What is a gnomon and how to use it to observe the apparent movement of the Sun over the horizon?
what the position of the Earth is in the Solar System;
what the shape of the Earth is;
what size the Earth is.
to explain what a gnomon is and how to use it;
to describe how to safely observe the Sun using a gnomon;
to determine the geographical directions and the local meridian, using a gnomon.
The apparent motion of the Sun over the horizon is an indirect proof of the rotational motion of the Earth. We can observe it every day.
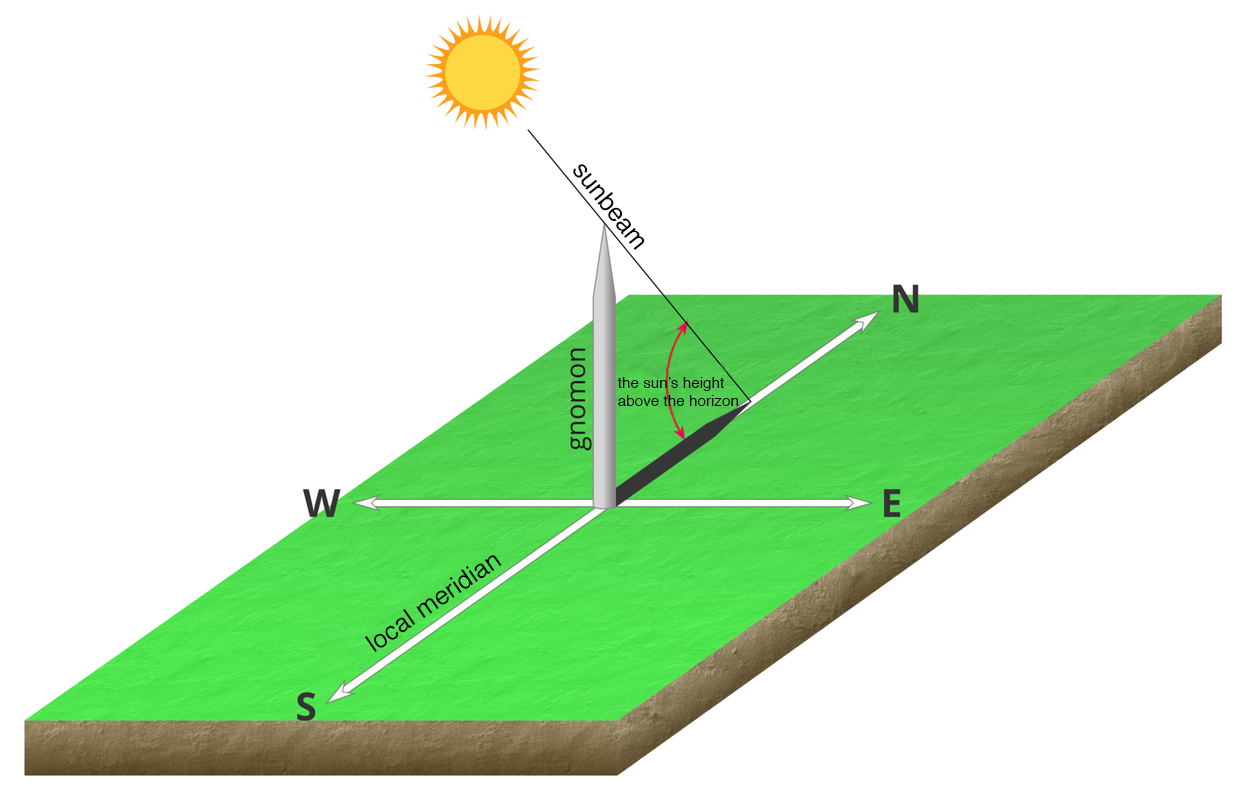
One of the ways to avoid the risk of damaging your eyes, while following the apparent movement of the Sun, is to observe the shadow cast by objects illuminated by direct sunlight. By observing the shadow, we can make conclusions about the apparent movement of the Sun. Every relatively thin, straight, and vertical rod stuck into the ground becomes a gnomongnomon, i.e., the instrument whose shadow determines the position of the Sun.
The following simulation shows changes in the shadow cast by a gnomon on the equinox day in the northern hemisphere.
