Variation of climate types in Europe
that geographic climate‑forming factors affect climate traits over a certain area;
that Europe is known for significant inter‑regional variation of climate types;
how to present climate traits in a certain place and recognise them in climatic charts.
how to indicate geographic climate‑forming factors affecting European climate;
how to describe the inter‑regional variation of climate types, existing in Europe;
describe major traits of climate types, existing in Europe;
Climate affects landscape in a certain area. This lesson will tell you about interconnections between climate‑forming factors and variation of climate types in Europe. Do you remember the difference between weather and climate?
Climatic factors forming climate types present in Europe
Geographical climate‑forming factors include: latitude which is a zonal factor; distribution of land and sea, influence of oceanic currents, land morphology, altitude above sea level and land cover.
Climate‑forming factor | Factor influence on climate variation in Europe |
Latitude | Europe spans from 35°58’N (Cape Marroqui) to 71°08’N (Cape Nordkyn); the land’s core lies in medium latitudes in the northern hemisphere, only a small tract of the continent spreads beyond the northern subpolar circle at 66°33’N. Geographical location of Europe means that areas in southernEurope receive more sun energy than its northern periphery.Average values of climate components are typified by distinctive distribution along the year in any climate; January is the coldest month, and July is the warmest one |
Distribution of land and sea | West Europe lies within the zone of influence of the Atlantic Ocean, and East Europe is affected by air masses from continental Asia. The huge dismemberment of shoreline, enormous number of coastal and inland seas are significant climatic factors.. |
Influence of oceanic currents | The shoreline of West and North Europe is rounded by the Gulf StreamGulf Stream which magnifies influence of the Atlantic Ocean on climate characteristics |
