We move heavy objects
that each object has a specific mass;
that the difficulty of lifting an object increases proportionately to its weight,
that a held object may slip out from a sweaty hand.
to explain what are friction and resistance;
to provide examples of using the force of friction in day‑to‑day life;
to indicate how to increase or reduce the force of friction as needed;
to provie examples of animals that use friction to move more efficiently;
to explain how simple machines, i.e. lever and pulley, operate.
Problematic friction
If you happened to have seen how adults move heavy furniture, e.g. a cabinet, you know that it’s not an easy task. First you should take all items out of the piece of furniture you wish to move. This will reduce its mass and weight. What good will that do? In order to move a piece of furniture you have to overcome the force with which it presses against the floor. When trying to move one surface over another, you always meet certain resistance. That is the frictionfriction that we have to overcome. It occurs always where two surfaces that we wish to move in relation to each other meet.
Before you watch the film titled “Friction”, write down a research question and a hypothesis. While watching the film, write down your observations and, in the end, your conclusions.
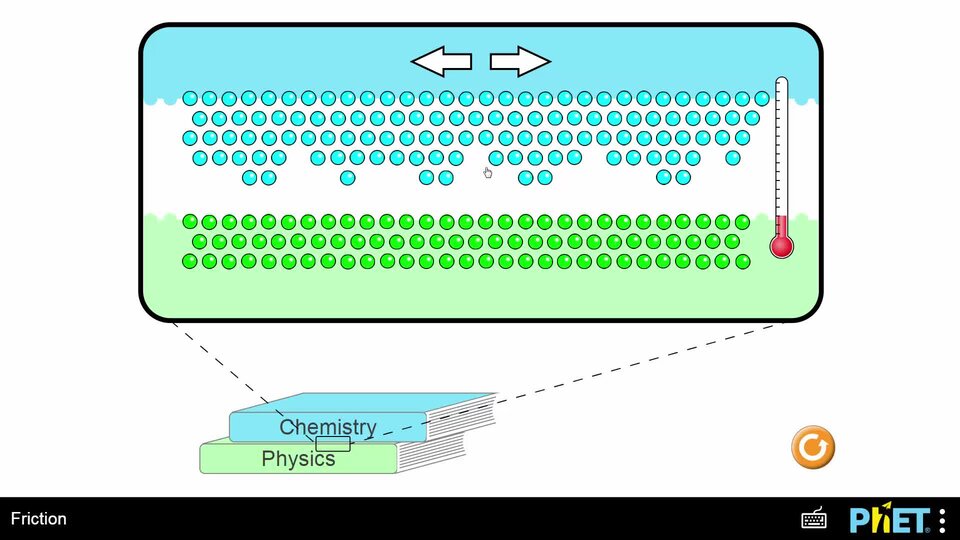
Film dostępny na portalu epodreczniki.pl
Film przedstawia działanie tarcia. Pierwsza część pokazuje ruch cząsteczek fizycznych i chemicznych przy zmianie temperatury. Gdy temperatura wzrasta cząsteczki fizyczne i chemiczne mocno drgają. Dodatkowo, cząsteczki chemiczne przemieszczają się poziomo. Gdy temperatura spada cząsteczki pozostają niemal nieruchome. Druga część filmu przedstawia chłopaka jeżdżącego na deskorolce po rampie w kształcie litery V. Podczas jazdy zmienia strony. Im większe tarcie tym niżej jest w stanie podjechać.
Factors affecting the force of friction are:
pressure force – the greater the pressure force exerted by one body (i.e. any object) on another, the greater the friction force present where they come into contact, that’s why lighter objects are easier to move;
type of surface of objects that come into contact – the rougher and more uneven the surfaces that come into contact, the harder it is to move them.
Increasing and reducing friction
If you want to move any objects, in particular heavy ones, you need to reduce friction. During friction individual particles are detached from the substance, which may lead to the complete destruction of objects or mechanisms. That’s why sometimes it’s necessary to reduce friction. Substances most commonly used for this purpose are greases and oils – e.g. in car engines. Motor oil protects moving engine components against destruction, allowing them to operate for a longer time. Sometimes it’s possible to use various materials that exhibit less friction against the floor, e.g. a blanket or towel – this also allows to move objects more easily.
