What are the types of land surface?
which are landscape devices;
what is the absolute cost;
which leads the terrain form.
describe the terrain;
specify the characteristics of lowlands, uplands and mountains;
distinguish between low, medium and high mountains.
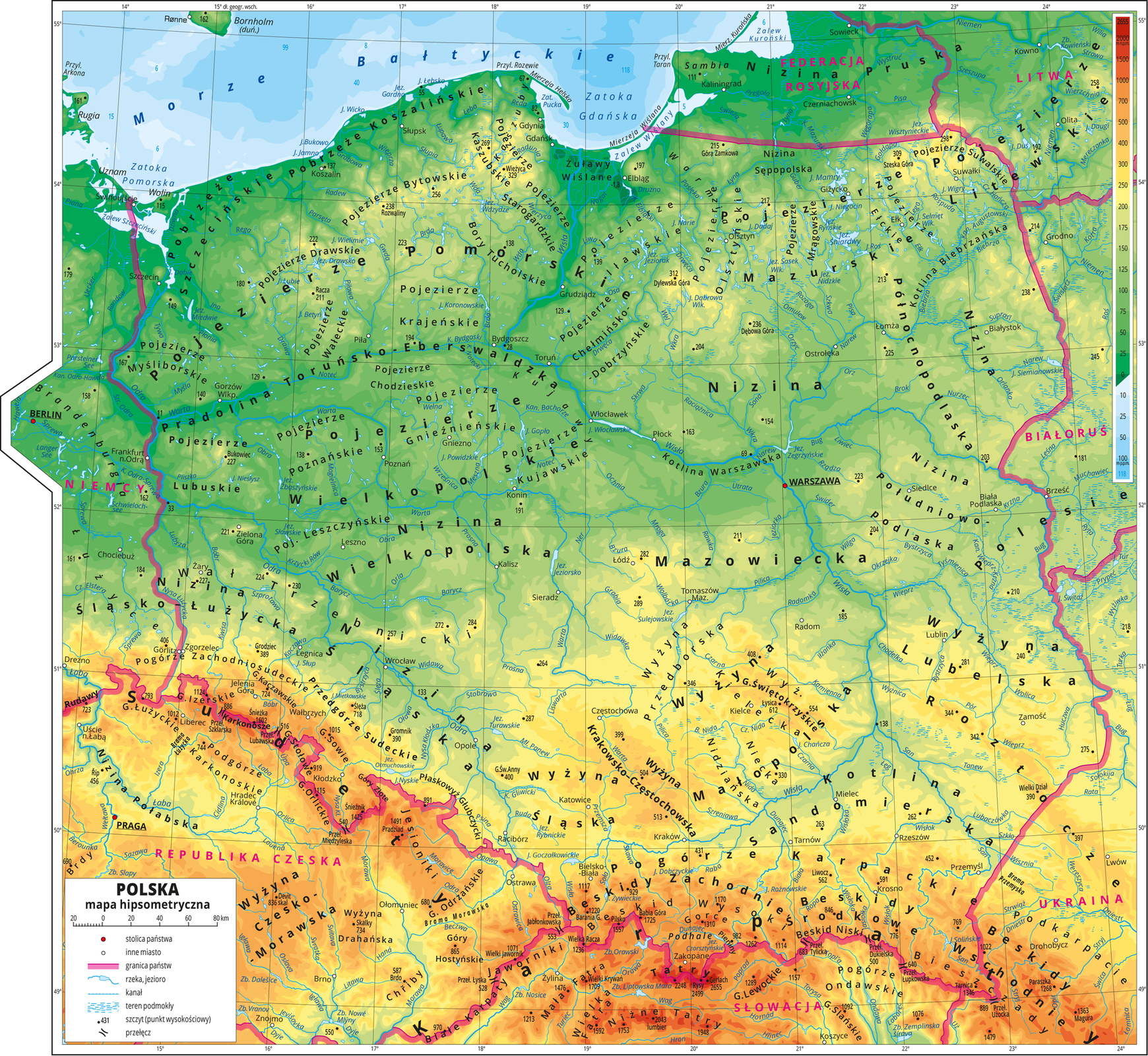
There are maps on which elevation is marked not only by contour lines, but also by colours. When you look at a map like this you will note that some areas are marked with different shades of green. The map will also have some yellow and red areas. Why is that? This is a representation of the lay of the land in different parts of our country and of the elevation above the sea level.
What is a hypsometric map?