Land morphology and its altitude above sea level | Parallel arrangement of major landforms allow for inflow of air masses from above the Atlantic Ocean inland as well as inflow of air masses from East Europe westward. Mountain chains prevent subtropical air masses coming from the south and arctic air coming from the north. In the mountain regions, altitudinal zonation appears, resulting from altitude above sea level. Moreover, the mountain regions are typified by lower annual air temperature and higher precipitation |
Land cover | Europe distinguishes itself among other continents by drastic changes in landscapes. It is evaluated that about 65% of the area of Europe underwent a great transformation – a lot of – a lot of agricultural landscapes appeared, however, significant areas were altered as a result of urbanisation, industrialisation, mining operations and development of transport network. Natural landscape survived in mere 15% of the land. |
To see what is the impact of the main geographical climatic factors on the climate in Europe, watch animation in the e- textbook.
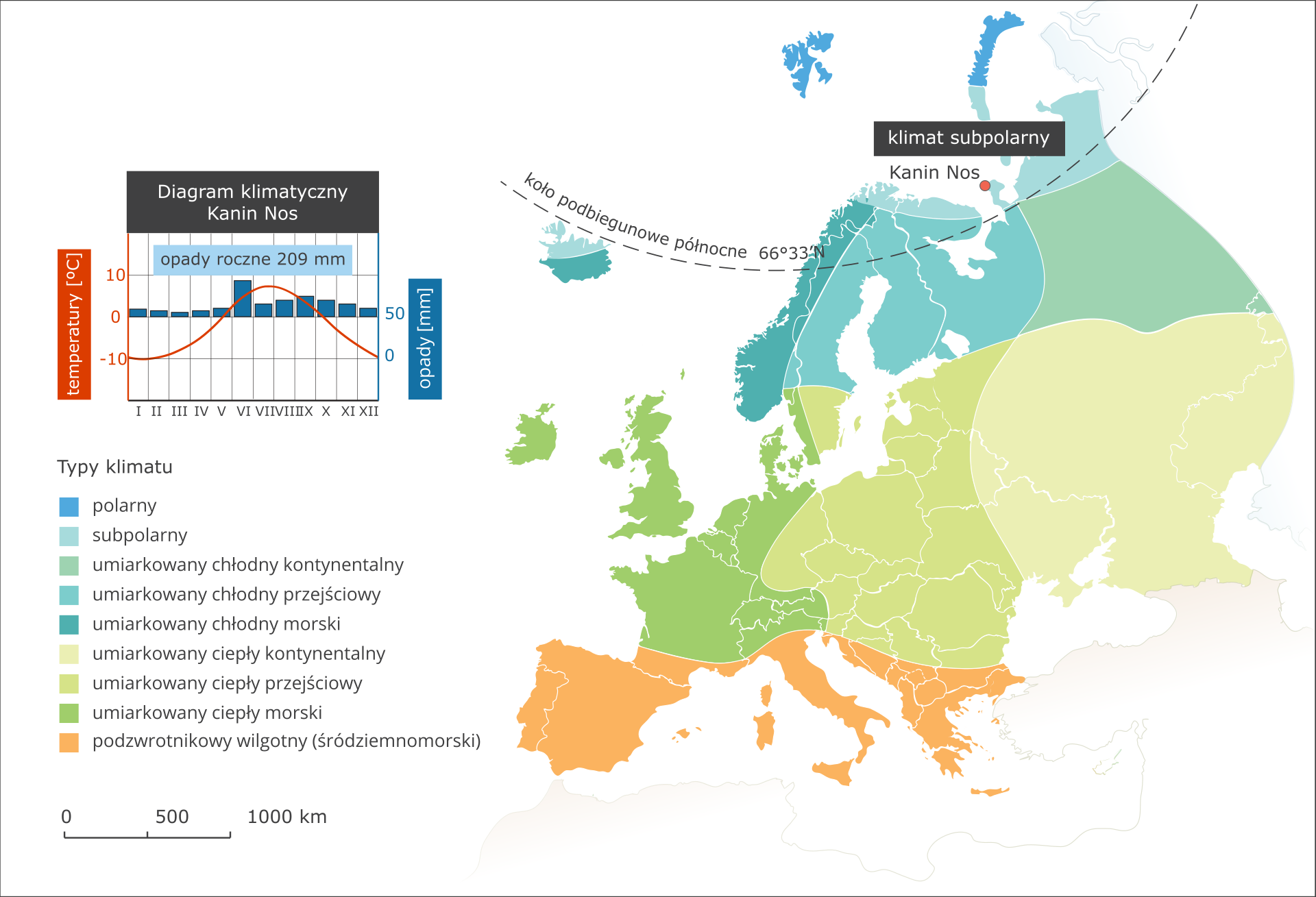
Climate types present in Europe
In the map above, ranges of climate types, present in Europe, have been visualised. Next to the map, climatic charts of typical stations will be shown. Using the map, proceed according to the following instructions.
- dry and hot summers with average air temperature ranging from 22°C to 28°C; Total annual precipitation differs from 400 mm to 600 mm.
, Subpolar climate - Kanin Nos climate station opis WCAG Cold climates prevail in northern outskirts of Europe. In the islands, lying far up the north, it may even a polar climate. Winter, i.e. the period when average air temperature drops below 0°C, spans over 7-8 months. In the warmest month, air temperature does not exceed 10°C. Precipitation is low, reaching 200 mm per year. A significant feature of this climate is high variability of weather types., Mountain climate In the mountainous regions of Europe, a type of climate with distinctive altitudinal zones prevails. Air temperature is always significantly lower than in the area surrounding a mountain chain, and precipitation amount is always higher. Depending on geographical location of a mountain massif, altitudinal zones may have their borders lying at different altitudes.
