Soil pollution
what a soil and soil fertility is;
the types of fertilizers and what their role is;
how to plan and carry out the testing of selected soil properties and the impact of soil constituents on plant development.
to define the terms of soil degradation and devastation
to list and discuss the sources and types of soil pollutants
to discuss, using examples, the harmful effects of selected chemical pollutants of soil (heavy metals, hydrocarbons, pesticides, nitrates
to justify the relationship between the development of civilization and the existing soil pollution
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
Nagrania abstraktu przedstawiające różne typy dokonywania oprysków.
Soil pollution
Soils, like the entire natural environment, may become polluted. Due to their sorptive properties, soils absorb a lot of chemical substances that penetrate into them in the form of:
solids – ashes, plastics;
liquids – wastewater discharged into water reservoirs and entering soil together with water;
gases – harmful gases absorbed by the soil or first dissolved by water, and then entering soil together with water;
We talk about soil pollution when chemical substances occur in it in quantities exceeding their typical content and cause changes in soil properties that do not allow for its normal use.
The main sources of soil pollution caused by human activity:
industrial – mining, energy, metallurgical, steel, chemical, construction industry;
agricultural – too intensive fertilization, excessive use of pesticides;
municipal – sewage and solid waste;
communication – toxic substances and heavy metals contained in the vehicle exhaust, salt, which is sprinkled on ice‑covered road surfaces.
Source of pollution | Types of pollutants |
industry | dust and smoke (containing, among others, heavy metals – lead, mercury, cadmium, poisonous chemicals), heaps |
gases – carbon oxides and nitrogen oxides | |
wastewater and post‑production waste | |
agriculture | pesticides |
fertilizers and their impurities | |
transport | car fumes – nitrogen oxides, carbon oxides |
hydrocarbons | |
salt | |
households | packaging |
sewage (including detergents) |
Pesticides
PesticidesPesticides are chemical compounds used, among others, for:
plant protection against pests (insecticides) and fungi (fungicides),
plant disease control (bactericides),
weed removal (herbicidesherbicides).
Pesticides spread in the environment through air and water, but they also remain in the soil. Due to the their exceptionally long shelf‑life, toxicity and high biological activity, pesticides pose a serious threat to the natural environment.
Pollutants of petroleum origin
When the significant amounts of hydrocarbons which originate, among others, from petroleum and the products of its processing, i.e. gasoline, diesel oil, get into the soil, they can cause its exclusion from biological activity for the period of 10 -15 years. Soil supersaturation with these products destroys soil and plant microorganisms and causes oxygen deficiency.

Inorganic salts
An excess of nitrates in the soil reduces the resistance of plants to diseases and pests. Overfertilization of plants may be the cause of their physiological diseases. High‑grade mineral fertilizers used in excessive amounts may in many cases be more harmful than a shortage of nutrients in the soil. The plants grown in the soil contaminated with nitrates may also be harmful to consumers. In certain conditions, nitrates accumulated in the tissues of plants may undergo conversion to nitrites, which have carcinogenic properties (they promote cancer development).
Formulate a research question and hypothesis before doing the experiment “Testing the presence of nitrites in vegetables”
Testing the presence of nitrates in vegetables.
