The Coast
how man affects the landscape;
how Poland is shaped.
indicate the location of the coasts on the map;
describe the climate of the coast;
explain the process of wind formation called breeze;
recognize and describe the cliff, beach, sandbar and sand dune.
The climate of the coast
CoastCoast is a lowland land area adjacent to the sea. The sea has a strong influence on the coastal climate and the shape of its surface. In summer, on the shores during the day it is cooler than inland (with the exception of lake districts), but the nights are warmer. In the winter, the sea gradually reflects the heat it accumulated in the summer and warms the neighboring coast, soothing the winter frosts. On the Polish coast, snow fall is the least and shortest compared to the rest of the country.
The terrain of coastal areas
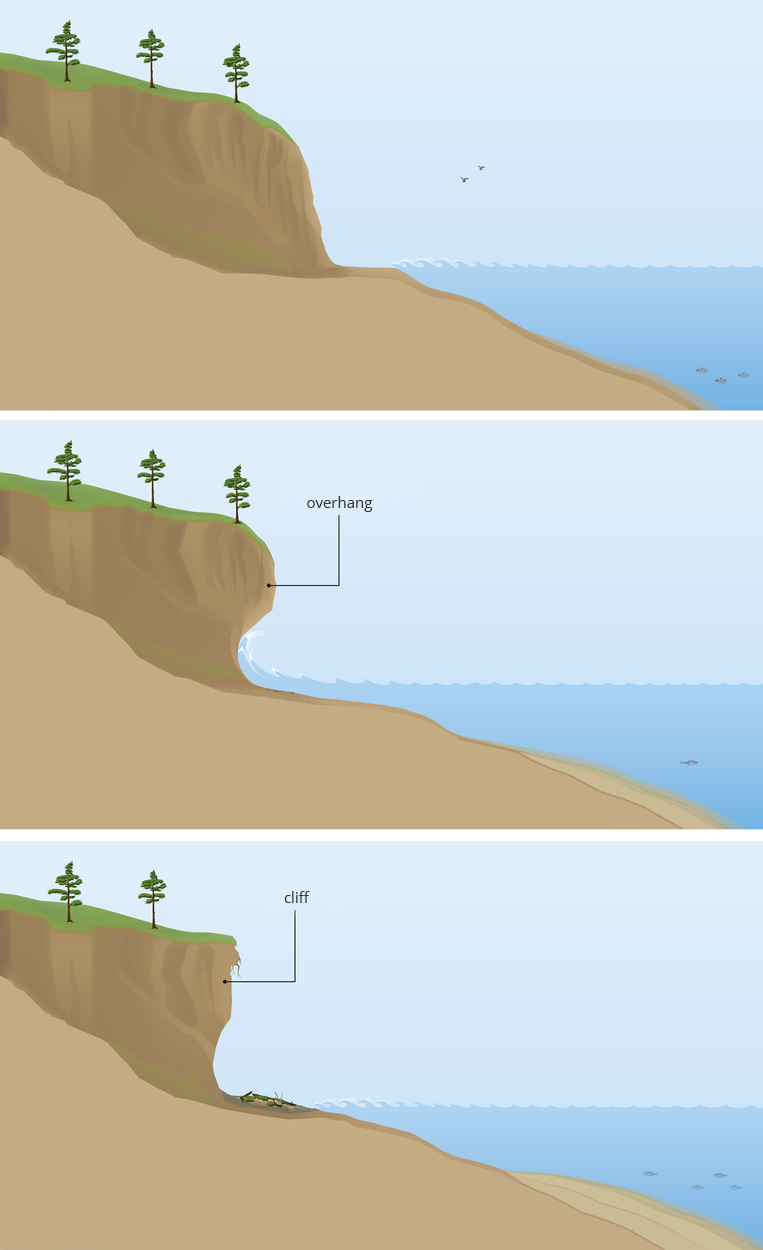
The sea has a big influence on the shaping of the coast. Where the shores are high, the sea waves can destroy them, creating steep cliffscliffs. They are found, for example, on the island of Wolin and in Gdynia. Characteristic are also long sandy strips of land called sandbarssandbars, located mainly in the eastern part of the coast. They arise when coastal ocean currents carry sand and deposit it along the shoreline.