Friction can also be reduced by rolling an object instead of moving it. Another method to reduce friction force is to reduce the mass of objects, i.e. the pressure force exerted on the surface. You can also try to smoothen surfaces that come into contact with each other as much as possible, for example by polishing them.
Sometimes it’s necessary to achieve better stability and grip, e.g. in the case of car tires. In such case, friction must be increased. It can be achieved by forming grooves on the surface. Friction also makes it possible to break safely.
Resistance
Friction is connected with drag forces. These are all the forces that we must overcome when we want objects to be move.
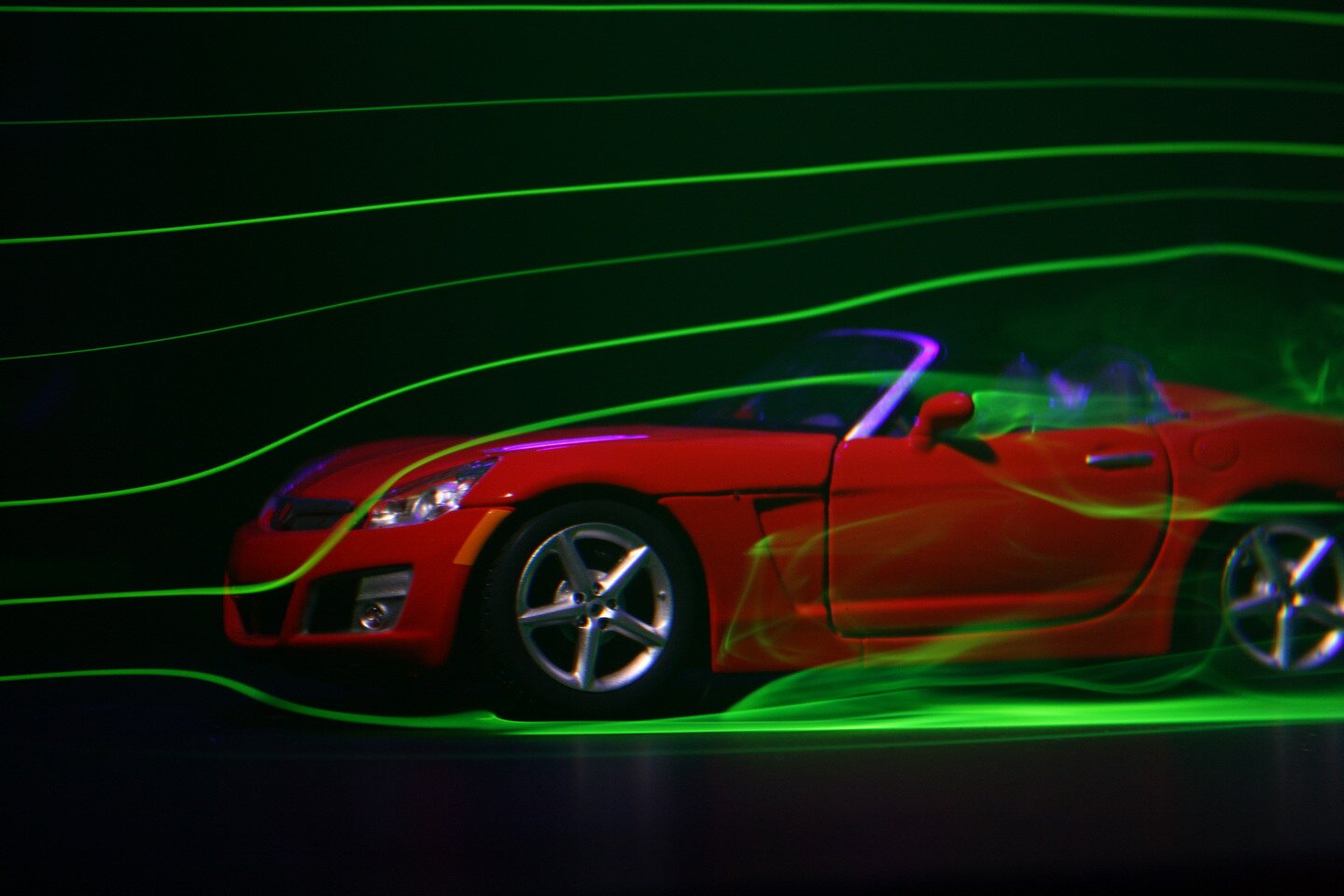
The greater the density of mediummedium surrounding the body, the greater the resistance. That’s why it’s easier to move in the air. The object’s shape is also of great importance. It’s said that the shape is aerodynamic when it enables improved flow of medium particles around the object.