test tubes,
Petri dishes or watchglasses,
pipette,
root vegetables, e.g. carrot, parsley, beetroot, radish and potato (from different cultivations),
indicator strips for detecting nitrates and nitrites,
Rivanol solution (dissolve 1 tablet in 20 cmIndeks górny 33 of distilled water),
hydrochloric acid, 5%,
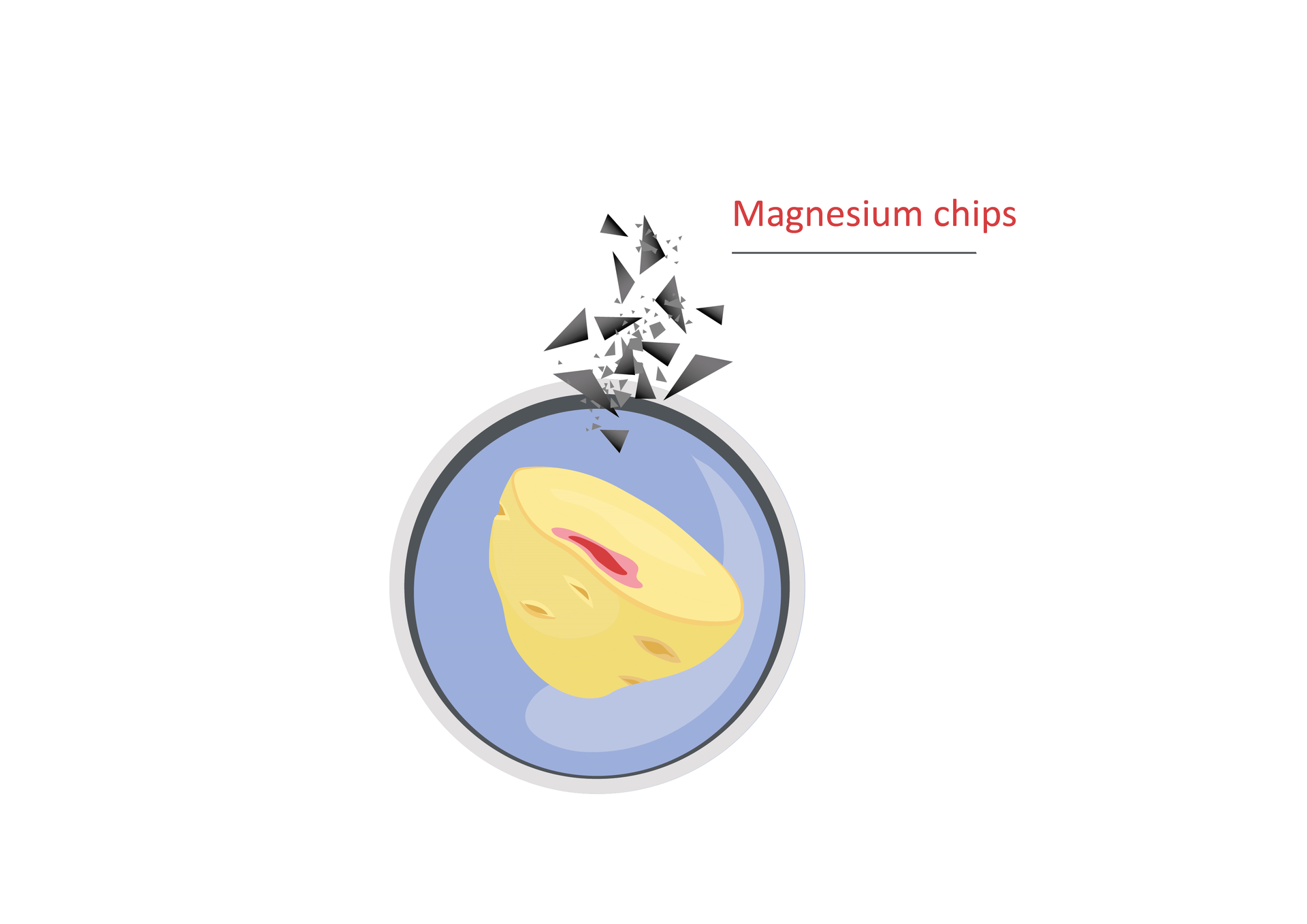
magnesium chips.
Prepare small pieces of peeled vegetables and place them on watchglasses.
