Valence of chemical elements pt 3
how the atoms of the elements create ionic and covalent bonds.
define the term valency;
read from the periodic table the maximum valences of chemical elements of groups 1st, 2nd and from 13th to 17th of the periodic table in their compounds with hydrogen or oxygen;
write molecular formulas of two‑element chemical compounds based on information of the valency of elements which create them;
determine the valency of one chemical element in relation to when the valency of the other is known;
recognize the oxide based on its molecular formula;
write the molecular formula of the oxide, knowing its name;
draw structural formulas of two‑element chemical compounds, knowing what is the valency of the elements which create them.
How do we create oxide names based on their molecular formulas?
Oxygen compounds with other elements are called oxides. The only exception is the oxygen‑fluorine compound, called oxygen fluoride. In all oxides, oxygen has a valency of two. On this basis, knowing the oxide formula, we can determine the valency of elements in oxides.
Molecular formula of oxide | Valency of oxygen in the oxide | Valency of the element in the oxide |
oxygen(II) | carbon(IV) | |
oxygen(II) | carbon(II) | |
oxygen(II) | sulfur(IV) | |
oxygen(II) | sulfur(VI) | |
oxygen(II) | copper(II) | |
oxygen(II) | silver(I) | |
oxygen(II) | manganese(IV) | |
oxygen(II) | chlorine(VII) |
The names of oxides are double‑segmented. The first term is the name of the element in the genitive and the second – the word oxide e.g. sodium oxide. Many elements create several oxides in which their valency is different. An example is the compounds of lead with oxygen with the following molecular formulas: and .
In the first oxide, lead has a valency of four, in the second - two. Therefore, to uniquely determine the type of compound, e.g. oxide, its name often gives the valency of the element connected with oxygen. The compounds of the formulas discussed above and are respectively: lead(IV) oxide and lead(II) oxide. Oxygen valency is not determined in the names of oxides, since it is always two (II).
Watch the presentation ‘Creating the name of a chemical compound based on its total formula’. Note your conclusions.
Compound molecular formula | Valency of oxygen in the oxide | Valency of the element in the oxide | Name of oxide |
oxide(II) | carbon(IV) | carbon dioxide | |
oxide(II) | carbon(II) | carbon monoxide | |
oxide(II) | sulfur(IV) | sulfur dioxide | |
oxide(II) | sulfur(VI) | sulfur trioxide | |
oxide(II) | lead(II) | lead(II) oxide | |
oxide(II) | lead(IV) | lead(IV) oxide | |
oxide(II) | silver(I) | silver(I) oxide | |
oxide(II) | copper(II) | copper(II) oxide | |
oxide(II) | manganese(IV) | manganese(IV) oxide | |
oxide(II) | chlorine(VII) | dichlorine heptoxide |
By creating the names of metal oxides belonging to groups 1st and 2nd, their valency is not given, because these elements always have only one characteristic valency in chemical compounds: metals from 1st group - one, from 2nd group – two. A similar principle applies to aluminum: due to the fact that this element has a valency of three, it has been assumed not to give its valency in the name of the compounds.
The group to which belongs the element | Molecular formula | Systematic name |
1. | sodium oxide | |
potassium oxide | ||
lithium oxide | ||
2. | calcium oxide | |
magnesium oxide | ||
barium oxide | ||
13. | aluminium oxide | |
14. | carbon monoxide | |
carbon dioxide | ||
tin(II) oxide | ||
tin(IV) oxide | ||
lead(II) oxide | ||
lead(IV) oxide | ||
15. | nitrogen monoxide | |
dinitrogen trioxide | ||
dinitrogen pentoxide | ||
tetraphosphorus decaoxide | ||
16. | sulfur dioxide | |
sulfur trioxide | ||
17. | dichlorine monoxide | |
chlorine dioxide | ||
dichlorine heptoxide |
How do we determine molecular formulas based on the name?
Based on the full name of the oxide, you can easily write its molecular formula. Remember that oxygen valency in these compounds is two. The valency of the second element must be known or it is given in the name. If the element belongs to the 1st group of the periodic table, its valency will be equal to one, if it is the element located in the 2nd group, it will have the valency equal to two.
Writting molecular formula of barium oxide
We determine the valency of particular elements that make up the oxide:
Element | Principle | Valency |
oxygen | oxygen in oxides has a valency of two | II |
barium | Barium is in the second group of the periodic table; the elements of this group have a valency of two | II |
We write the molecular formula of barium oxide: BaO
Writting molecular formula of dinitrogen pentoxide
We determine the valency of particular elements that make up the oxide:
Element | Principle | Valency |
oxygen | oxygen in oxides has a valency of two | II |
nitrogen | the valency of non‑metal was given in the name | V |
We are writting molecular formula of dinitrogen pentoxide: NIndeks dolny 22OIndeks dolny 55
How do we create structural formulas of covalent compounds based on the knowledge of the valency of elements?
