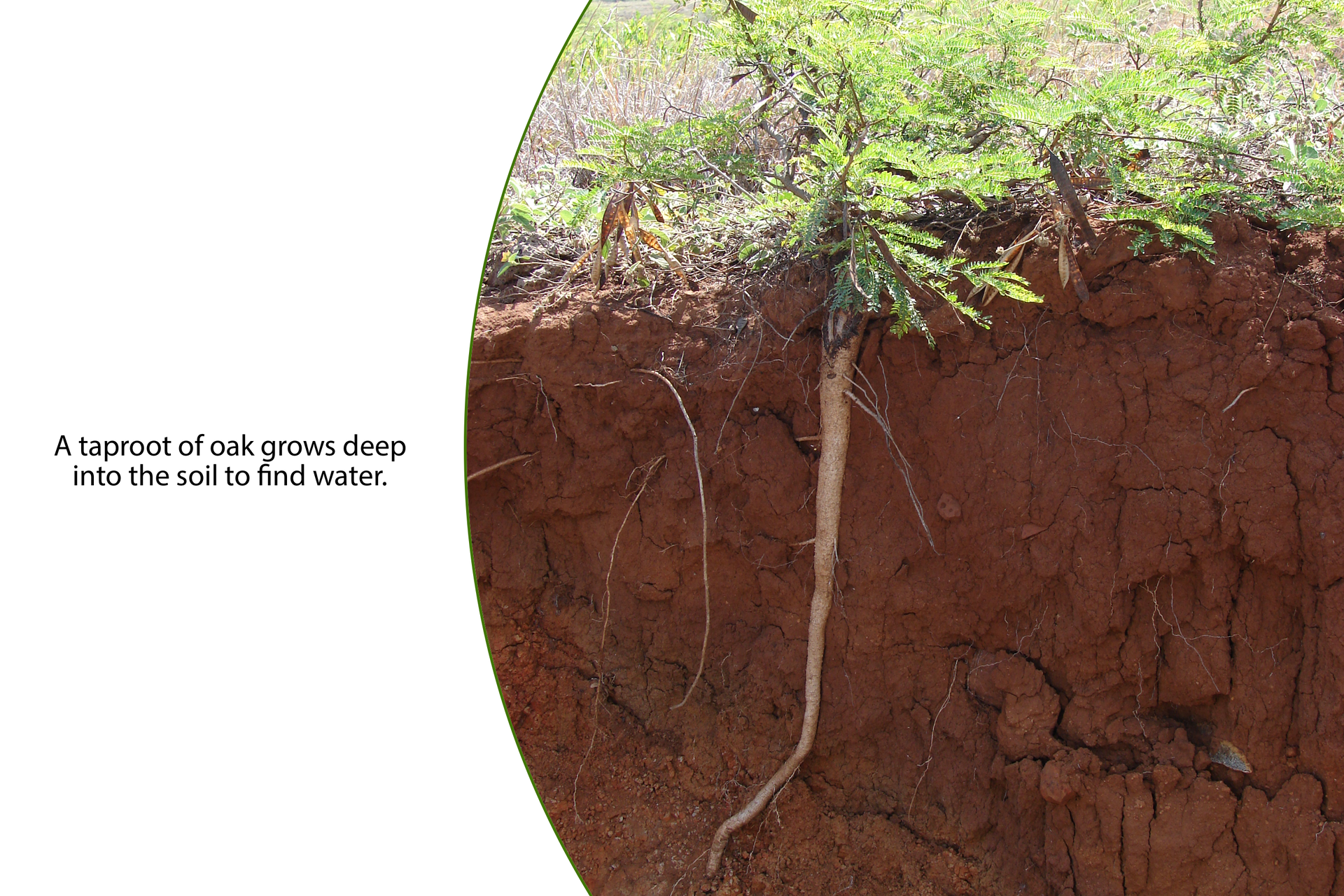
Root
organisms are made of cells;
tissues are groups of cells of a similar structure, which have a specific function in an organism;
plants such as wheat and an apple tree are composed of roots, stems, leaves, flowers and fruits.
name basic functions of the root;
show the relationship between root zones and its functions;
show the diversity of plant root structures;
identify and describe root modifications.