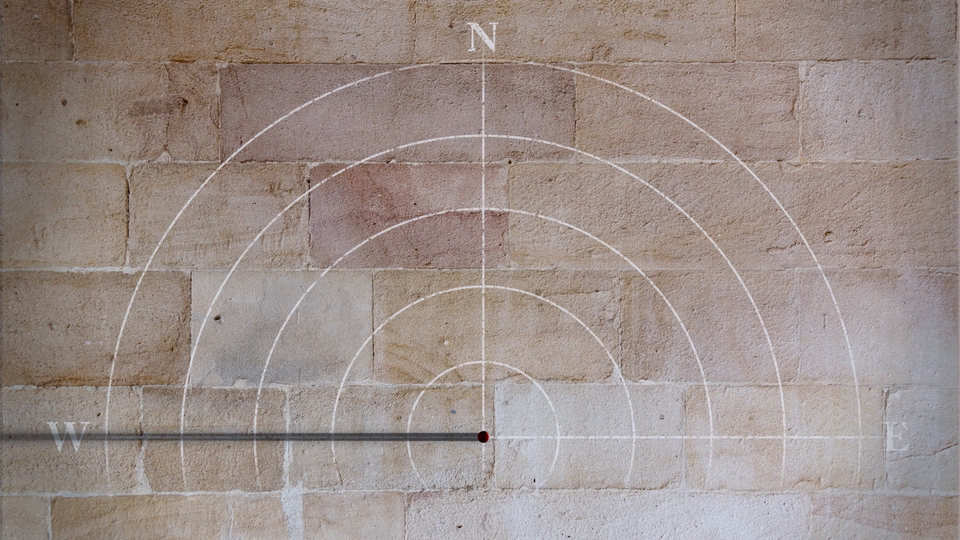

Film dostępny na portalu epodreczniki.pl
Nagranie filmowe przedstawia sposób działania gnomonu. Gnomon oświetlany przez Słońce rzuca cień na ziemię. Wraz z dobowym i rocznym ruchem Słońca po niebie, zmienia się kierunek i długość cienia rzucanego przez gnomon. To proste zjawisko pozwala z gnomona uczynić kalendarz słoneczny lub prostszą, mniej dokładną wersję zegara słonecznego. Gnomon umożliwia też odczytanie położenia Słońca (ewentualnie Księżyca) na niebie, tzn. możemy zmierzyć wysokość Słońca na horyzontem i azymut, czyli kierunek na Słońce względem stron świata.
The length and direction of a gnomon’s shadow are determined by the height of the Sun and its azimuth. When establishing the directions based on the shadow cast by a gnomon, you should remember that in Poland and in the whole area of the northern hemisphere, except for the intertropical zone, the Sun is always at its highest point on the southern side of the sky. The shadow cast by a gnomon at noon is the shortest and precisely indicates the north. We may conclude from this that the moment of the Sun’s highest pointSun’s highest point (the moment of the solar noon) has come. When this happens, the position of the Sun in the sky indicates the south. The extension of the line set by the gnomon’s shadow is the local meridianlocal meridian of the point at which the gnomon is stuck into the ground. The sun rises exactly in the east and sets exactly in the west only twice a year (March 21 and September 23). If we could observe the gnomon’s shadow on those days at sunrise or sunset, then the extension of the line of this shadow would be the local parallellocal parallel, because the gnomon’s shadow would indicate the east–west direction.
However, it is easy to determine geographical directions with a gnomon on other days too. At the moment when a gnomon casts the shortest shadow, it indicates the north (N). The south is, therefore, the opposite direction (S). 90° to the left of the gnomon is the west (W), and 90° to the right is the east (E).
Put a globe in the light of the Sun or a lamp. Slowly rotate the globe around its axis. At different moments of its illumination, determine which parts of the globe correspond to the phenomenon of the Earth's day, and which of the night.
Developing the ability to conduct astronomical observations using a gnomon, as well as to interpret the results obtained.
gnomon, i.e., a simple stick, rod or post.
Perform your observations on a sunny day.
Due to the differences in longitude and the setting of clocks to summer time, the observations should be made between 11 a.m. and 1 p.m.
Install the object that will act as a gnomon. You can use an existing post, pile, or another vertical, straight, relatively thin object.
Every now and then, mark the area on the ground where the end of the shadow falls.
When the shadow begins to elongate, determine the spot where it was the shortest and connect this spot to the base of the gnomon. Write down what direction was shown by the shortest shadow.
Extend this line from the base of the gnomon in the direction opposite to the one indicated by the shortest shadow, and describe the direction it determines.
Draw a line perpendicular to the previously determined one, passing through the base of the gnomon, and describe the other directions.
For most places in Poland, the moment of the Sun’s highest point is different than the noon indicated by clocks.
Regardless of the calendar day or longitude, when the Sun is at its highest point the shadow is the shortest and indicates the north.
On a sunny day, the ability to use a gnomon allows you to determine all geographical directions as well as the course of the local meridian.
