Sugars – glucose and fructose
that sugars are an essential part of everyday human diet.
what atoms of the elements are present in the sugar molecules;
subdivide sugars into simple and complex ones;
what is the total formula of glucose and fructose;
what are the properties and use of glucose.
Structure and division of sugars
Fats and proteins are important elements of our daily diet. These biologically important substances also include sugarssugars called saccharides. These compounds are composed of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms.
Due to the structure of sugars, we divide them into simple and complex ones.

Glucose
One of nature's most common simple sugars is glucoseglucose – one of the products of the photosynthesis process.
What is the structure of the glucose molecule?
The molecular formula for glucose is This formula also describes other compounds. This is why, in organic chemistry, structural, semi‑structural or skeletal formulas are most often used.

What are the properties of glucose?
Glucose is a solid that is well soluble in water.
glucose,
ethanol,
water,
multi‑purpose indicator paper,
watch glass,
glass rod,
test tubes.
Determine the properties of glucose: state of aggregation, colour and odour.
Fill one test tube with water, and another one with ethanol. Test the solubility of glucose in these solvents.
Investigate the reaction of the glucose solution.
The following results were obtained in the experiment:
state of aggregation | colour | odour | water solubility | ethanol solubility | change of colour of the all‑purpose indicator paper |
solid | white | odourless | dissolves well | does not dissolve | no change |
Before conducting experiment formulate research question and hypothesis.

Film dostępny na portalu epodreczniki.pl
Film pokazuje eksperyment. Problem badawczy: Jakie właściwości ma glukoza? Testing properties of glucose. Hipoteza: Glukoza jest substancją stałą, dobrze rozpuszczalną w wodzie. Będziesz potrzebować: glukozę, glucose, zlewki z wodą, beakers with water, probówki, test tubes, stojak na probówki, test tube stand, pipetę, pipette, szczypce do probówek, test tube clamp, probówkę z niebieskim roztworem cooper (dwa) sulfate, Ce u es o cztery solution, probówkę z bezbarwnym roztworem sodium hydroxide, en a o ha solution, palnik laboratoryjny, torch. Za pomocą pipety do probówki wprowadzamy niewielką ilość niebieskiego roztworu siarczanu sześć miedzi dwa, następnie wodorotlenku sodu. Chwytamy probówkę z powstałą mieszaniną roztworów szczypcami i umieszczamy w zlewce wypełnionej wodą. Zlewkę umieszczamy nad palnikiem. W wyniku ogrzania zawartość probówki zmienia kolor z niebieskiego na czarny. Probówkę odstawiamy na stojak. Do zlewki z wodą dodajemy szczyptę glukozy i mieszamy roztwór glucose solution. Za pomocą pipety do probówki wprowadzamy niewielką ilość niebieskiego roztworu siarczanu sześć miedzi dwa, następnie wodorotlenku sodu oraz roztworu glukozy. Chwytamy probówkę z powstałą mieszaniną szczypcami i umieszczamy w zlewce wypełnionej wodą. Zlewkę umieszczamy nad palnikiem. W wyniku ogrzania zawartość probówki zmienia kolor z niebieskiego na pomarańczowy. Probówkę odstawiamy na stojak. Probówka z pomarańczowym roztworem oznaczona jest jako test właściwy, proper test. Probówka z roztworem czarnym oznaczona jest jako próbka kontrolna, control sample.
Does glucose react with freshly precipitated copper(II) hydroxide?
The reaction of glucose with copper(II) hydroxide produces a characteristic colour.
aqueous solution of glucose,
copper(II) sulphate,
sodium hydroxide solution,
beaker,
water,
burner,
tripod,
test tube.
Add a few cubic centimeters of the sodium hydroxide solution to the solution of copper(II) sulphate.
The resulting blue gelatinous sediment is copper(II) hydroxide.
Heat the mixture in a beaker with hot water.
Observe the changes that occur.
What reactions occurred during the experiment?
The reaction of copper(II) sulphate with the sodium hydroxide solution produces copper(II) hydroxide.
As a result of heating, copper(II) hydroxide is decomposed into copper(II) oxide and water.
Glucose reacts with copper(II) oxide.
This reaction is called Trommer's testTrommer's test. Glucose has reducing properties.
Fructose
The second most commonly known simple sugar is fructosefructose. Its molecular formula is the same as the formula of glucose , but differs from it in terms of structure.