Plant organs
Plants that currently dominate on land are embryophytes, i.e., autotrophic organisms made of tissues and organsorgans. Among them, the most numerous group is vascular plants, which in the conducting tissue have specialized cells that are responsible for conducting water - vessels. Most of them produce seeds hidden in the fruit, which is why they are called angiosperms, the therm that comes form the Greek words angeion („case” or „casing”) and sperma („seed”).
An organ is a part of a plant organism with a characteristic structure and a specific function. Vascular plants form underground and above‑ground organs. The former include the rootroot, and the latter - the stem, leaves, flower and fruit. An efficient cooperation of all organs allows the plant to function properly and reproduce.
Identification of plant organs.
observation‑what‑it will be needed
various pot plants (spider plant, spiderwort, poinsettia, fern, spath, air plant, and other plants).
Observe the structure of plants, point and name their organs.
If any plant blooms, carry out an observation to know if it is to develop fruits.
Pay attention to the fern. Observe if flowers and fruits appear on it.
Sometimes, it is difficult to identify plant organs, because aside from basic functions they can also perform additional ones. Moreover, at a given stage of development they do not have flowers or fruits. Another reason for the lack of some organs is that many potted plants come from exotic climate zones, and at home conditions do not produce, for example, flowers.
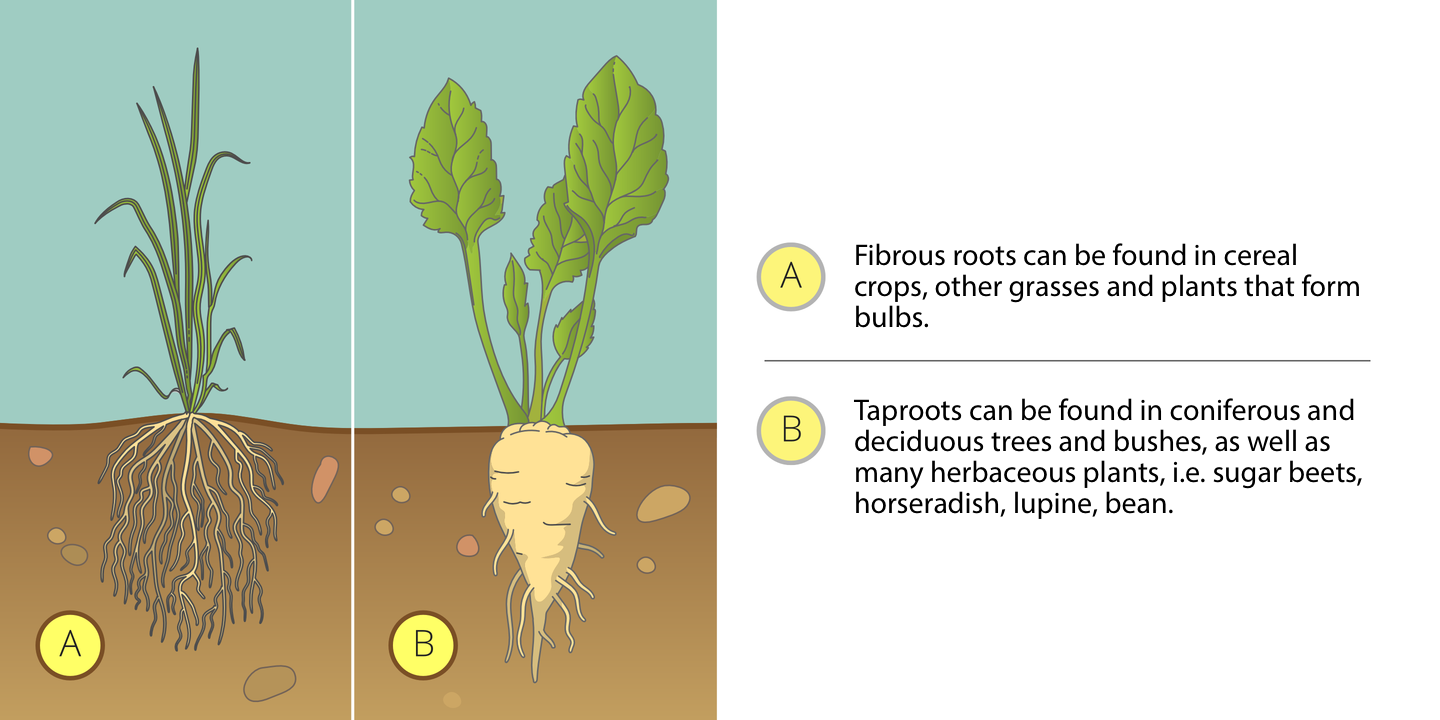
Root systems
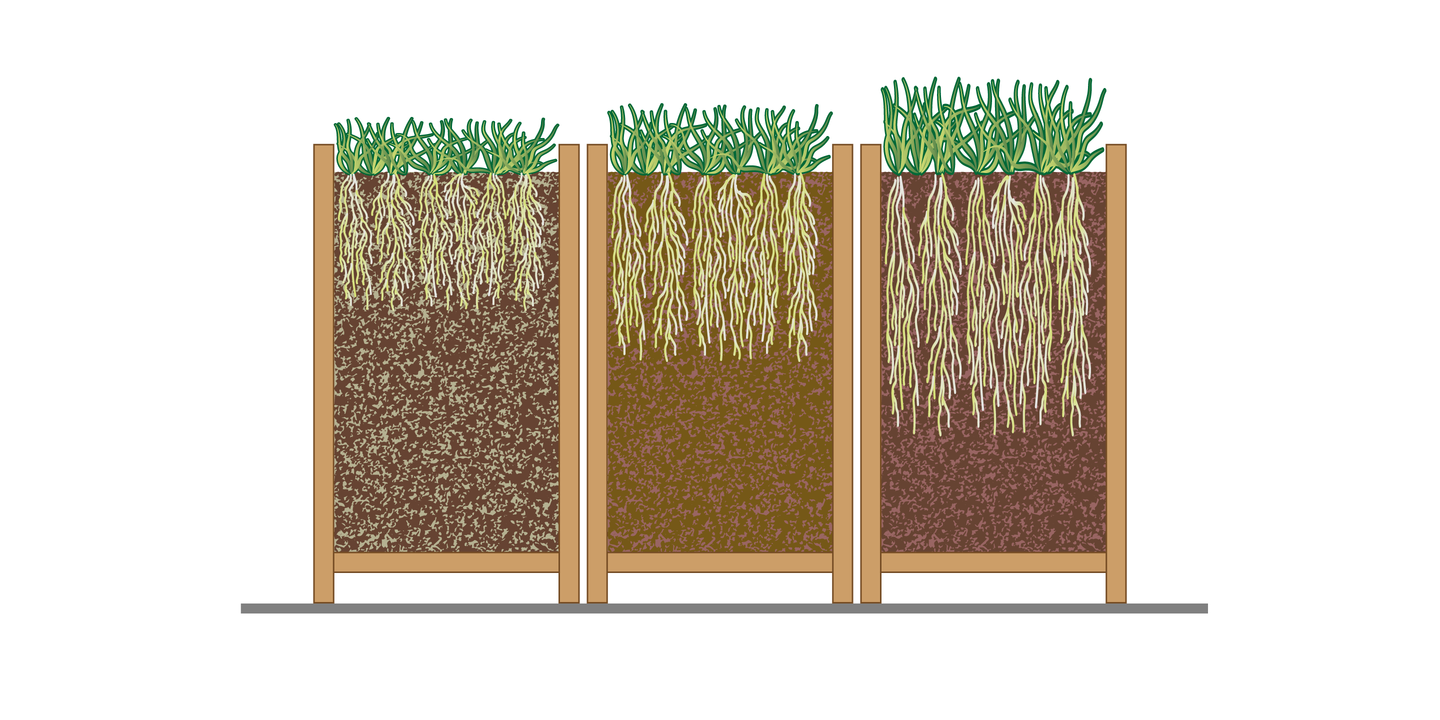
The root is an underground plant organ that keeps it in the soil and collects water along with mineral salts from the ground. Complexes of many roots in one individual are called root systems. In seed plants there are distinguished two types of root systems: taproots and fibrous roots. In plants that have the taproot system there is a long main root from which many shorter and finer branch roots derive. Such an extended system can reach deep into the ground. Other plants form dense fibrous systems consisting of a bundle of numerous roots growing from the lower part of the shootshoot. They are similar in thickness and length, they can branch out. They occupy a significant area - the greater it is, the larger the plant. Well‑developed root systems are conducive to a more efficient collection of water accumulated in the soil.