Determining the structural formula of a compound molecule based on its molecular formula is not always possible. For example, without knowing about the existing connections between individual atoms, we will not draw a formula of a compound molecule consisting of three elements with a molecular formula . In the case of two‑element compounds, it is possible if you know the valency of both elements. The easiest way to draw a formula of a molecule made of two atoms. An example is a molecule created by combining nitrogen and oxygen, the valency of which is two. It has the following structural formula:
Both atoms of elements have a valency equal to two and form two bonds each.
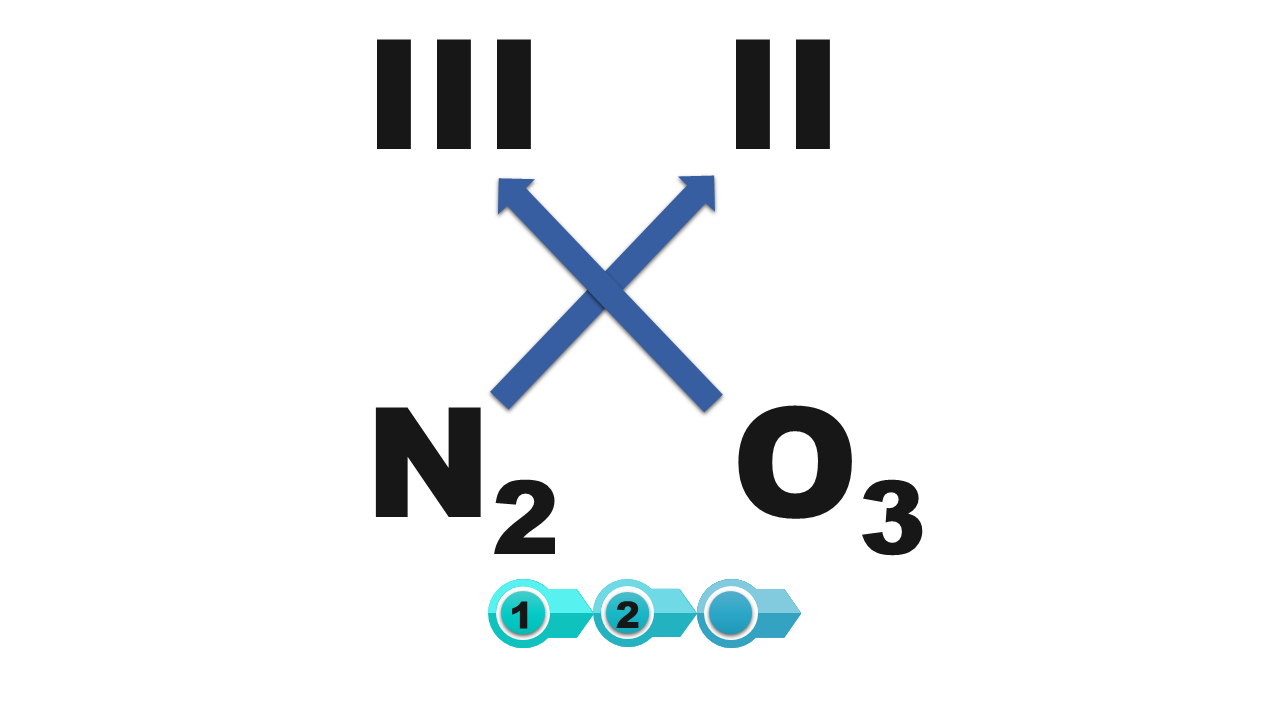
Indicate the answer showing the correct systematic name of the chemical compound of the structural formula N2O3
- nitrogen monoxide
- dinitrogen pentoxide
- dinitrogen trioxide
- dinitrogen monoxide
Indicate the answer showing the correct molecular formula of the chemical compound based on the systematic name - sulfur trioxide:
- S2O6
- SO2
- SO3
- SO6
Summary
Oxygen in oxides has valency equal to two. Based on this information and compound molecular formula, valency of the second element in the connections with oxygen can be determined.
The names of oxides give the valency of the element which in chemical compounds may have different valency.
Key words
structural formula, valency
Glossary
wzór, który odzwierciedla sposób połączenia atomów w cząsteczce; na jego podstawie można określić liczbę, rodzaj atomów oraz ich wartościowość
liczba wiązań, które tworzy atom danego pierwiastka chemicznego, łącząc się z innymi atomami