Space flights
how the motion of the satellites around the Earth looks like,
to describe what types of artificial satellites orbit the Earth.
Before you start, answer the question.
What are the benefits of space flights?
For hundreds of years, people have dreamed of extra‑terrestrial travel. It was not until the mid‑20Indeks górny thth century that these dreams were realized. The first object to reach the Earth's orbit was the Soviet Sputnik 1, which was launched on October 4, 1957 and circled Earth for 92 days and then destroyed. This event began an intensive exploration of outer space.
Artificial satellites revolve around the Earth in orbits at different altitudes.
A low Earth orbitlow Earth orbit - is an orbit at an altitude of 200‑2000 km from the Earth's surfacesurface.
Medium Earth orbit - this term is defined as the space between a low Earth orbitlow Earth orbit and a geostationary orbit. This orbit is mainly used by navigational satellites.
Geostationary orbit - is a circular orbit located in the plane of the Earth's equator. It is located at an altitude of 35786 km from the Earth's equator, and the body speed in this orbit is 3,08 . The period in this orbit is 23 hours 56 minutes and 4 seconds (this time corresponds to the stellar day), which means that the body is always in a fixed position above the chosen point of the Earth's equator.
Currently, there are hundreds of objects in space that serve research and utilitarian purposes.
Telecommunications satellites
The telecommunications satellite enables tele‑transmission of radio and television signals. The task of such a satellite is to receive a signal from a ground station, amplify it and send it back to Earth. Almost all satellites of this type revolve on a geostationary orbit, which ensures them to maintain a fixed position over a given point on the Earth's equator.
Navigational satellites
The navigational satellite emits radio signals that are used to determine the position of objects on the surface of the Earth. They allow to measure latitude and longitude, altitude above sea level, and speed of movement of the object. The navigational satellites revolve about 20000 km above the Earth's surfacesurface.
The most popular is the American GPS system (Global Positioning System). Simultaneously operates the Russian GLONASS system.
In 2020, the European GALILEO system will achieve full functionality.
These systems cover the entire Earth.
The Chinese BeiDou system, which is also expected to achieve full operational capacity in 2020, covers China and neighbouring countries.
Navigation systems are used for military and civilian purposes; they can be used by the owners not only of special receivers, but also of smartphones.