a
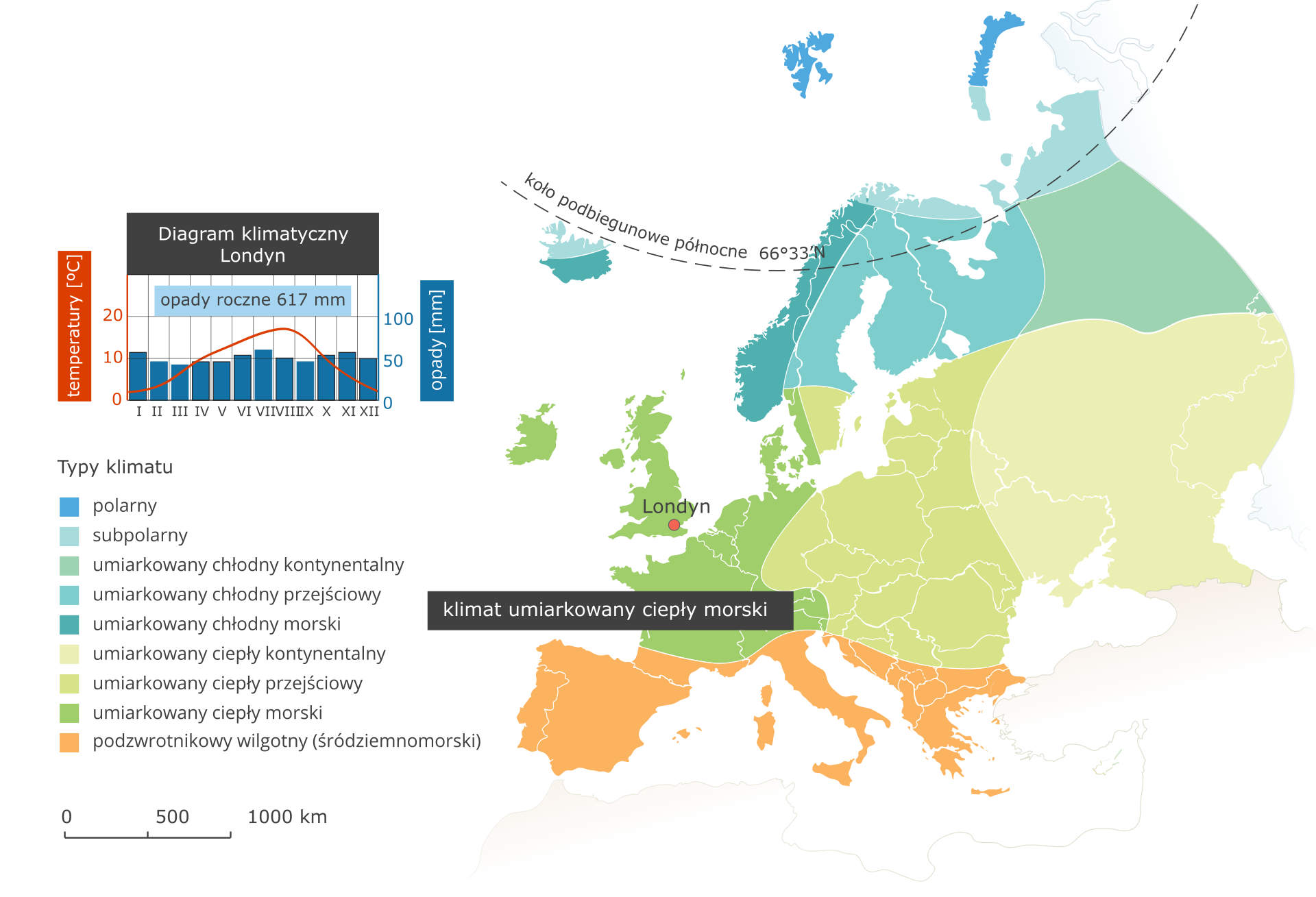
Warm marine (oceanic) temperate climate - London climate station
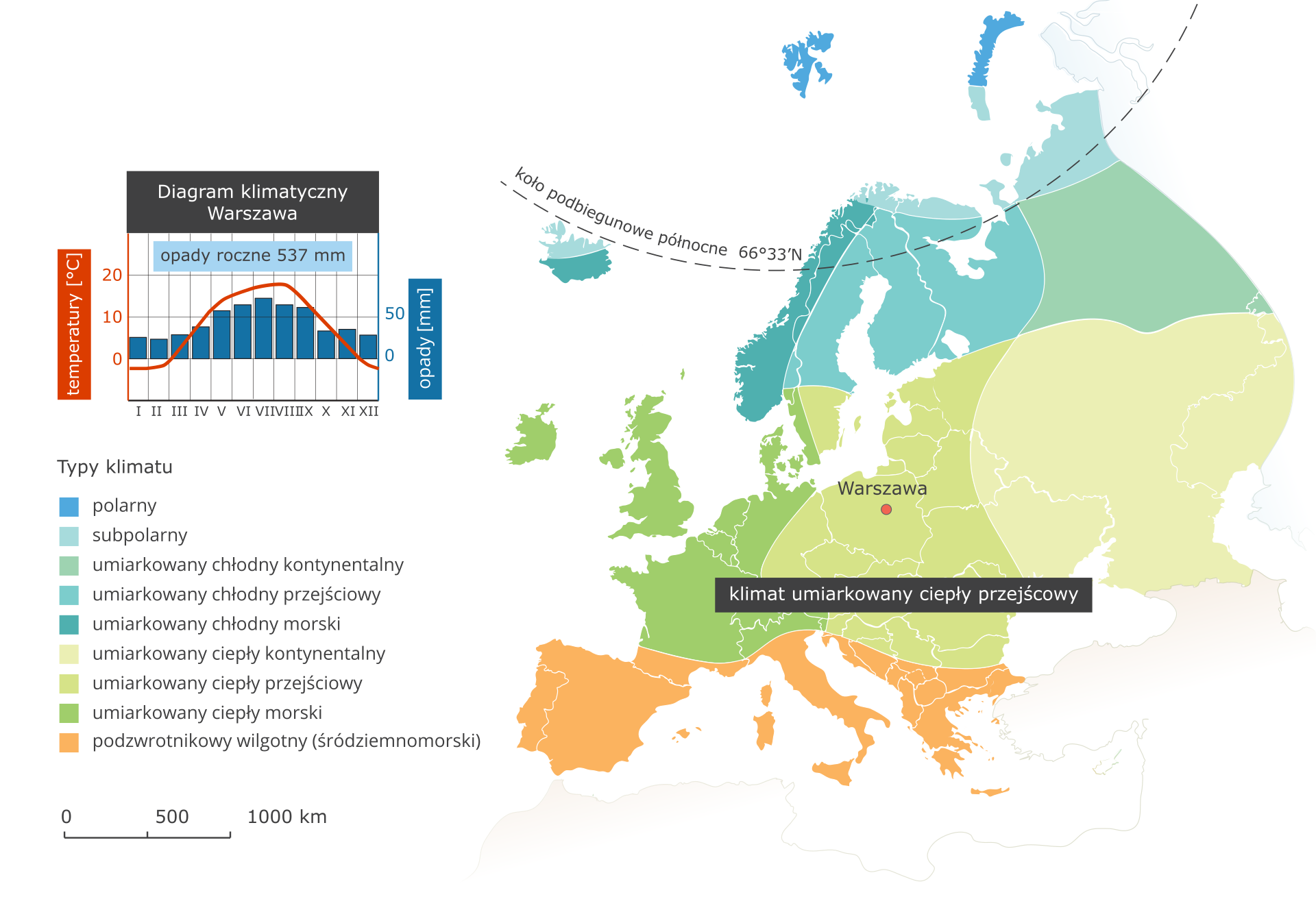
Warm transitional temperate warm climate - Warsaw climate station
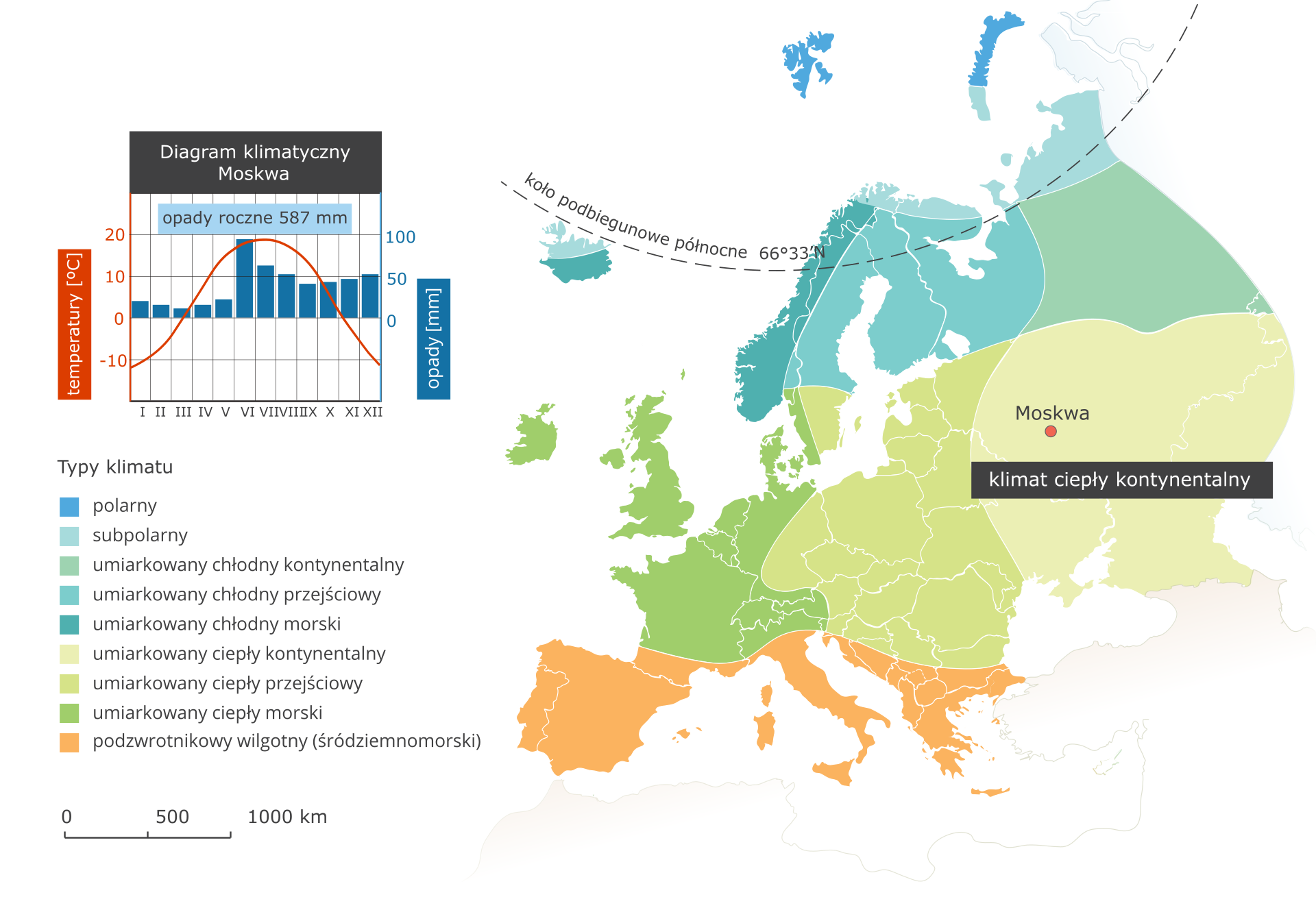
Warm continental temperate climate - Moscow climate station
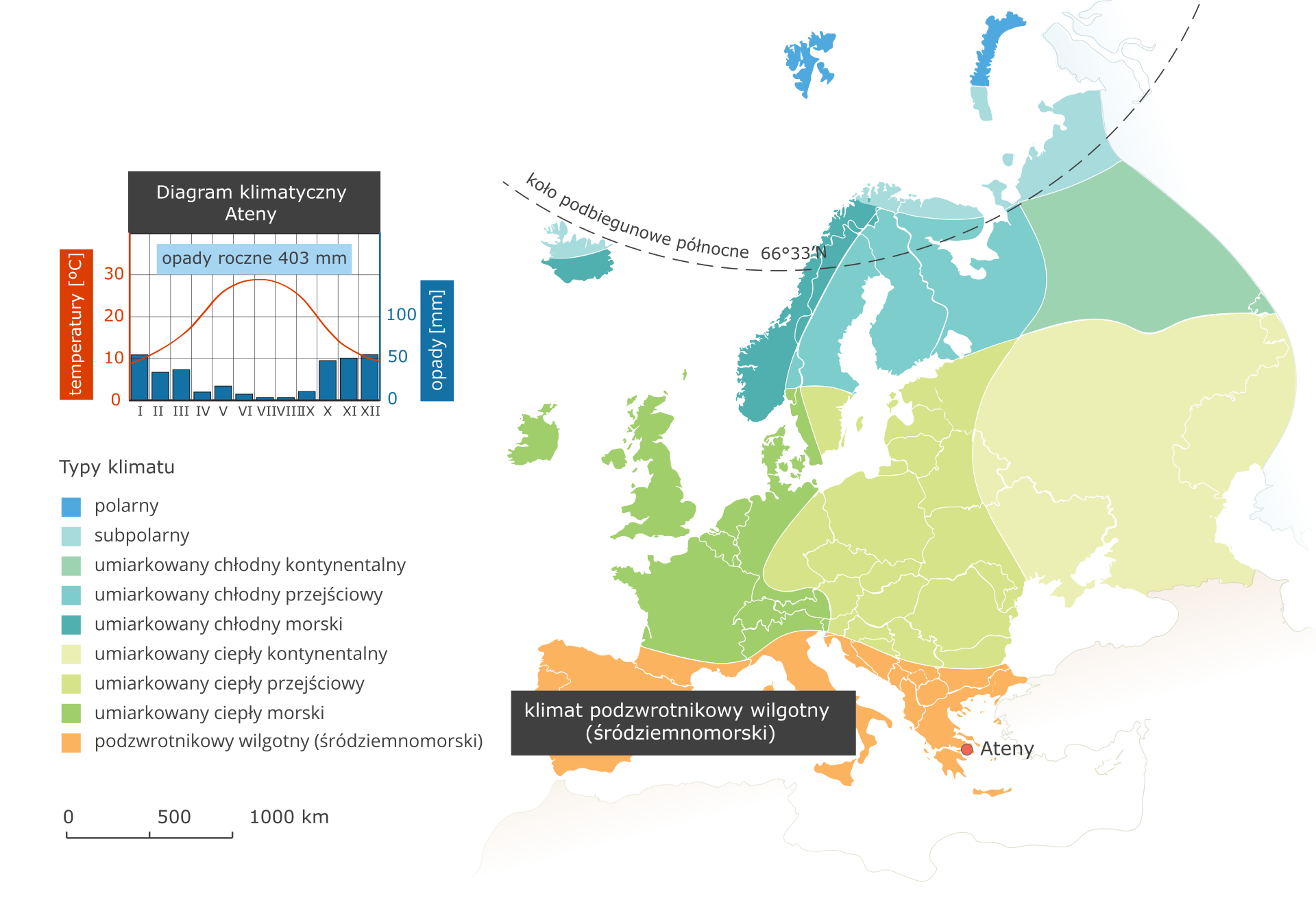
Subtropical humid (Mediterranean) climate - Athens climate station
- dry and hot summers with average air temperature ranging from 22°C to 28°C; Total annual precipitation differs from 400 mm to 600 mm.
Subpolar climate - Kanin Nos climate station
Mountain climate