Description of the external structure of roots.
roots of beans, carrots, beetroots, grass, onions, spider plant.
Look at the roots of plants.
Pay attention to the characteristic features of the structure.
Sort the roots into taproots and fibrous roots.
Show strongly thickened roots.
Make schematic drawings of taproots and fibrous roots.
Thickened storage roots can occur in both taproot and fibrous systems.

External structure and root functions
In the external structure of the root there are several sections called zones. These are: root cap, meristematic zone, elongation zone, root hair zone and lateral root zoneroot zone. Individual zones appear successively as the root grows. Each zone has a different structure and a different task in the root. Each lateral root in the taproot system consists of the same zones as the main root.
Determining which part of the root is responsible for its growth.
sunflower seeds,
saucer,
lignin or paper towel,
water,
marker.
Place a few sunflower seeds on the saucer between very moist layers of lignin.
Keep proper seed moisture for two days.
When the roots are one centimetre long, remove the seeds from the lignin.
Use the marker to mark thin lines on each root at 1 mm distances.
Sprouting seeds should be put back on the saucer, on the moist lignin.
Within the next few days, observe which lines spaced the most.
If the distances between lines in one section of the root have increased more than in others, it means that the root does not extend equally over the entire length. Evaluate in what part of the root the lines are the most distant from each other, and in which they are closest to each other? Draw conclusions based on your observations.
Assess whether this sentence is true: The plant absorbs food from the soil using its roots. Justify the answer.
Modifications of roots
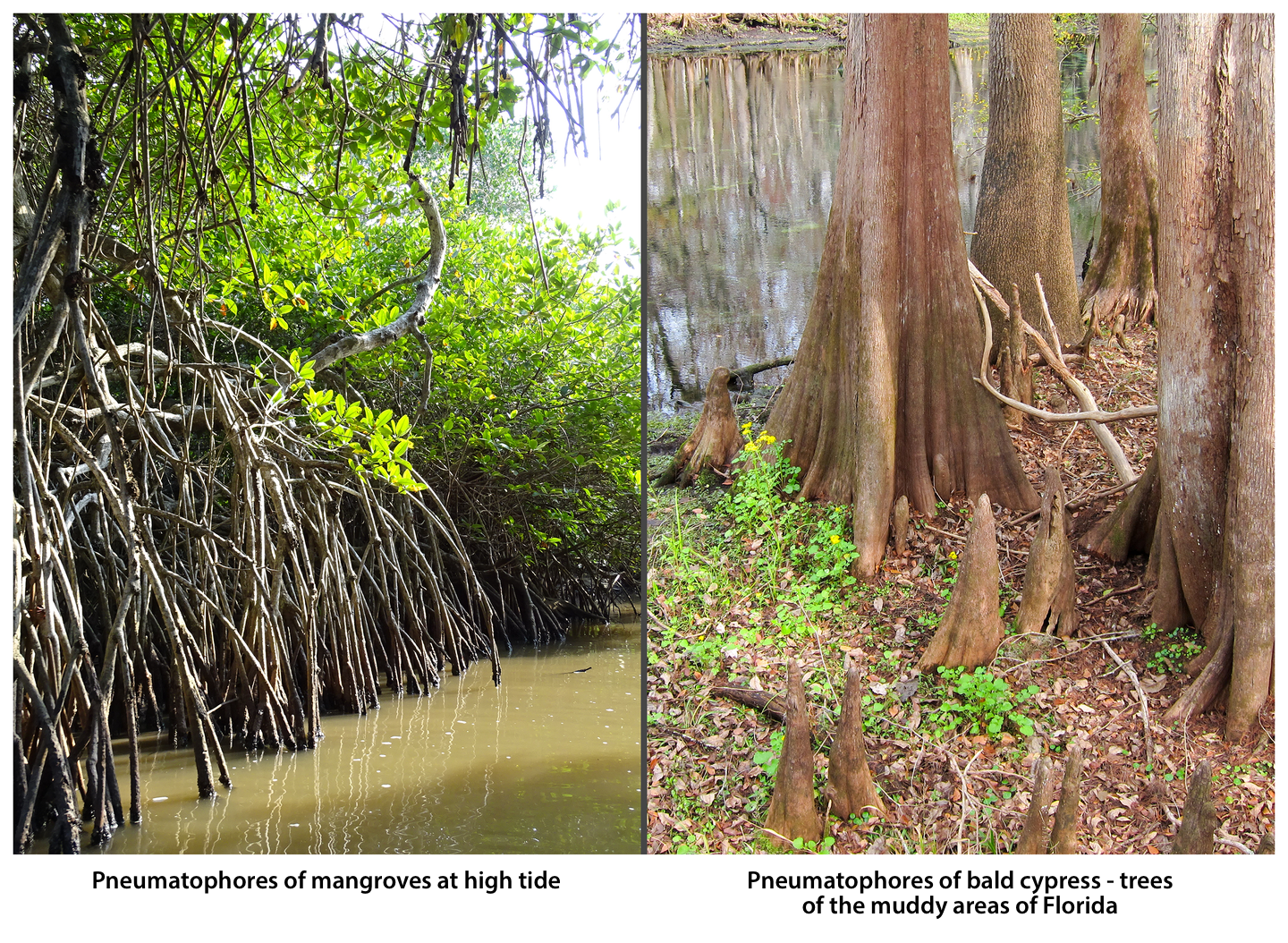
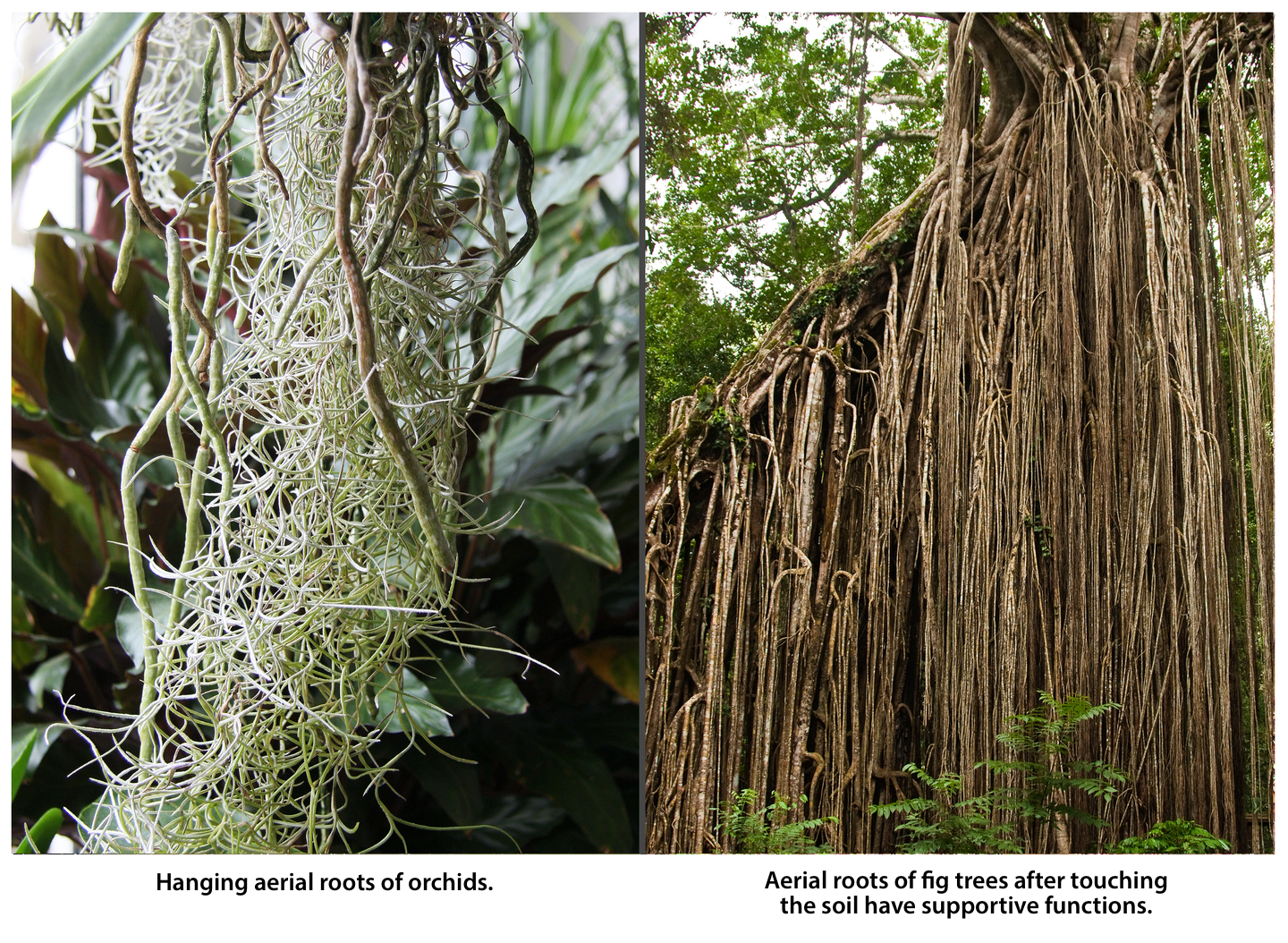
In addition to their basic functions, i.e. keeping the plant in the soil and absorbing substances out of it, roots can also perform additional functions. In this case, they have some characteristic structure features. Roots that perform additional functions are defined as modified or transformed. Among the most common root modificationsroot modifications there are special adaptations to collecting food, taking oxygen, supporting the plant with flexible stems on supports, producing additional supports that keep the plant in the ground. Roots that grow from the stem or leaves are called adventitious roots. They can support or replace the main root.
