The neutralization reaction part 1
that there are water‑soluble hydroxides (e.g. NaOH, KOH) and poor and hardly soluble in water (e.g. Mg(OH)Indeks dolny 22, Al(OH)Indeks dolny 33);
that hydroxides dissociate in water into metal cations and hydroxide anions;
that hydroxide solutions are alkaline,
that the acids dissociate in water into hydronium cations and anions of the acid residue;
that the reaction of acidic solutions is acidic.
to show in molecular and ionic form (complete and net) the equation of the reaction between hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide taking place in an aqueous solution;
to explain what neutralization reaction is;
to indicate substances that undergo neutralization.
Can hydroxides react with acids?
Before watching the video ‘Experiment: Sodium hydroxide + Hydrochloric Acid’, think about the reaction you will observe. Formulate a research question and hypotheses, and then also observations and conclusions.

Film dostępny na portalu epodreczniki.pl
Film prezentuje doświadczenie chemiczne. Czy wodorotlenek sodu reaguje w roztworze wodnym z kwasem solnym? Hipoteza numer jeden: Wodorotlenek sodu reaguje w roztworze wodnym z kwasem solnym. Hipoteza numer dwa: Wodorotlenek sodu nie reaguje w roztworze wodnym z kwasem solnym. Co będzie potrzebne do przeprowadzenia doświadczenia: kolba stożkowa, pipety, rozcieńczony roztwór wodorotlenku sodu, rozcieńczony kwas solny, bagietka, wskaźnik kwasowo‑zasadowy: fenoloftaleina. Instrukcja: Do kolby stożkowej wlej kilkadziesiąt centymetrów sześciennych roztworu wodorotlenku sodu. Dodaj kilka kropli roztworu fenoloftaleiny. Do roztworu wodorotlenku dodawaj kroplami, za pomocą pipety, kwas solny. Stale mieszaj zawartość kolby stożkowej. Nie dodawaj zbyt dużo kropli kwasu solnego. Przenieś roztwór do parownicy. Ogrzewaj delikatnie parownicę i odparuj jej zawartość do sucha. Porównaj pozostałość w parownicy ze stałym wodorotlenkiem sodu. Dodaj wodę do osadu, a następnie zbadaj odczyn powstałego roztworu za pomocą fenoloftaleiny.
Does sodium hydroxide react in aqueous solution with hydrochloric acid?
Select one of the presented hypotheses, and then test it.
Sodium hydroxide react in aqueous solution with hydrochloric acid.
Sodium hydroxide doesn’t react in aqueous solution with hydrochloric acid.
conical flasks,
pipettes,
diluted solution of sodium hydroxide,
diluted hydrochloric acid,
glass rod,
acid‑base indicator: phenolphthalein.
Put several dozen cm Indeks górny 33 of sodium hydroxide solution into the conical flask.
Add a few drops of phenolphthalein.
Add hydrochloric acid dropwise to the hydroxide solution with a pipette. Constantly stir the contents of the conical flask.
Observe what is happening. End the experience when you see changes. Do not add too much drops of hydrochloric acid.
Transfer the solution to the evaporating dish.
Heat the evaporating dish slightly and evaporate its contents to dryness.
Compare the residue in the dish with solid sodium hydroxide.
Add water to the residue, and then testing the pH of the resulting solution using phenolphthalein.
Phenolphthalein in the sodium hydroxide solution turned to raspberry color. During the addition of hydrochloric acid, the solution was discolored after some time. After evaporating the water from the solution, a white solid substance was formed which did not resemble the substances used for the reaction. Phenolphthalein did not stain in the solution of this substance.
Sodium hydroxide reacted with hydrochloric acid. As a result of this reaction, a new substance was formed – sodium chloride. The reaction is described with the following equation:
NaOH + HCl → NaCl + HIndeks dolny 22O
sodium hydroxide + hydrochloric acid → sodium chloride + water
Sodium hydroxide reacts not only with hydrochloric acid, but also with other acids, e.g. sulfuric acid, nitric acid or phosphoric acid. All water‑soluble hydroxides behave in a similar manner.