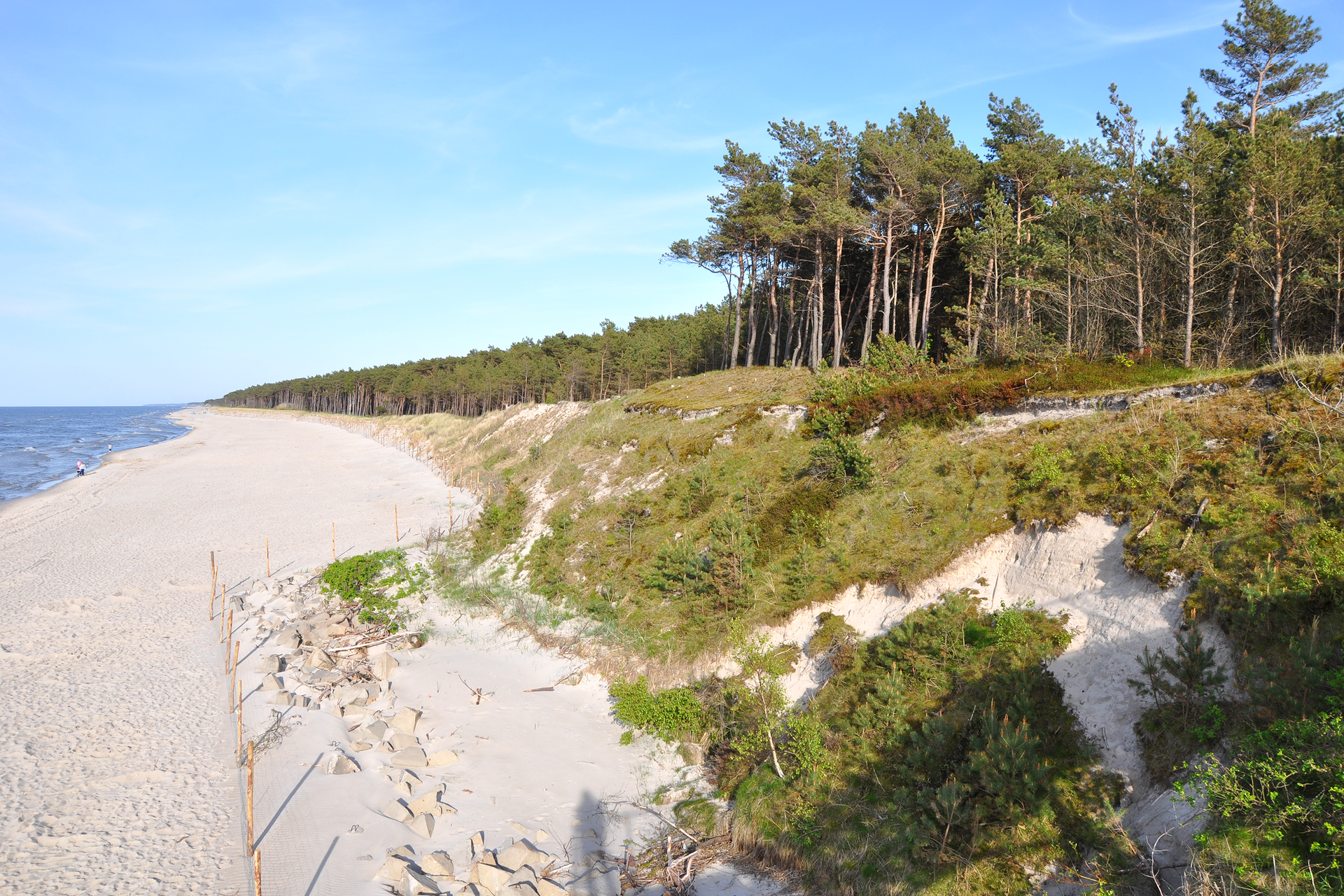
Along the coast beachesbeaches often stretch. Polish beaches are usually wide (they are even over 100 m) and covered with fine sand. They can also be muddy or stony. During autumn storms, the beaches are completely flooded by waves.