In the mountainous regions of Europe, a type of climate with distinctive altitudinal zones prevails. Air temperature is always significantly lower than in the area surrounding a mountain chain, and precipitation amount is always higher. Depending on geographical location of a mountain massif, altitudinal zones may have their borders lying at different altitudes.
The infographic below presents locations with different climate types.
Determine how high is air temperature on a mountain slope at 1,600 m above sea level if air temperature at 400 m above sea level, at its base, is +8°C. Assume gradual reduction of 0.6°C per 100 m. Write down solution in your notebook.
Employing knowledge gained during the lessons, do the following exercises.
Match the flag to the correct country and type of climate prevailing in this country.

|
Portugal
|
Temperate warm climate
|

|
Greece
|
Marine temperate warm climate
|

|
Czech Republic
|
Transitional temperate warm climate
|

|
United Kingdom
|
Mediterranean (subtropical) climate
|

|
Poland
|
Mediterranean (subtropical) climate
|
A warm oceanic current that starts its course in the southern part of the Sargasso Sea, flows along the eastern coasts of North America up to Newfoundland, then as the North Atlantic stream flows through the Atlantic Ocean to the shores of Western Europe and continues as the Norwegian Current flows around Northern Europe is called:
- Gulf Stream.
- monsoon.
- fehn.
Keywords
climate, climate‑forming factors, climate types
Glossary
Prąd Zatokowy - ciepły prąd oceaniczny, który rozpoczyna swój bieg w południowej części Morza Sargassowego, płynie wzdłuż wschodnich wybrzeży Ameryki Północnej aż do Nowej Funlandii, następnie jako Prąd Północnoatlantycki przepływa przez Ocean Atlantycki do brzegów Europy Zachodniej i dalej jako Prąd Norweski opływa Europę Północną