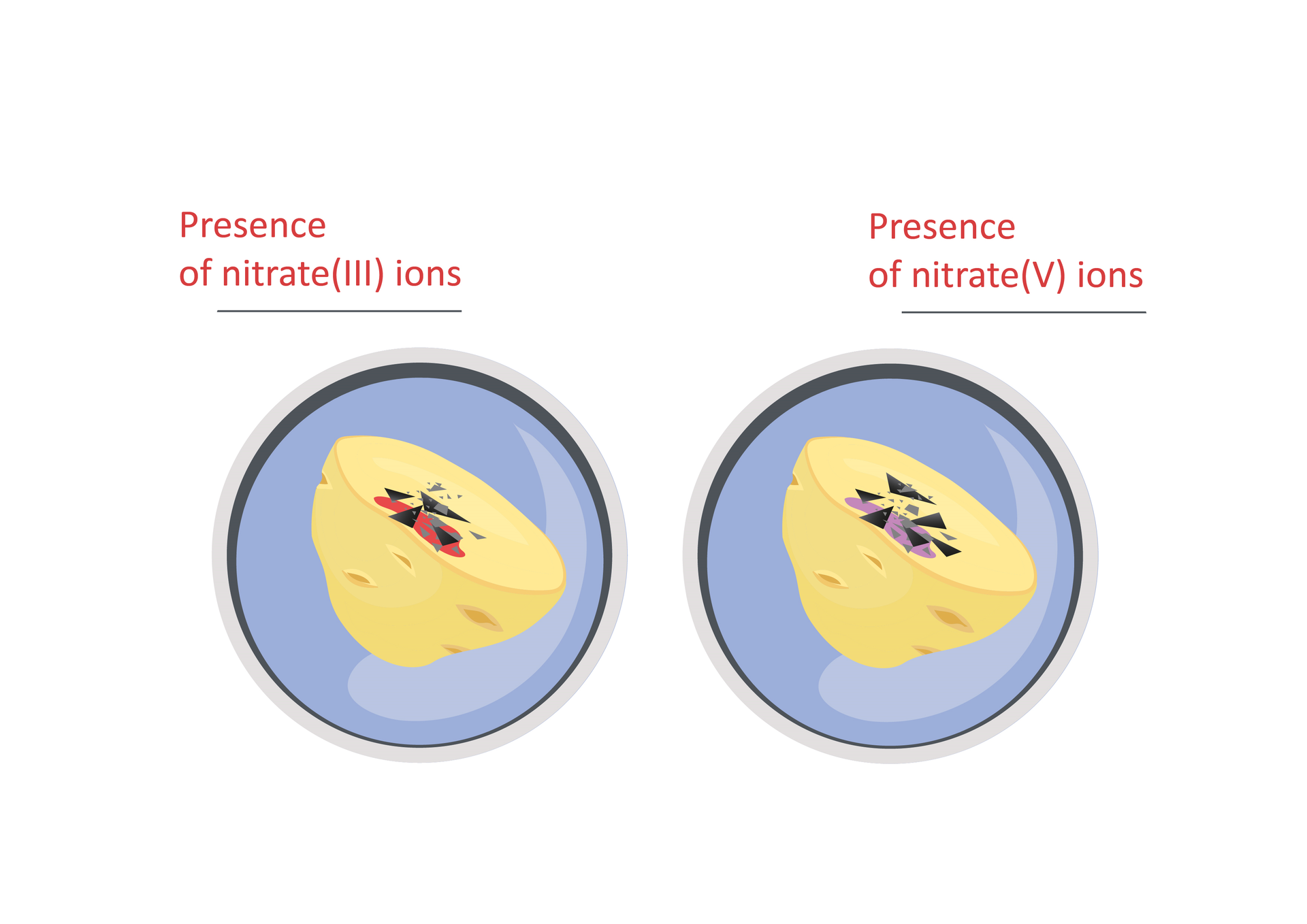
Carry out, one by one, tests for the presence of nitrates; to this aim: apply 2–3 drops of Rivanol solution on a vegetable sample, add 2–3 drops of hydrochloric acid, watch the color; if a pinkish‑red color appears around the place on the sample where liquid was applied, confirming the high amount of nitrates, end the test; if such a color does not occur, sprinkle the sample with magnesium chips and observe changes in colour – nitrite ions will cause the sample to turn red and nitrate ions – to light violet.
You can also perform a test for nitrate and nitrite ion concentration using test strips. Follow the instructions on the packaging.
Nitrogen needed for plant growth is taken up by plants in the nitrate or ammonium form . However, it may also occur in the soil in the form of nitrites which are toxic to many plants. Not all vegetables accumulate nitrates and nitrites equally. These compounds are accumulated to a high extent by, for example: radish, beets, parsley, to a lesser extent – carrot, celery, potato and onion.
This pollution may lead to a significant reduction in plant resistance to diseases and pests. Plants grown in soils polluted with nitrates and nitrites contain an excess of these substances and have a negative impact on the health of consumers. Excess nitrates can be converted to nitrites, which contribute to the formation of very toxic compounds exerting carcinogenic activity. Processes of this type may occur, for example, when storing vegetables containing excessive amounts of nitrates.
Formulate a research question and hypothesis before doing the experiment “Testing the effect of soil salinity on plant growth”

Does soil salinity affect the development of plants?
Excessive concentration of sodium chloride in the soil has a negative effect on plant development.
4 measuring cylinders (100 cmIndeks górny 33) or 4 test tubes,
marker,
dropper,
saline solutions 1%, 5%, 10%,
tap water,
edible oil,
4 stems of lilac or hazel with well developed leaves (or 4 shoots of spiderwort).