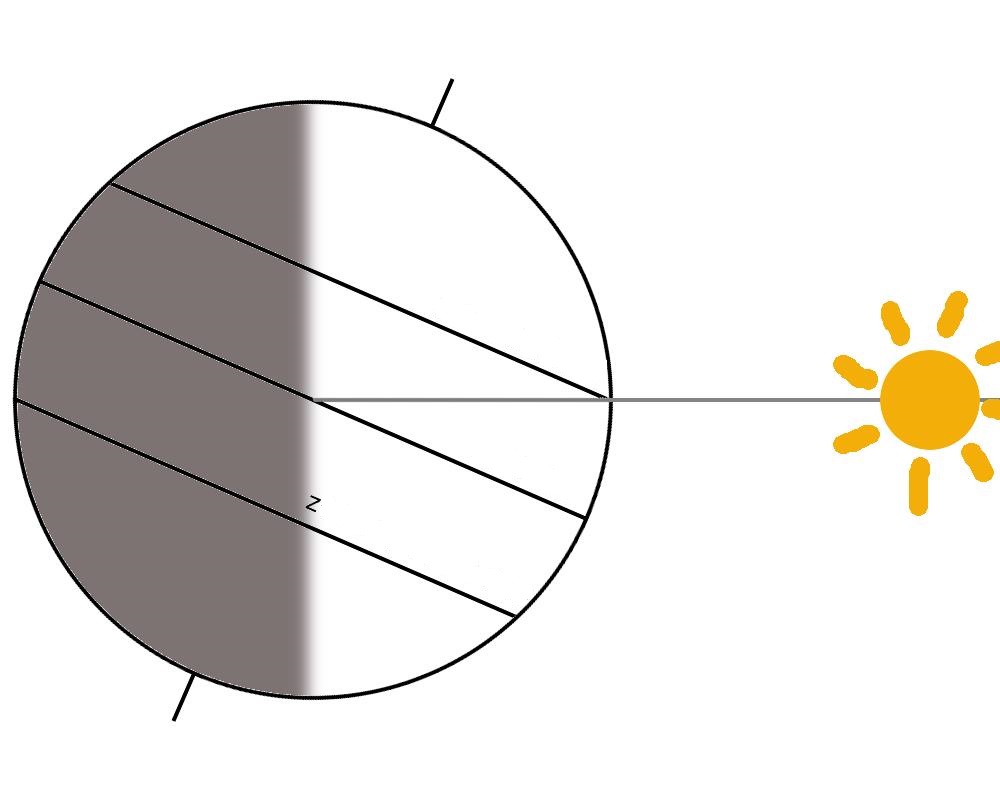
In the area between the tropics, twice a year, the Sun’s highest point matches the zenithzenith. On the equator, this happens on March 21 and September 23. On the Tropic of Cancer, the Sun appears at the zenith only on June 22, and on the Tropic of Capricorn only on December 22. When the Sun’s highest point matches the zenith, gnomons do not cast a shadow at all.
You should remember that in Poland and in the whole area of the northern hemisphere, except for the intertropical zone, the Sun is always at its highest point on the southern side of the sky. However, in the intertropical zone of both hemispheres, the sun is at its highest point on the northern side in one part of the year, and on the southern side in another. On the rest of the southern hemisphere, the Sun is at its highest point on the northern side of the sky all year, and the shadow cast by gnomons indicates the south.
The following figure shows the position of the Earth in relation to the Sun on June 22. Analyze the figure and then select three correct endings for the sentence below.
When the Sun is at its highest point on June 22....
- the shadow of a gnomon located in the northern hemisphere outside the intertropical zone indicates the north.
- a gnomon located on the Tropic of Cancer does not cast a shadow.
- the shadow of a gnomon located in the intertropical zone indicates the south.
- the shadow of a gnomon located on the Tropic of Capricorn indicates the north.
- a gnomon located on the equator does not cast a shadow.
- the shadow of a gnomon located on the south pole indicates the south.
Match the correct definition to each of the following terms
a parallel that passes through a given place on the Earth’s surface, a meridian that passes through a given place on the Earth’s surface, the moment when the Sun is at its highest point above the horizon during the whole day, the point in the celestial sphere directly above an observer
| solar noon | |
| local meridian | |
| local parallel | |
| zenith |
Keywords
gnomon, local meridian, local parallel, Sun’s highest point, zenith
Glossary
gnomon – zwykle jest to pręt, kolumna lub prosty kij wbity w ziemię, którego cień wskazuje położenie Słońca; to jeden z najstarszych i najprostszych przyrządów astronomicznych; precyzyjnie skonstruowane i ustawione gnomony są przyrządami astronomicznymi albo częściami zegarów słonecznych
górowanie Słońca – moment, w którym w ciągu doby Słońce znajduje się na maksymalnej wysokości kątowej nad horyzontem; moment ten bywa nazywany także południem słonecznym
południe słoneczne – moment, w którym w ciągu doby Słońce znajduje się na maksymalnej wysokości kątowej nad horyzontem; moment ten bywa nazywany także górowaniem Słońca
południk miejscowy – południk lokalny przechodzący przez dane miejsce na powierzchni Ziemi
równoleżnik miejscowy – równoleżnik przechodzący przez dane miejsce na powierzchni Ziemi
zenit – punkt na sferze niebieskiej znajdujący się dokładnie ponad pozycją obserwatora