Strengthening tissues
all organisms are made of cells;
cells perform functions in basic life processes;
plant cells have chloroplasts, cell walls and vacuoles.
recognize plant tissues;
discuss the basic functions of individual plant tissues;
show the relationship between the structure of tissues and the function they perform;
microscopic observation of plant tissues.
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
Nagranie dźwiękowe abstraktu dotyczące tkanek wzmacniających
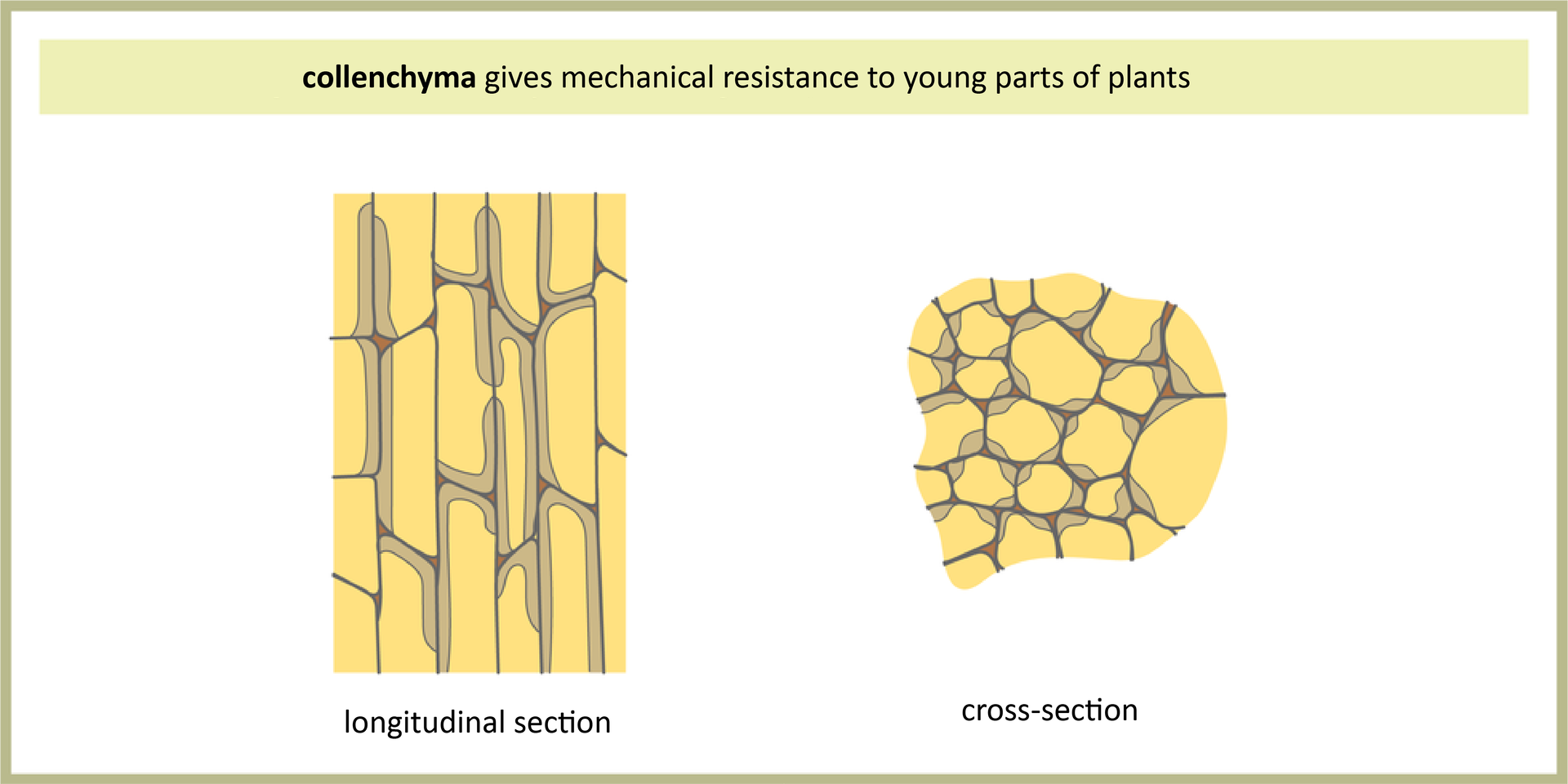
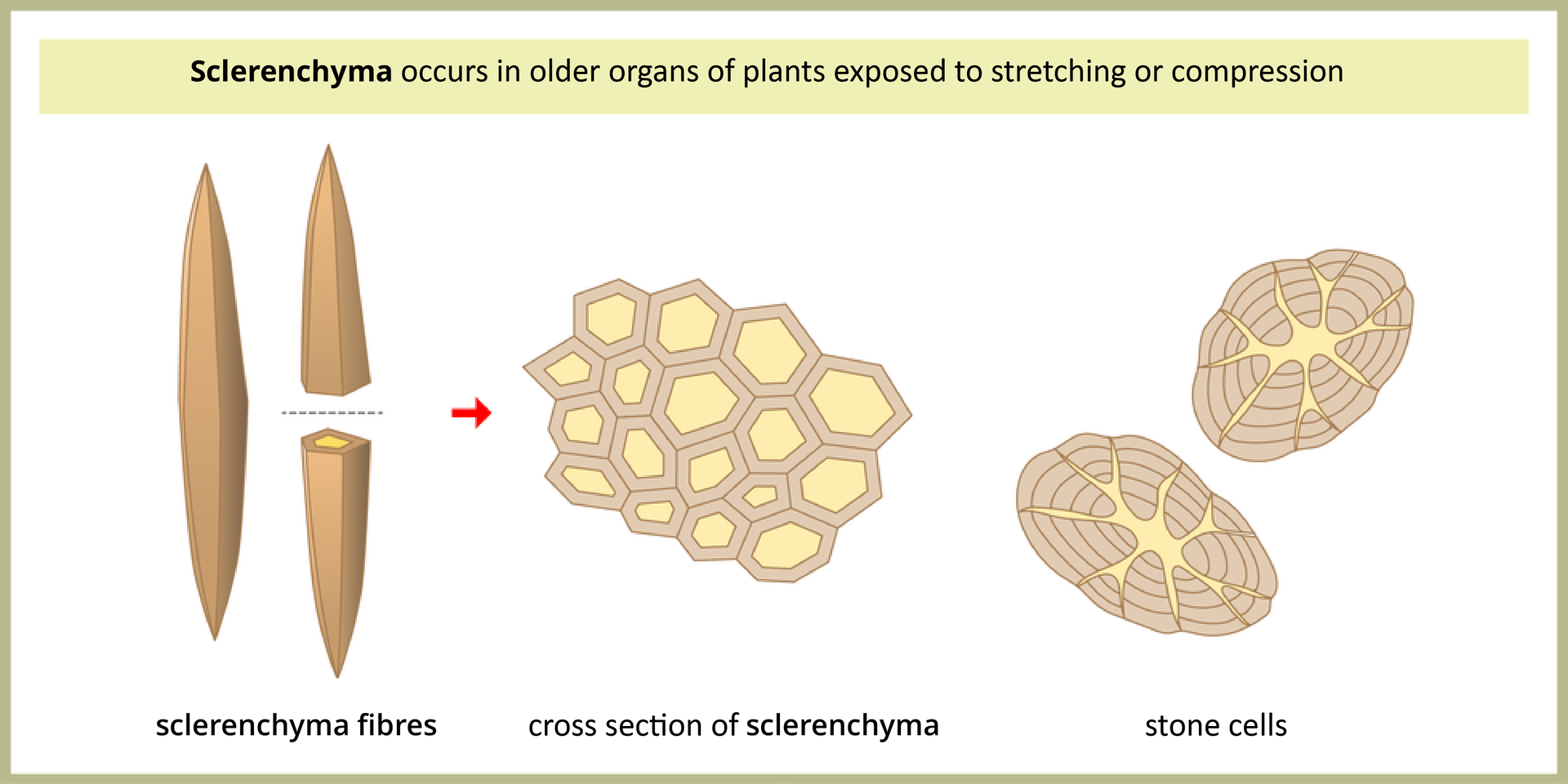
Strengthening tissuesStrengthening tissues (supporting tissues) give the plant rigidity and flexibility. This is especially important for those terrestrial plants that reach large sizes. There are two types of strengthening tissues: collenchyma and sclerenchyma. Colenchyma occurs in young, quickly growing parts of plants, like petioles and stems. It is made of living, elongated cells that form closely to each other. Their cell walls are strengthened by uneven thickening (the largest in the cell angles), which increases the plant's resistance to tearing. Sclerenchyma occurs in the grown‑up, older parts of plants. It is made of dead cells with thick, woody walls. The shape of the cells depends on their location in the plant. Heavily elongated and pointed fibers are found in flax and hemp stalks. Small, irregular sclereids can be found in pear fruit, nut shell or fruit seeds.