Pour the same amount (80 cmIndeks górny 33) of saline solutions to 3 cylinders and pour water to the fourth cylinder. Make sure that each cylinder is labeled with the information about its content.
Place one shoot in each cylinder, then pour the edible oil in a quantity sufficient to form a 5 mm thick layer; this will prevent water vaporization. Mark the initial liquid level in the cylinders.
Leave samples for 2–3 days. Observe the occurring changes.
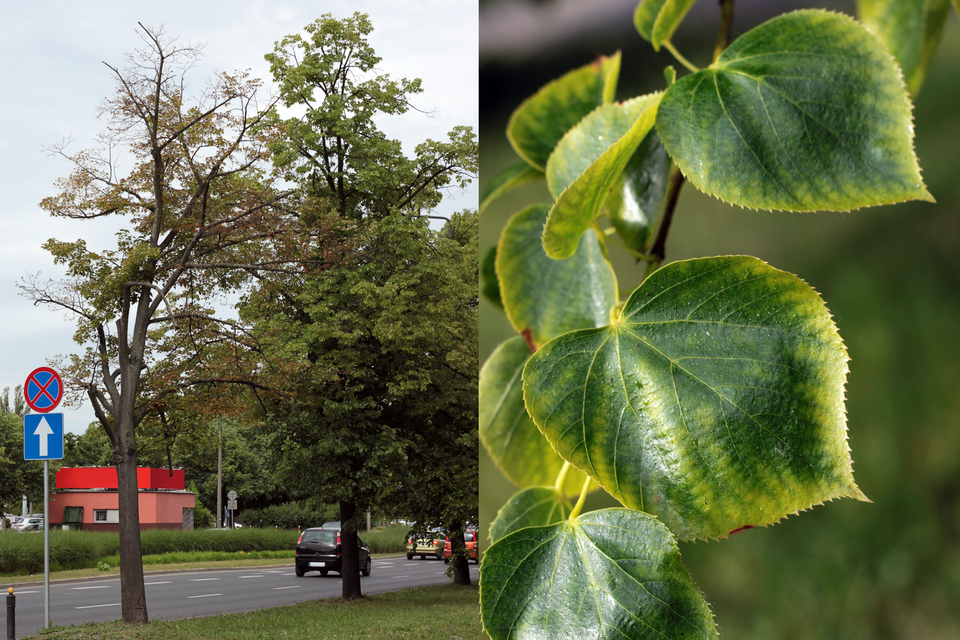
Excessive concentration of salt in the soil solution makes it difficult or impossible for the plants to take up water. The degree of salinity depends on the amount of water in the soil. The negative reaction of plants to excess salt is their wilting, and at higher concentrations – dieback (halophytes are an exception). Salinity is caused by: chlorides, sulfates, sodium and potassium carbonates.
The effects of excessive salinity in Poland may be observed on the leaves of roadside trees in June and July.
Heavy metals
Heavy metals – lead , copper , mercury , cadmium – are another group of the chemical pollutants of soil. Over 90% of the total content of cadmium, copper, zinc and lead in soils comes from anthropogenic sources. A particularly high content of heavy metals in the soil was found in the areas adjacent to steel mills, galvanizing plants and mines.
Heavy metals polluting the soil accumulate in the tissues of plants and cause irreversible changes in their organisms. They are also toxic to consumers (they can cause many diseases, including cancer).
Detection of lead(II) ions in soil.
test tubes,
filter papers,
conical flasks,
spoon,
pipette,
funnels,
acetic acid,
sodium sulfide,
soil samples (taken in various sites).
Pour about 150 cmIndeks górny 33 of distilled water into the conical flask and add 2 cmIndeks górny 33 of acetic acid.
Add a tablespoon of the tested soil to the solution, stir it, and shake for about 5 minutes.
Filter the contents of the flask.
Add 2 drops of sodium sulfide solution to the solution obtained. Observe the occurring changes.
Similarly, test other soil samples.