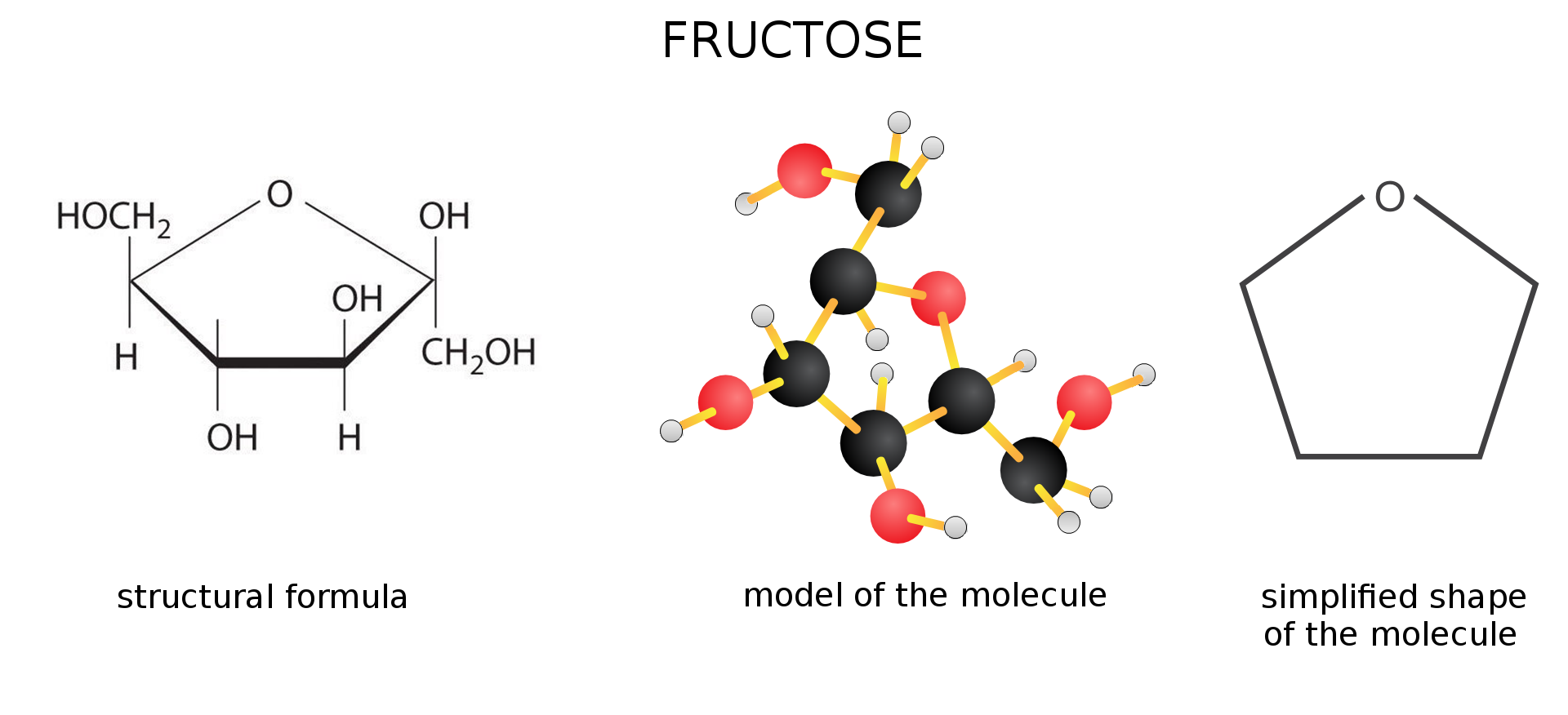
Fructose is found, among others, in fruit and honey. It is the sweetest and the most soluble sugar in water. It is used as a sweetener for people with diabetes.

What are the properties of fructose?
Fructose is a solid that is well soluble in water.
fructose,
ethanol,
water,
multi‑purpose indicator paper,
watch glass,
glass rod,
test tubes.
Determine the properties of fructose: state of aggregation, colour and odour.
Fill one test tube with water, and another one with ethanol. Test the solubility of fructose in these solvents.
Investigate the reaction of the fructose solution.
The following results were obtained in the experiment:
state of aggregation | colour | odour | water solubility | ethanol solubility | change of colour of the all‑purpose indicator paper |
solid | white | odourless | dissolves well | dissolves | no change |
Before conducting experiment formulate research question and hypothesis.
Does fructose give a positive result to the Tollens test?
During the positive test of Tollens, metallic silver is formed, depositing in the form of a mirror coating on the test tube.
aqueous solution of fructose,
silver nitrate ,
potassium hydroxide solution,
5% ammonia solution ,
beaker with hot water,
pipette,
test tube rack,
test tubes.
Add a few cubic centimeters of the sodium silver nitrate to the test tube and then add solution of potassium hydroxide.
Add a few drops of ammonia water to the resulting sediment until the sediment is dissolved.
Add a few drops of the fructose solution.
Place the tube in a beaker with hot water.
Observe the changes that occur.