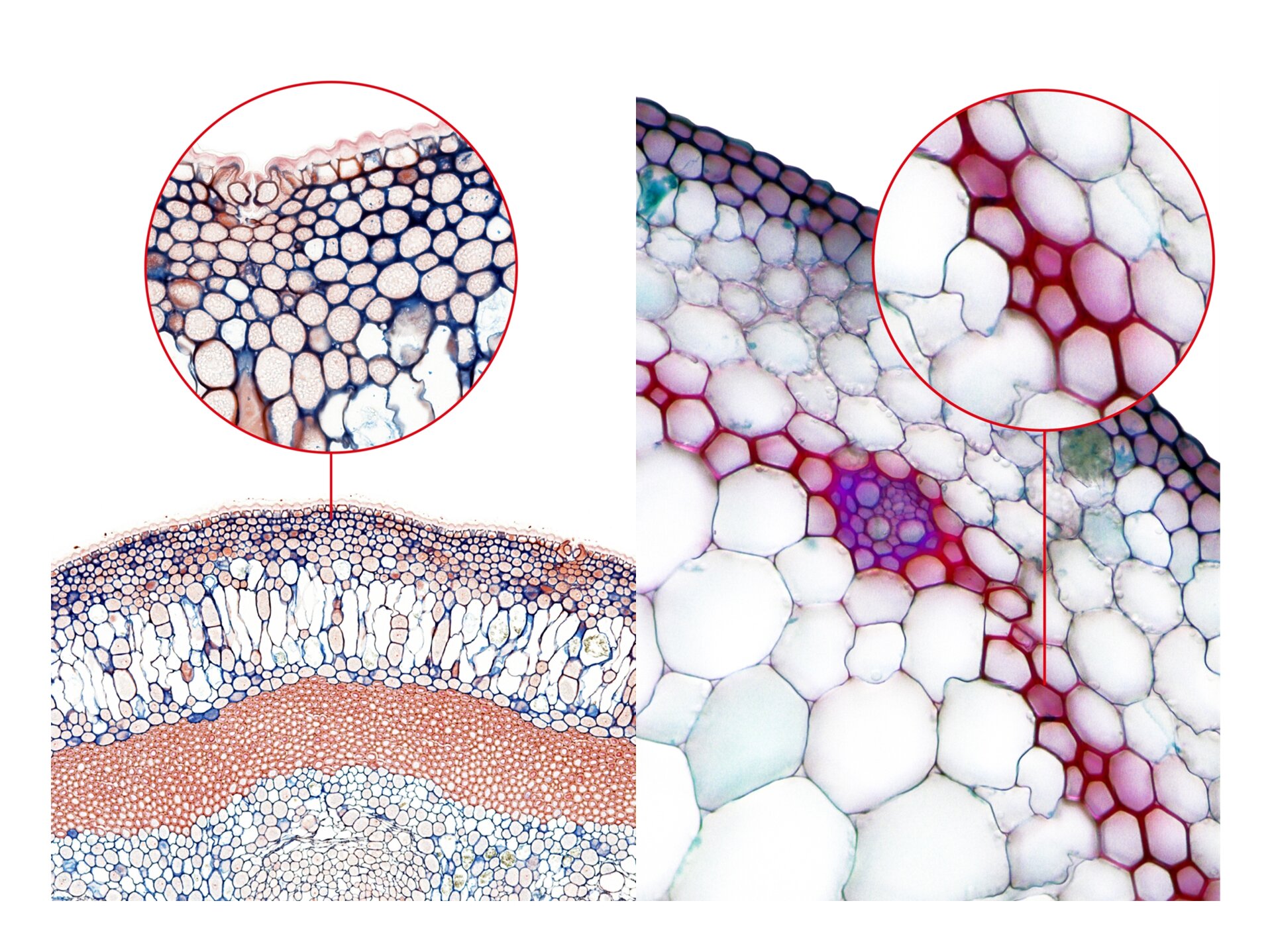
Indication of the characteristics of sclereids cell structure.
pear fruit,
microscope,
microscope equipment.
A small amount of the pulp of the pear fruit from the vicinity of the seed chambers scrape the razor blade and blend it on the slide.
Use a dropper to put a drop of water on the slide.
Cover the preparation with a cover slip and observe it under 100x magnification.
Observe the aggregation of sclereids cells at 100x magnification.
Make a schematic drawing.