How does the neutralization reaction?
The reaction between sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid can be represented by the equation:
HCl + NaOH → NaCl + HIndeks dolny 22O
hydrochloric acid + sodium hydroxide → sodium chloride + water
We know that water soluble hydroxides and acids in the aqueous solution undergo a dissociation process:
HCl + HIndeks dolny 22O → HIndeks dolny 33OIndeks górny ++ + ClIndeks górny --
(simplified: )
hydrochloric acid
sodium hydroxide
Therefore, ions take part in the reaction between these substances. So write down the equation with their use:
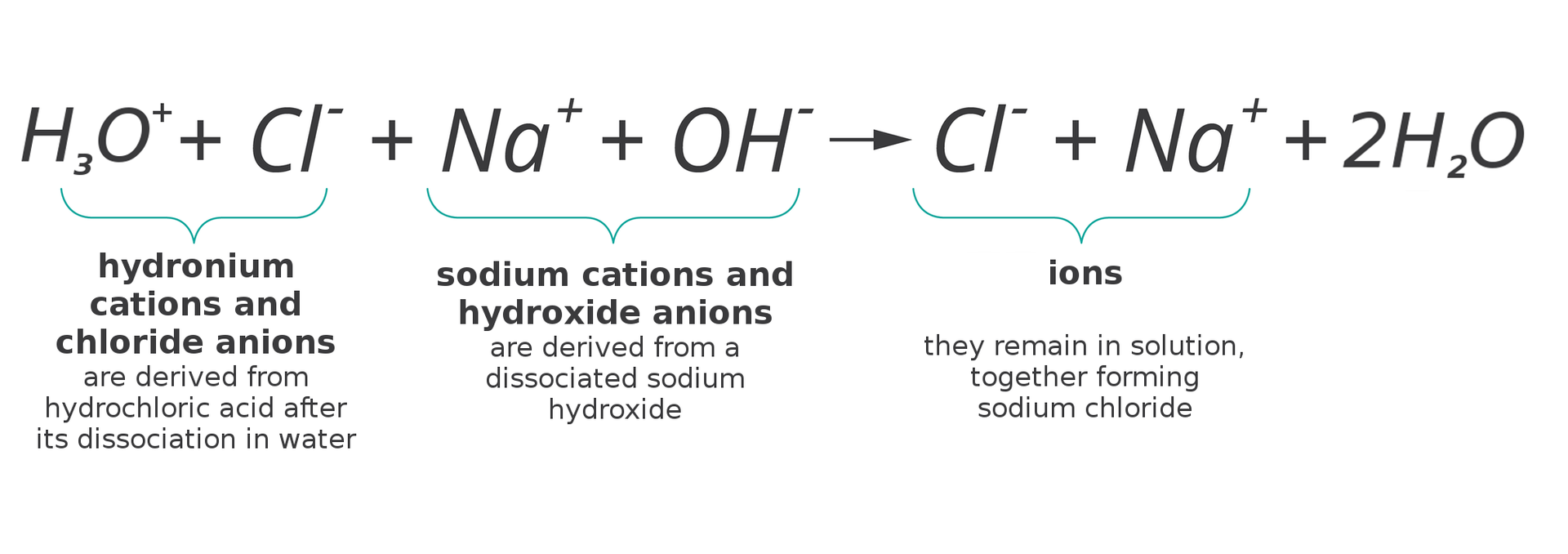
HIndeks dolny 33OIndeks górny ++ + ClIndeks górny -- + NaIndeks górny ++ + OHIndeks górny -- → ClIndeks górny -- + NaIndeks górny ++ + 2HIndeks dolny 22O
Such a record of the course of the reaction is called complete ionic equationcomplete ionic equation.