The following figure shows the characteristic quantities, and their values, describing the movement of the satellites, such as the period of circulation, the radius of the orbit, the speed at which the satellite moves in a given orbit, the altitude above the sea level on which the satellite is located.
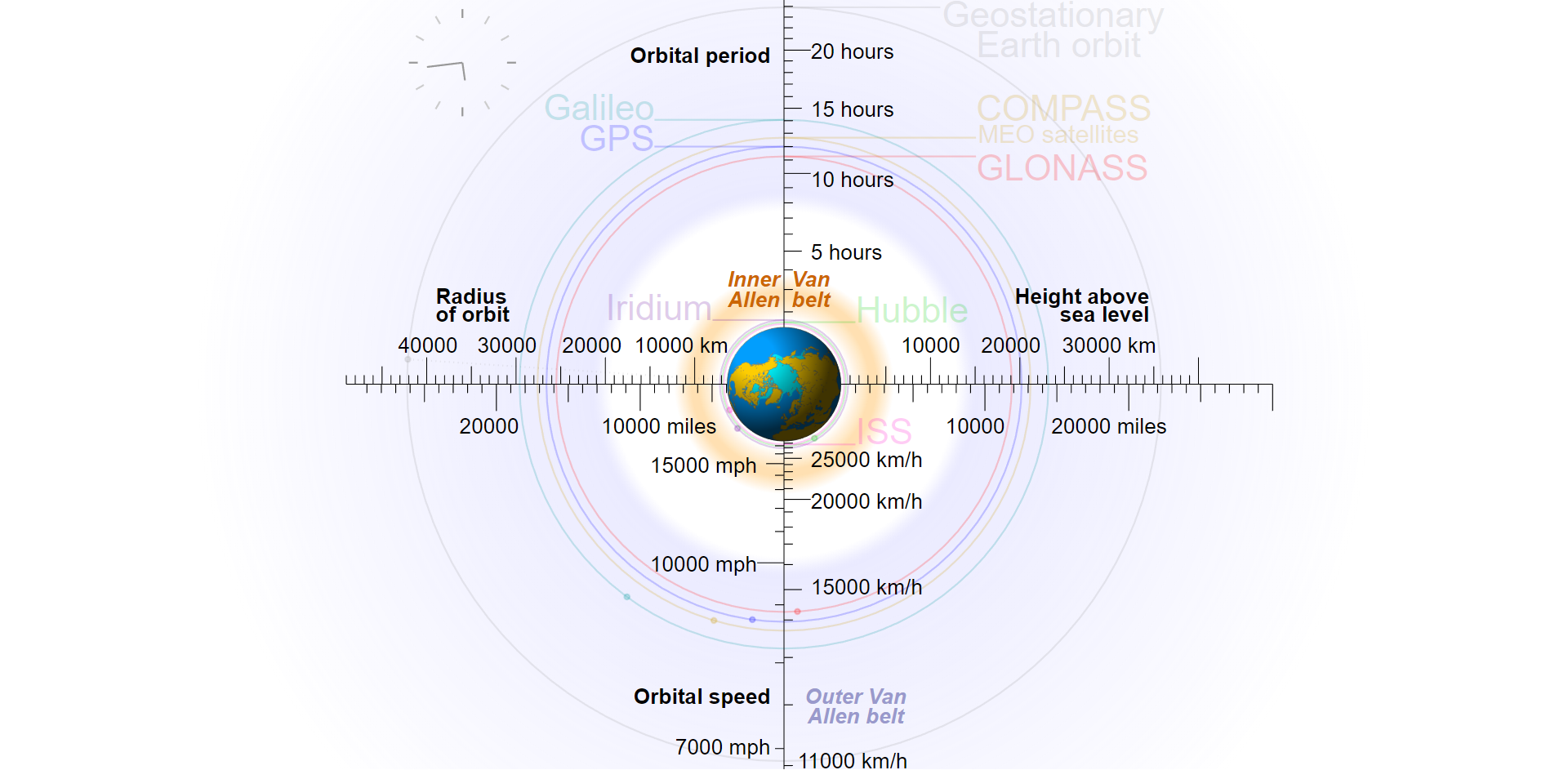
Satellites and scientific probes
In addition to navigational satellites, there are other satellites in space, such as meteorological, research, space telescopes. These satellites are at different altitudes and revolve around the Earth with different speeds.
Hubble telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) was elevated to a low Earth orbitlow Earth orbit in 1990. It revolves around the Earth in less than 97 minutes. It was created thanks to the cooperation of two astronomical agencies - American NASA and European ESA. The Hubble telescope provides interesting research material for astronomers.
Chandra telescope
The Chandra space telescope was launched in 1999. This telescope records X‑ray sources - this radiation allows the observation of white dwarfs, neutron stars and black holes.
The mission time of the satellite, initially anticipated for five years, has been extended, and the telescope, after 18 years of use, still provides a lot of important information.
Spitzer telescope
The range of infrared radiation is examined using the Spitzer space telescope. This telescope was placed in orbit around the Sun in 2003 and has remained there until now. It moves in the same orbit as the Earth - it follows it at some distance.
Webb telescope
The Webb telescope is currently under construction and the date of its launch has been delayed several times and is expected to be 2021. It will move in an elliptical orbit around the Sun. Webb telescope will be used for infrared radiation research.
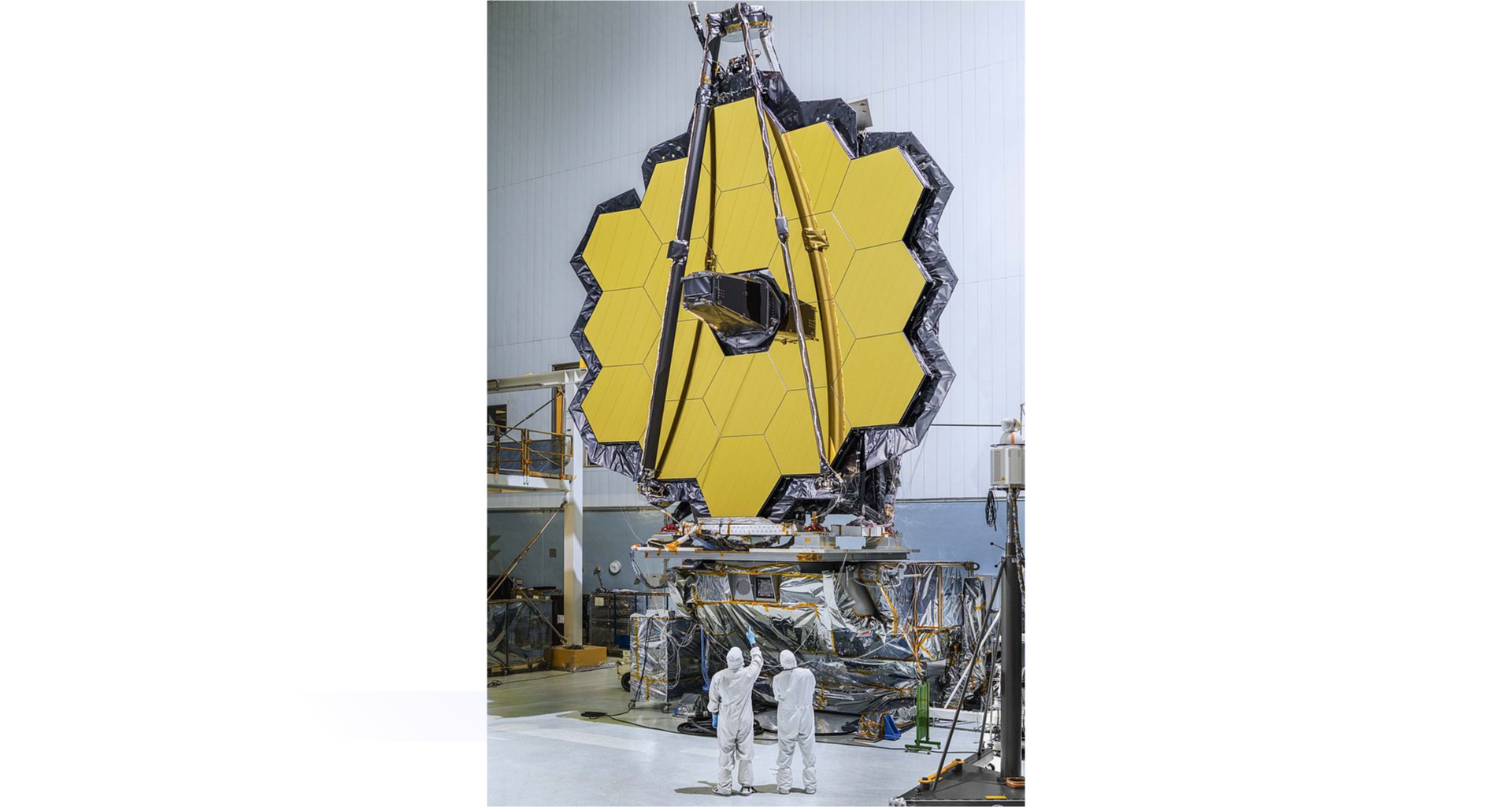

Space stations
On space stations not only scientific experiments in various fields of physics and astronomy are performed. Research related to the specific conditions prevailing at the station, namely the state of weightlessnessweightlessness, is equally important. These are, for example, the study of the crystallization of bodies in this state (there is no convection) and the effect of weightlessness on the human body.
Mir station
In the years 1986‑2001, the Soviet station Mir („Peace”) acted as a research space station. It was expanded by adding further modules until 1996. As a result of the expansion, the mass of the station reached over 130 tons. For over a dozen years, there were 137 astronauts from many countries who conducted thousands of scientific experiments and gained invaluable experience related to the reaction of the human body to a long‑term stay in the state of weightlessnessweightlessness.
ISS station