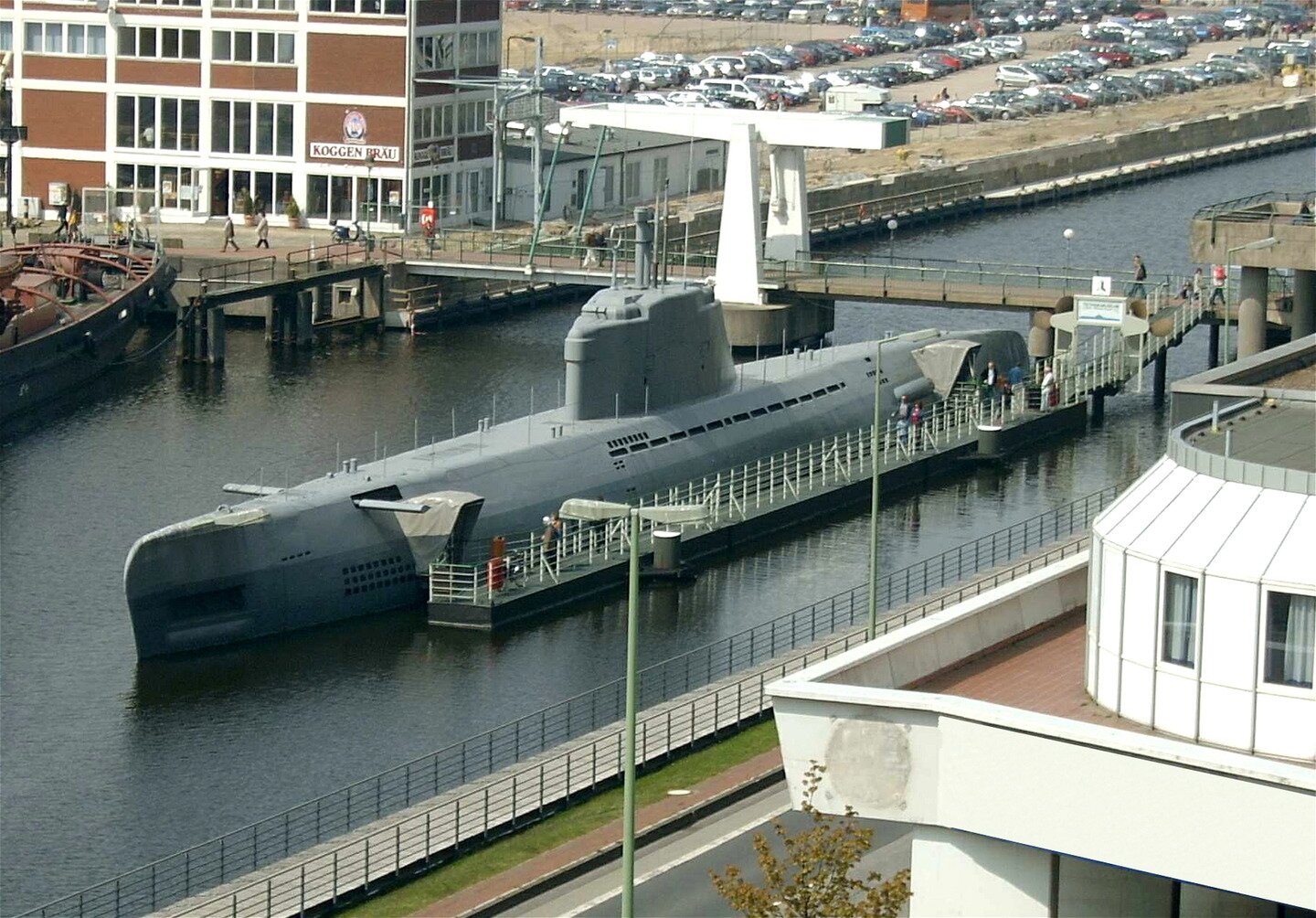
Aerodynamic shapes are very common in the animal world: they enable fish to swim fast and birds to fly. By watching animals, humans also began constructing vehicles in a way that allows them to experience the least drag. Aircraft and their hulls are modelled based on the silhouettes of birds, whereas the shape of submarine hulls evokes fish. However, not only vehicles that move through the air or water must have the most aerodynamic shape. Giving an aerodynamic shape to a motor vehicle allows to reduce drag, which affects fuel consumption. Nevertheless, there are situtations where increasing drag forces can also be useful.