Note that during the reaction of sodium hydroxide with hydrochloric acid only two ions react: hydronium cation and hydroxide anion, which together form a water molecule. Let us omit the non‑reacting ions in the reaction equation:
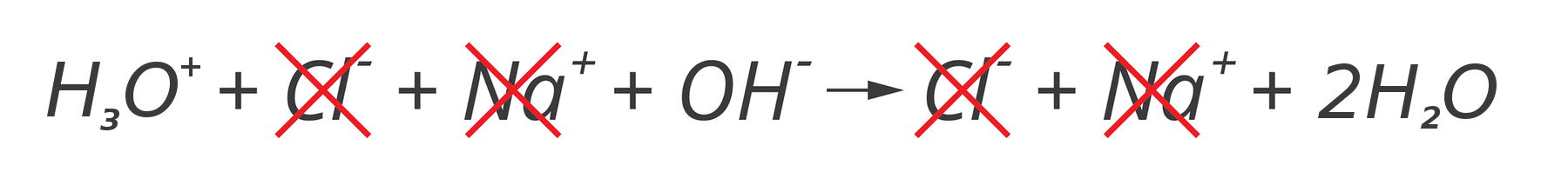
and write the equation that describes the proper processes occurring during a chemical reaction:
HIndeks dolny 33OIndeks górny ++ + OHIndeks górny -- → 2HIndeks dolny 22O
This way of presenting the course of the chemical reaction – using only the ions involved in the reaction – is called net ionic equationnet ionic equation.
As we remember, hydroxide anions are responsible for alkaline reaction, while hydrogen cations - for acid reaction. The pH of the solution formed after the reaction of sodium hydroxide with hydrochloric acid was neutral. That is why the reaction between the acid and the hydroxide was called the neutralization reactionneutralization reaction. Sometimes it is referred to as a neutralization reaction. Its essence is based on combination of hydrogen cations with hydroxide anions and the formation of water molecules.
Complete the sentence.
In .............. solution, the hydroxides react with ............. The reaction of sodium hydroxide with hydrochloric acid generates .............................. and water.
Complete the reaction equations.
H2O, H2SO4, 2H2O, 4, 2, H2SO
KOH + → K2SO4 +
Complete the reaction equations.
4H2O, 4, 2H2O, 2OH-, 2
K+ + + 2H3O+ + SO42- → 2K+ + SO42- +
Complete the reaction equations.
2H2O, Ca(OH)2, H2O, Ca(OH)4
+ 2HCl → CaCl2 +
Complete the reaction equations.
2H3O+, H2O, 2H, 4H2O
Ca2+ + 2OH- + + 2Cl- → Ca2+ + 2Cl- +
Summary
The reaction of sodium hydroxide with hydrochloric acid generates sodium chloride.
The transformation involving the reaction of hydroxide anions with hydrogen cations, resulting in neutral water molecules, is called the neutralization reaction.
In aqueous solution, the hydroxides react with acids.
Explain why there is no sodium hydroxide in the antacid composition in the stomach. For suggestions, search for example in the safety data sheet of this substance.
Key words
acid, base, neutralization reaction, full ionic record, shortened ionic record
Match the pairs: English words with Polish definition.
zapis przedstawiający przebieg reakcji w roztworze wodnym; przedstawia rozpuszczalne w wodzie substraty i produkty jako jony (zgodnie z ich dysocjacją), reakcja między kwasem a wodorotlenkiem, która polega na reakcji kationów wodoru z anionami wodorotlenkowymi z utworzeniem cząsteczek wody, równanie reakcji przebiegającej w roztworze wodnym; przedstawia substancje i jony faktycznie biorące udział w reakcji
| complete ionic equation | |
| neutralization reaction | |
| net ionic equation |
Glossary
pełny zapis jonowy – zapis przedstawiający przebieg reakcji w roztworze wodnym; przedstawia rozpuszczalne w wodzie substraty i produkty jako jony (zgodnie z ich dysocjacją)
reakcja zobojętniania – reakcja między kwasem a wodorotlenkiem, która polega na reakcji kationów wodoru z anionami wodorotlenkowymi z utworzeniem cząsteczek wody
skrócony zapis jonowy – równanie reakcji przebiegającej w roztworze wodnym; przedstawia substancje i jony faktycznie biorące udział w reakcji