Types of modified or transformed roots:
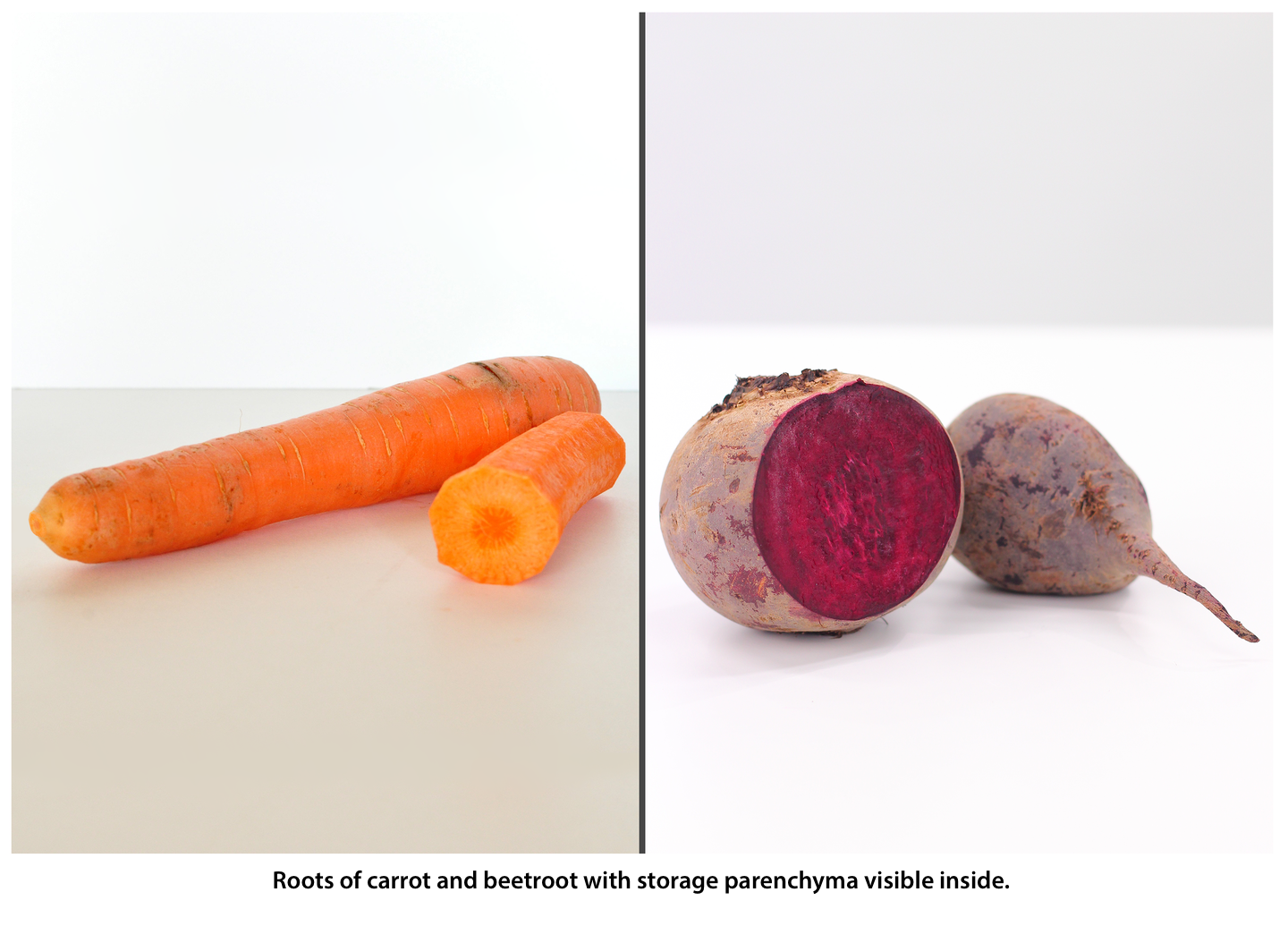
storage roots are thickened and develop as a result of expansion of the storage parenchyma inside the root; plants store large amounts of nutrients there, which they use in spring to produce new shoots; such roots are found in carrots and beets;
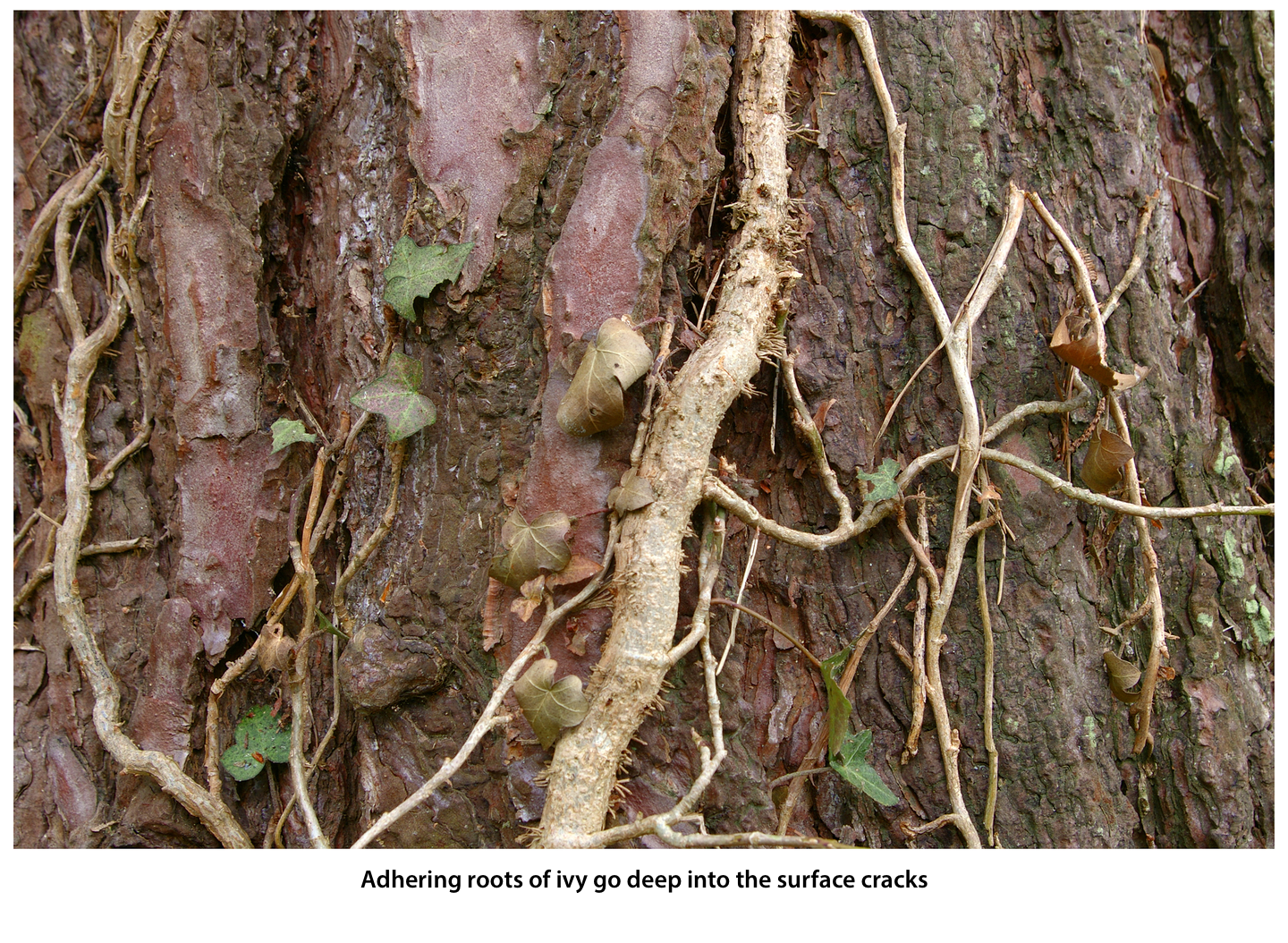
climbing roots grow from the stems of climbing plants and creeping plants; they allow the plants to attach themselves to supports in the form of branches or tree trunks, and strive upwards in search of light; they can be found in such plants as ivy, Virginia creeper;
Complete the missing words
substances, takes, propagation, soil
The root of the carrot ...................... water from the soil, fixes the plant in the ......................, accumulates many reserve ......................, can be used for plant .......................
Summary
The root keeps the plant in the soil and absorbs water with mineral salts from the soil, and in some plants it stores spare substances.