The International Space Station (ISS) became the successor of the Mir station. This is the first space station built with the cooperation of many countries. It allows six permanent crew members to stay at the same time. The first station modules were launched into the orbit and connected to each other in 1998. The first permanent crew started to live on it in 2000.
The ISS station, like the previous Mir station, moves around the low Earth orbitlow Earth orbit.
Remember
Satellites, or objects circulating around the Earth, other planets or the Sun, have a variety of applications - from scientific to commercial (telecommunications, radio and television). Some satellites are intended for military or intelligence purposes.
Satellites allow observation of phenomena not available from the surfacesurface of the Earth or the collection of experiences related to the long stay in a state of weightlessnessweightlessness.
Exercises
Determine which sentences are true.
- The first artificial satellite was the Soviet Sputnik 1 mission, launched in 1957.
- Geostationary orbit is this one, where a satellite might only be a few hundred kilometres above the planet.
- A satellite takes 24 hours to orbit the Earth in the geostationary orbit.
- Communication satellites refer to satellites used for telephone and television.
Search in internet and explain what a graveyard orbit is.
Explain in English: what benefits space flights bring?
Indicate which pairs of expressions or words are translated correctly.
- niska orbita okołoziemska - low Earth orbit
- sonda badawcza - scientific probe
- powierzchnia - surface
- nieważkość - weightlessness
- stacja badawcza - artificial satellite
- sztuczny satelita - research station
- sztuczny satelita
- orbita geostacjonarna
- niska orbita okołoziemska
- stacja badawcza
- satelita geostacjonarny
- geostationary satellite
- research station
- artificial satellite
- low Earth orbit
- geostationary orbit
Glossary
sztuczny satelita
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: artificial satellite
satelita geostacjonarny
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: geostationary satellites
orbita geostacjonarna
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: geosynchronous orbit
niska orbita okołoziemska
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: low Earth orbit
stacja badawcza
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: research station
sonda badawcza
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: scientific probe
powierzchnia
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: surface
nieważkość
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: weightlessness
Keywords
artificial satelliteartificial satellite
geostationary satellitesgeostationary satellites
low Earth orbitlow Earth orbit
research stationresearch station