When you ride your bike you will easily notice that the ride gets harder when you go uphill and easier when you go downhill. We already know that certain maps have contour lines connecting points with the same elevation. On a hypsometric map colour is used for an area located between two contours. Hypsometric map’s legend always contains information about the range of elevation denoted by each colour. Based on true altitude and lay of the land three main types of terrain may be distinguished: lowlands, uplands and mountains.
Lowlands
Lowlands are areas of true altitude between 0 and 300 m above the sea level and flat, undulating or hilly terrain. Relative altitude differences in lowlands are hardly ever greater than 60 m. On hypsometric maps different shades of green are used for lowlands. Lowlands vary; they may be flat or hilly.
Uplands
Uplands are areas that fulfil two conditions:
their true altitude must be above 300 m above the sea level,
relative altitude differences are smaller than 300 m. The terrain in uplands is usually more varied than in lowlands – it may be flat, but usually it is undulating or hilly (e.g. Świętokrzyskie Mountains are classified as uplands!) The boundary between lowlands and uplands is blurred, usually the transition between the two is gradual.
In Poland, sometimes areas higher than 200 m above sea level are considered as high places. Therefore, on the hypsometric maps of Poland, areas located above this height are already marked with yellow.
Mountains
Mountains are areas with true altitude above 300 m above the sea level and relative altitude differences above 300 m. Mountains are subdivided into low, medium and tall.
Low mountains (counted to highlands) | Highlands | High mountains | |
Absolute altitudes | rarely exceeding 600 m n.m. | up to approx. 1,600 m n.p.m | in Poland up to 2499 m above sea level |
Relative heights | rarely exceeding 300 m | significantly exceeding 300 m | significantly exceeding 300 m |
Example | Góry Świętokrzyskie | Sudety, Beskidy, Bieszczady | Western |
On the hypsometric maps the mountains are marked with orange, red and brown, depending on their height. The hypsometric maps use blue tones to mark water bodies. The darker the color – the deeper the water body.
Combine the main surface-forming units with the corresponding colors on the hypsometric map.
blue, yellow, green color, red color
| lowland | |
| highlands | |
| top | |
| water reservoirs |
Exercise
1. hilly, 2. upland, 3. Highlands, 4. Mountains, 5. Relative, 6. built-up, 7. Absolute, 8. lowland, 9. Lowlands, 10. mountainous, 11. Mountain peaks, 12. Above sea level, 13. mountain, 14. steep height differences in these areas can reach up to 60 m.
In our country, 1. hilly, 2. upland, 3. Highlands, 4. Mountains, 5. Relative, 6. built-up, 7. Absolute, 8. lowland, 9. Lowlands, 10. mountainous, 11. Mountain peaks, 12. Above sea level, 13. mountain, 14. steep areas prevail.
Complete the sentences with the correct expressions.
upland, Mountains, built-up, Highlands, Relative, steep, Mountain peaks, mountainous, Lowlands, lowland, hilly, Absolute, mountain, Above sea level
.............................. are areas with altitudes from 0 to 300 m above sea level and plain, wavy or .............................. surface.
.............................. height differences in these areas can reach up to 60 m.
In our country, .............................. areas prevail.
Evaluate the truthfulness of the opinions listed below.
| True | False | |
| The highlands are located higher than the lowlands, but do not exceed 100 m above sea level. | □ | □ |
| 300 m above sea level is considered the lower boundary of the highlands. or 200 m above sea level. | □ | □ |
| The highlands are above 400 m above sea level. | □ | □ |
| There are the highest mountains in the highlands. | □ | □ |
Summary
The terrain units are distinguished on the basis of their altitude and differences in relative heights.
Lowlands are areas with an altitude of up to 300 m above sea level.
Uplands are areas with altitudes above 300 m above sea level. and relative heights not exceeding 300 m.
Mountains are areas with altitudes above 300 m above sea level and differences in relative heights above 300 m.
Keywords
hipsometric map, mountains, lowlands, highlands
Glossary
góry – czyli obszary o wysokości powyżej 300 m n.p.m., gdzie między szczytami i dolinami jest więcej niż 300 m różnicy wysokości.
mapa hipsometryczna – czyli taka, na której odwzorowano ukształtowanie powierzchni terenu, nanosząc poziomice i określone barwy między nimi.
niziny – czyli obszary położone na wysokościach od 0 do 300 m n.p.m.
wyżyny – czyli obszary położone powyżej 300 m n.p.m. z niewielkimi różnicami wysokości względnych.