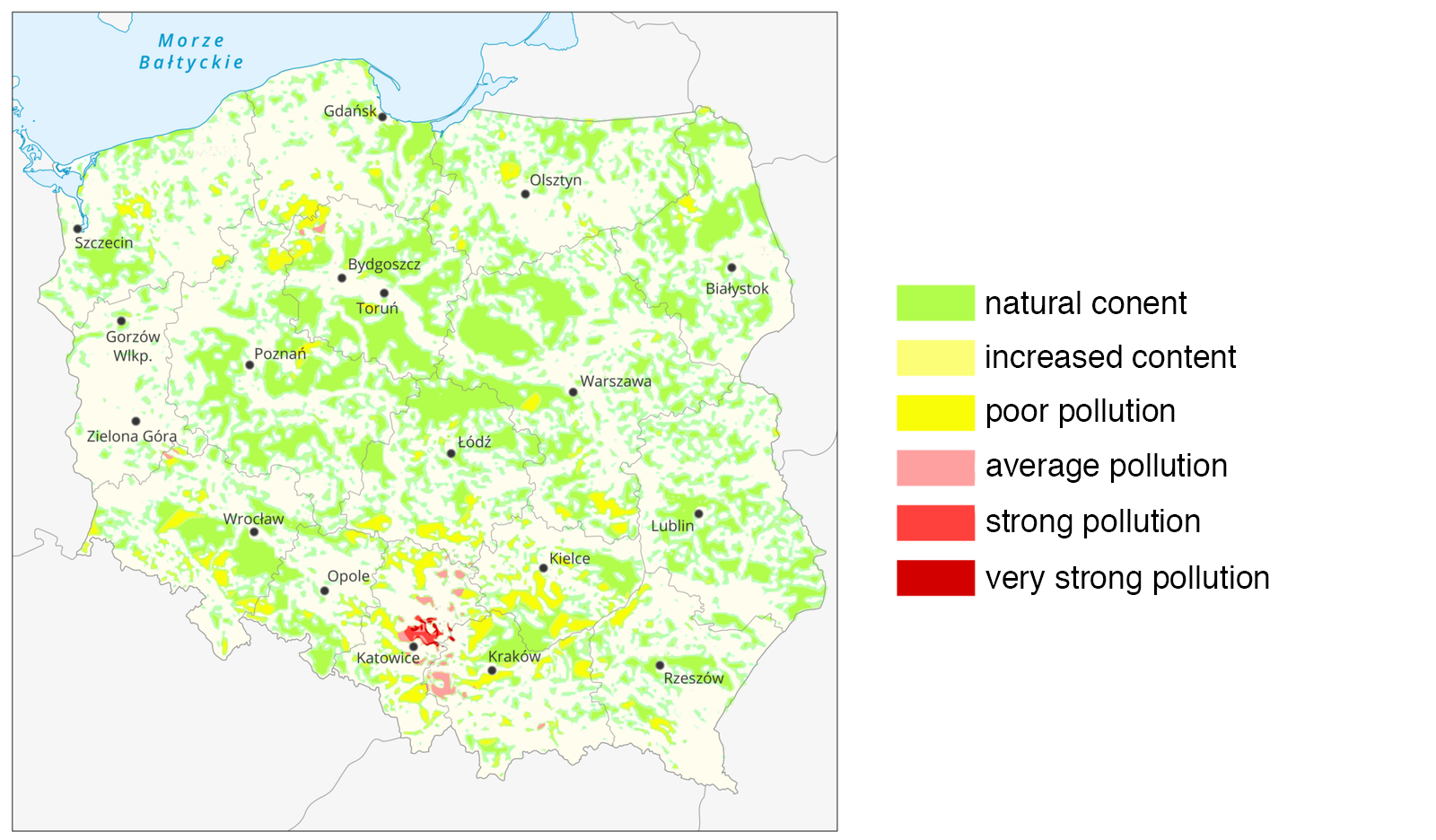
Mark true statements.
- Soils most contaminated with heavy metals are found in Upper Silesia
- Plants need nitrogen to grow, so the residues of nitrites in vegetables, regardless of their amount, are harmless to humans
- The source of soil pollution with fertilizers and pesticides is industry
- Heavy metals contribute to the development of cancer diseases in humans
Summary
The chemical sources of soil pollution include, among others, hydrocarbons and their derivatives, chemical fertilizers, pesticides, heavy metals.
Contaminated soil is unsuitable for cultivation as harmful substances enter the consumer's organisms along with the plants grown.
Keywords
herbicides, pesticides
Glossary
herbicydy – rodzaj pestycydów, które służą ochronie upraw przed chwastami
pestycydy – chemiczne środki ochrony roślin uprawnych przed organizmami szkodliwymi lub niepożądanymi, szczególnym ich rodzajem są używane do zwalczania owadów insektycydy