How to make moving heavy objects even easier?
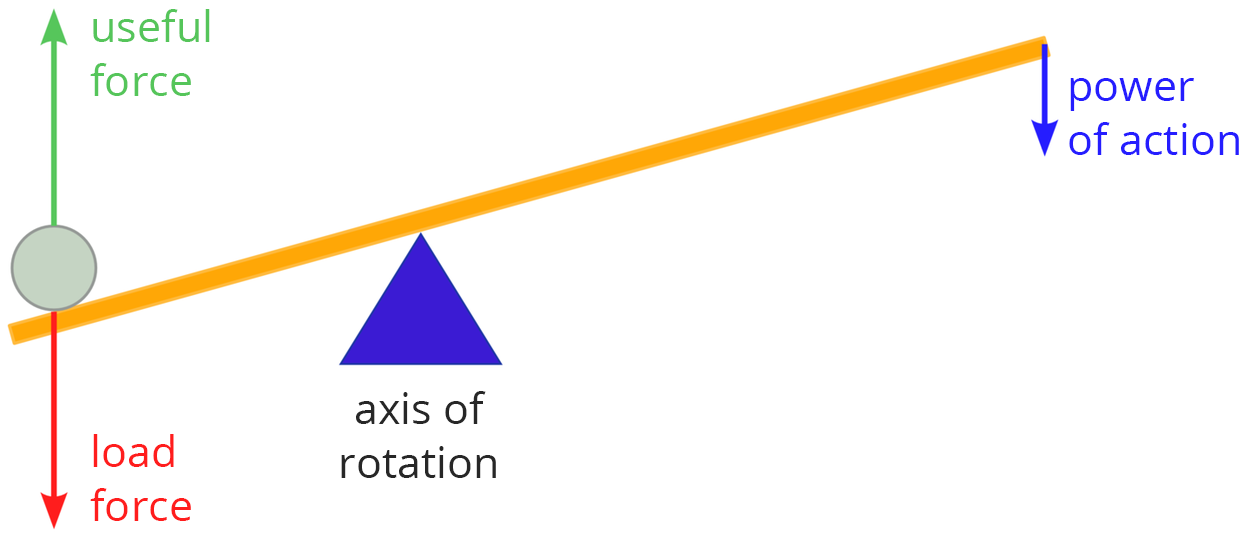
Using a device known as the double‑ended lever, it’s possible to move large objects. The longer the lever arm on which pressure is exerted and the shorter the arm on which the object being lifted rests, the less force is required to lift it.
In order to transport a heavy object to a higher storey, it’s not necessary to lift it directly off the ground. Instead, it’s possible to use a pully or a system of pulleys. This will allow to pull the heavy object high up.
Mark which of the following are examples of useful friction and which are examples of harmful friction.
| Useful friction | Harmful friction | |
| Writing on a blackboard using chalk | □ | □ |
| A bicycle braking | □ | □ |
| Engine’s pistons moving up and down | □ | □ |
| Locomotive’s wheels rolling down the track | □ | □ |
Summary
Friction is a force created when two surfaces that come into contact move against each other.
Drag is created when moving an object through a medium, e.g. water and air.
Fiction and drag can be increased or reduced as needed.
A double‑sided lever and pulleys are simple machines that allow to perform the same work using less force.
Keywords
friction, resistance, forces
Match the pairs: English words with Polish definition.
opór podczas przesuwania dwóch stykających się powierzchni i przemieszczających się względem siebie; tarcie zależy od rodzaju materiałów, siły nacisku, w fizyce jest to na przykład ciecz lub gaz, w którym przemieszcza się dany obiekt
| medium | |
| friction |
Glossary
ośrodek – w fizyce jest to na przykład ciecz lub gaz, w którym przemieszcza się dany obiekt
tarcie – opór podczas przesuwania dwóch stykających się powierzchni i przemieszczających się względem siebie; tarcie zależy od rodzaju materiałów, siły nacisku