When the sand dries, the wind can move it. When it encounters an obstacle, such as vegetation, a sand hill arises – dunedune. The wind can move sand, which results in the dune gradually moving – we are dealing with a moving dune.
The cliff is unstable and literally at any moment parts of it can fall to the beach. Therefore, do not walk at the very base of the cliff, as well as too close to its edge.
Dense thickets are often planted along the sandy shores. Contrary to appearances, these are not ornamental plants. Their main task is to strengthen the banks. The roots of these plants are holding the ground and means the wind does not move the sand. Remember, being by the sea, do not pick these plants and destroy them!

Polish coasts
We divide the Polish Coast into three large regions.
Szczecin coast covering areas near the Odra estuary around the Szczecinski Lagoon. There are both plain landscapes of the Odra estuary and hilly areas. To this shore there are parts of the island Uznam and the entire island of Wolin, two large lakes (Dąbie and Miedwie) and many smaller ones.
Koszalińskie Coast this is the central part of the coast. Characteristic for this land are sandy beaches, coastal lakes cut off from the sea with sandbars and high moving dunes. The shores here are both high with cliffs and low with wide beaches. The largest movable dunes are found in the Słowiński National Park.
Gdansk coast is the easternmost part of the coast lying semicircular around the Gulf of Gdansk. It stretches from Cape Rozewie to the border with Russia. High tens of meters separated by valleys, long sandbars and the area around the mouth of the Vistula are sometimes characteristic here, in depressions.
Bathing in the sea is pleasant, but it also involves a lot of risk. For your own safety, swim or take a bath only in designated places, in the presence of a lifeguard and at a time when the weather and conditions are favorable (which is signaled by the placement of a white flag). If a red flag is hung, do not enter the water.
Summary
The coast is a land zone adjacent to the sea, which exerts a great influence on the climate and terrain of this part of the land.
A wind called a breeze is characteristic for the coast.
In Poland, the coasts are distinguished between: Szczecińskie Coast, Koszalińskie Coast and Gdańskie Coast.
Keywords
coast, beach, dunes
Match the pairs: English words with Polish definition.
wąski pas lądu zamykający przybrzeżne akweny; mierzeja odcina zatokę od pełnego morza; zbudowana jest z piasku zabieranego w innym miejscu, pas lądu rozciągający się wzdłuż brzegów morza, tworzący krainę geograficzną o cechach powiązanych z działalnością morza, wzgórze zbudowane z piasku przemieszczanego przez wiatr, płaski nadbrzeżny pas lądu pokryty piaskiem lub żwirem, stromy brzeg morza powstający w wyniku podmywania podstawy tego brzegu przez fale
| cliff | |
| sandbar | |
| beach | |
| coast | |
| dune |
Glossary
klif – stromy brzeg morza powstający w wyniku podmywania podstawy tego brzegu przez fale
mierzeja – wąski pas lądu zamykający przybrzeżne akweny; mierzeja odcina zatokę od pełnego morza; zbudowana jest z piasku zabieranego w innym miejscu
plaża – płaski nadbrzeżny pas lądu pokryty piaskiem lub żwirem
pobrzeże – pas lądu rozciągający się wzdłuż brzegów morza, tworzący krainę geograficzną o cechach powiązanych z działalnością morza
wydma – wzgórze zbudowane z piasku przemieszczanego przez wiatr