The National Bank of Poland
Banks are a part of our everyday economic life.
People, firms and other entities keep their savings in banks, and take loans from banks to finance their expenditure.
You will be able to present the history of banking, and explain why such institutions were created.
You will be able to describe what a banking system is, and what it consists of.
You will be able to explain the functions of a central bank, as well as the activities of commercial banks.
You will be able to describe and analyze the structure of the National Bank of Poland.
The National Bank of Poland (NBP) fulfills the tasks set out in the Constitution of the Republic of Poland, the Act on NBP and the Banking Act of 29 August 1997. These legal acts guarantee the independence of the NBP from other state authorities.
The Constitution of the Republic of PolandArticle 227
(...) The National Bank of Poland shall be responsible for the value of Polish currency.
Source: The Constitution of the Republic of Poland.
The Act on NBP of 29 August 1997Article 3
Source: The Act on NBP of 29 August 1997.
In accordance with the Monetary Policy Strategy developed by the Monetary Policy Council after 2003, the NBP's objective is to stabilize inflation at 2.5% with an acceptable fluctuation band of +/– 1 percentage point (that is, inflation may be between 1.5% and 3.5 %).
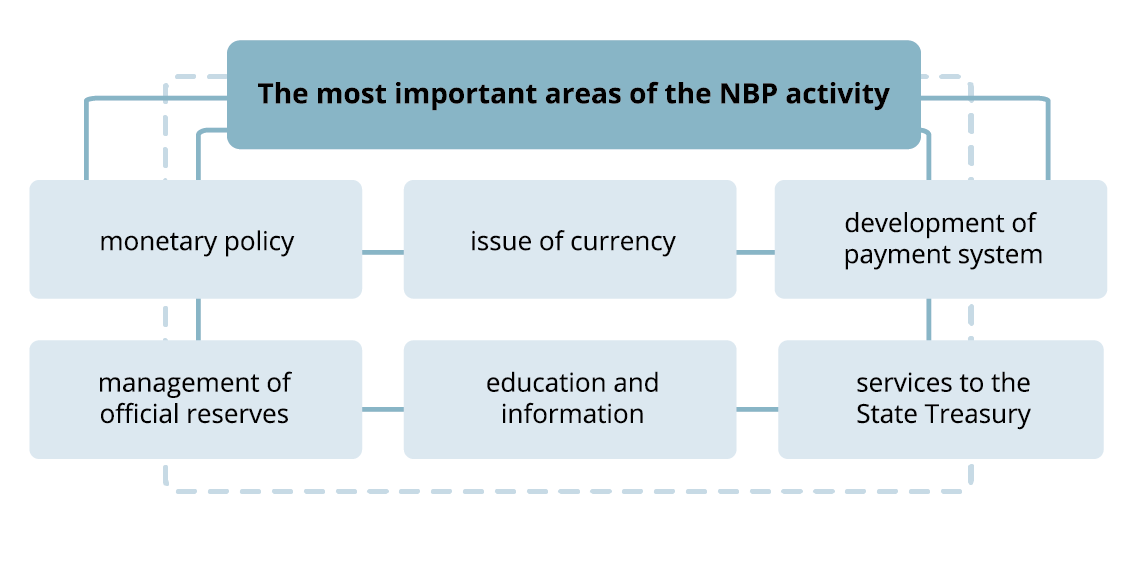
The bodies of the National Bank of Poland are the President of the NBP, the Monetary Policy Council and the Management Board of the NBP.
The President of the NBP is appointed by the Sejm at the request ofat the request of the President of the Republic of Poland for a six‑year term. He is responsible for the organization and functioning of the National Bank of Poland. The same person cannot be the President of the NBP for more than two terms. The President of the NBP:
is the head of all employees of this institution,
is the chairperson of the Monetary Policy Council, the Management Board of the NBP,
represents the NBP outside,
is the representative of the interests of the Republic of Poland in international banking institutions and, if the Council of Ministers does not decide otherwiseotherwise, in international financial institutions.
The Monetary Policy Council includes: the President of the NBP (as the chairperson of the Monetary Policy Council), and nine other members, appointed in equal numbers by the President of the Republic of Poland, the Sejm and the Senate for six years.
The day‑to‑day activity of the NBP is managed by its Management Board, which includes the President of the NBP and 6 to 8 other members (including two NBP vice presidents). The main task of the Management Board is the implementation of resolutions of the Monetary Policy Council, adoption and implementation of the NBP plan of activities, the execution of the financial plan approved by the Council and the performance of tasks related to the exchange rate policy and the payment system.
The other banks of the banking system are commercial banks. Commercial banks deal with financial services for business entities and individuals. For this purpose the banks:
conduct deposit activity (consisting in receiving and storing cash of their clients on specific terms),
conduct loaning activity (consisting in granting short-, medium- and long‑term loans by the bank and guaranteeing loans from other entities),
provide operational services (meaning that the bank keeps bank accounts of its clients and performs banking operations on them).
It should be emphasized that a bank is a kind of enterprise, which is why, like any enterprise, it should bring profit. The activities of banks are not limited to collecting funds paid by their clients.
Currently, banks offer more and more of their products, including:
Internet banking,
the issue and management of payment instruments (e.g. credit cards),
brokeragebrokerage in securities and the issue of bank securities,
advice on all services the bank offers,
money delivery services,
safe services.
Banks are constantly expanding and modifying their offer.
Banks are just as important as money in the economy – they improve its functioning. The most visible effect of the lack of banks and the banking system would be the functioning of the money flow in the economy almost exclusively in the form of cash. We would have to keep money for current expenses and any savings in their physical form, bearing the riskbearing the risk of losing them as a result of damage, loss or theft. In the era of online transactions and non‑cash settlements, it is difficult to imagine an economy without these institutions.
Listen to the abstract recording to review the material and new vocabulary. Then do the vocabulary exercise. Match the pairs: English and Polish words.
założenie, powstrzymywać, ograniczać (np. ruchy), pośrednictwo, stopy procentowe, projekt ustawy budżetowej, Skarb Państwa, ponieść ryzyko, wytyczne
| to constrain | |
| State Treasury | |
| draft budget act | |
| guidelines | |
| interest rates | |
| brokerage | |
| to bear the risk | |
| sumption |
Keywords
National Bank of Poland, the Act on NBP, the Banking Act of 29 August 1997, Monetary Policy Strategy, Monetary Policy Council, President of the NBP, Management Board of the NBP, interest rates
Glossary
o ile
powstrzymywać, ograniczać (np. ruchy)
Skarb Państwa
na prośbę/wniosek
inaczej
projekt ustawy budżetowej
wytyczne
stopy procentowe
pośrednictwo
ponieść ryzyko
założenie