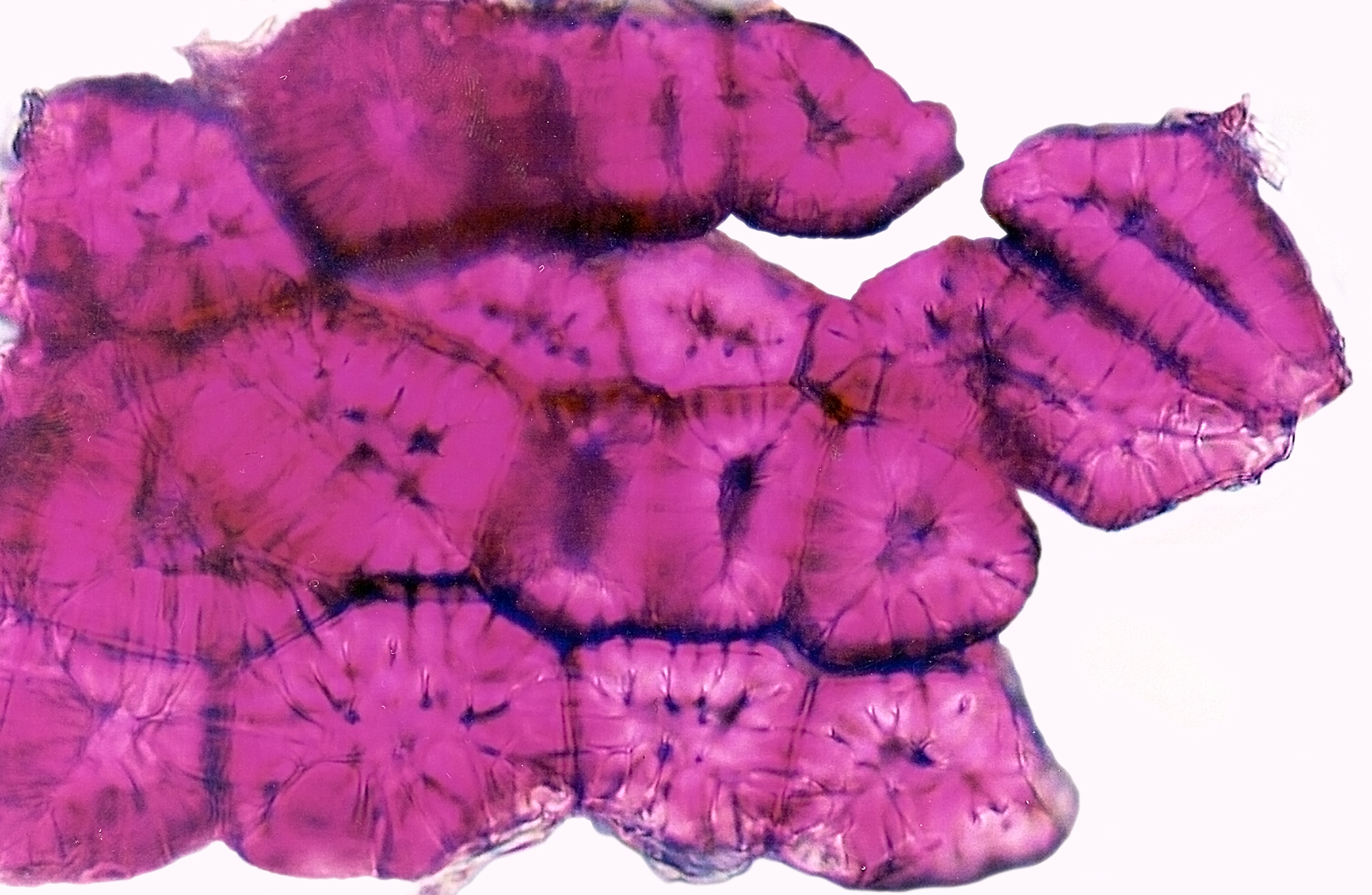
The cells of the pear fruit strengthening tissue are tightly arranged and have very thick cell walls.
Plant tissue with rigid cell walls, providing plants with resistance to bending, stretching and allowing the organs to maintain their shape is called the:
- strengthening tissue.
- chloroplasts.
- parenchyma.
Summary
The body of plants is filled with tissues, i.e. assemblies of cells with a similar structure specialized to perform specific functions.
Strengthening tissues give the plant stems rigidity and flexibility.
Keywords
strengthening tissues, colenchyma, sclerenchyma, sclereids
Glossary
tkanka wzmacniająca – tkanka roślinna o sztywnych ścianach komórkowych, zapewniająca roślinom odporność na zginanie, rozciąganie oraz umożliwiająca organom zachowanie kształtu; wyróżnia się dwa rodzaje tej tkanki: zwarcicę (żywa tkanka w młodych roślinach) i twardzicę (martwa tkanka w starszych roślinach)