The Tollens test or the silver mirror test is a chemical reaction used to detect aldehydes. Ketones give a negative test result, with the exception of ketoses, such as fructose. During the positive Tollens test, a metallic silver is formed, depositing in the form of a mirror coating on the surface of the tube.
For the Tollens test, a Tollens reagent is used, i.e. a solution containing diamminesilver(I) ions . The Tollens reagent is obtained by adding ammonia water to the silver nitrate solution. In the first stage, a brown silver oxide precipitate:
The precipitate is reconstituted with an excess of ammonia:
Both glucose and fructose belong to the reducing sugars that give a positive test of Tollens and Trommer:
in the case of glucose, the aldehyde group is oxidized to the carboxyl group and gluconic acid is formed,
in the case of fructose, which contains a ketone group, a positive result indicates that the fructose undergoes transformation (isomerization) in the alkaline environment to form epimers: D‑glucose and D‑mannose, these molecules contain reducing aldehyde groups, hence the positive tests .
How can you distinguish glucose from fructose?
Look at the structural formula of both monosaccharides and perform the experiment:
aqueous solution of glucose,
aqueous solution of fructose,
sodium hydrogen carbonate ,
bromine water,
pipette,
test tube rack,
test tubes.
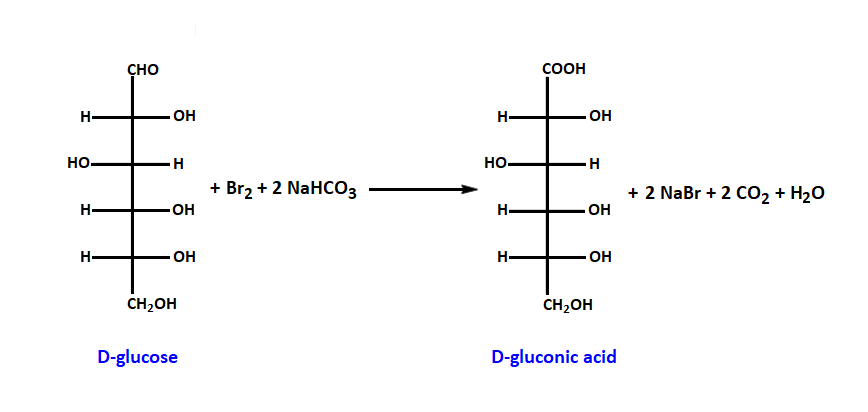
Add to the test tube with a solution of glucose, a solution of sodium bicarbonate and then a few drops of bromine water.
Add to the test tube with a solution of fructose, a solution of sodium bicarbonate and then a few drops of bromine water.
Observe the changes that occur.
Glucose and fructose have identical molecular formulas, but a different arrangement of atoms in the molecule. In a fructose molecule, oxygen is combined with a double bond with carbon occurring within the chain and not with the final carbon, as is the case in glucose.
The different arrangement of atoms in the glucose and fructose molecule causes both sugars to have different chemical properties. Fructose is, for example, much sweeter. To distinguish glucose from fructose, bromine water should be added in the presence of sodium hydrogen carbonate. Bromine water will decolorize in the glucose solution.
The product / products of the photosynthesis process is / are:
- carbon dioxide and water.
- glucose and oxygen.
- only glucose.
- only oxygen.
Select the reagent you will use to detect the presence of glucose and indicate the expected effects of the experiment.
- copper(II) hydroxide; a brick red precipitate forms
- nitric acid; a brick red precipitate forms
- copper(II) hydroxide; a black precipitate forms
- nitric acid; a black precipitate forms
Conclusion
Sugars, also called saccharides, are compounds composed of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms.
Sugars are divided into simple and complex ones.
Simple sugars include, among others, glucose and fructose. These compounds have the same molecular formula – , but they differ in terms of structure.
Glucose is a white crystalline substance which dissolves well in water. Its aqueous solution has a neutral reaction.
Glucose is the product of the photosynthesis process.
The reaction of glucose with copper(II) hydroxide, under the influence of temperature, results in the formation of brick‑red sediment. This is a indicative reaction for glucose.
Keywords
glucose, fructose, carbohydrates, sugars, molecular formula, simple sugar, complex sugar
Glossary
cukry (sacharydy) – związki chemiczne zbudowane z atomów węgla, wodoru i tlenu; dzielimy je na proste i złożone
glukoza – cukier prosty o wzorze sumarycznym ; produkt fotosyntezy; jest substancją stałą o słodkim smaku; dobrze rozpuszcza się w wodzie
fruktoza – cukier prosty o wzorze sumarycznym ; ma podobne właściwości do glukozy, ale jest od niej słodsza
próba Trommera – reakcja rozpoznawcza dla glukozy; reakcja z wodorotlenkiem miedzi(II), która zachodzi pod wpływem temperatury; w wyniku tej reakcji powstaje ceglastoczerwony osad