There are two types of root systems: fibrous – occurring, for example, in grasses, and taproot - found in trees.
In the external root structure, the root cap, the meristematic zone, the elongation zone, the root hair zone, and the lateral roots zone are distinguished.
The roots undergo modifications which adapt the plants to the conditions of the environment in which they grow.
1. On the example of the selected root, show the relationship between its structure and function.
Match the pairs: English words with Polish definition.
odcinki korzenia pełniące różne funkcje; w strefie wierzchołkowej odbywa się namnażanie komórek, w strefie wzrostu --- ich wydłużanie, w strefie włośnikowej --- pobieranie wody; korzenie strefy bocznej utrzymują roślinę w podłożu, przystosowania kształtu i tkankowej budowy korzenia do pełnienia innych funkcji niż utrzymywanie rośliny w glebie i pobieranie wody; wyróżnia się m.in. przystosowania do gromadzenia pokarmu, rozmnażania, pobierania tlenu, prowadzenia fotosyntezy, część organizmu rośliny przystosowana do pełnienia określonych funkcji, np. liść, łodyga, korzeń, kwiat, nadziemna część rośliny złożona z łodygi, będącej osią pędu, oraz osadzonych na niej liści, pąków, kwiatów i owoców; może być zielona lub zdrewniała, organ, którego podstawową funkcją jest zakotwiczenie rośliny w glebie oraz pobieranie z niej wody i soli mineralnych;
| root | |
| root modifications | |
| organ | |
| shoot | |
| root zone |
Keywords
root, organ, root modifications
Glossary
korzeń – organ, którego podstawową funkcją jest zakotwiczenie rośliny w glebie oraz pobieranie z niej wody i soli mineralnych;
modyfikacje korzeni – przystosowania kształtu i tkankowej budowy korzenia do pełnienia innych funkcji niż utrzymywanie rośliny w glebie i pobieranie wody; wyróżnia się m.in. przystosowania do gromadzenia pokarmu, rozmnażania, pobierania tlenu, prowadzenia fotosyntezy
organ – część organizmu rośliny przystosowana do pełnienia określonych funkcji, np. liść, łodyga, korzeń, kwiat
pęd – nadziemna część rośliny złożona z łodygi, będącej osią pędu, oraz osadzonych na niej liści, pąków, kwiatów i owoców; może być zielona lub zdrewniała
strefy korzenia – odcinki korzenia pełniące różne funkcje; w strefie wierzchołkowej odbywa się namnażanie komórek, w strefie wzrostu – ich wydłużanie, w strefie włośnikowej – pobieranie wody; korzenie strefy bocznej utrzymują roślinę w podłożu













