Causes and significance of genetic variation
Sexual reproduction is the cause of genetic variation;
some diseases are the result of errors that arise in the DNA.
explain what it causes and significance of genetic variation
Children are similar to their parents. Siblings also have many common features. In addition to the similarities, each member of the family has individual characteristics that do not appear among his relatives. When all human populations are observed, it can be seen that within some of them people are more similar to each other than in others. For example, the ethnic Swedes are very homogeneous. A population much more diverse than the Swedish population is, for example, the population of the United States of America, which was formed by the Native Americans and emigrants from all continents. This diversity of traits within the population and, more broadly, the species – is called genetic variabilitygenetic variability. Therefore, we will say that the variability in the population of Swedes is smaller than in the population of Americans.
There are several reasons why even closely related organisms show genetic variation, that is, they differ from each other by some features. These are:
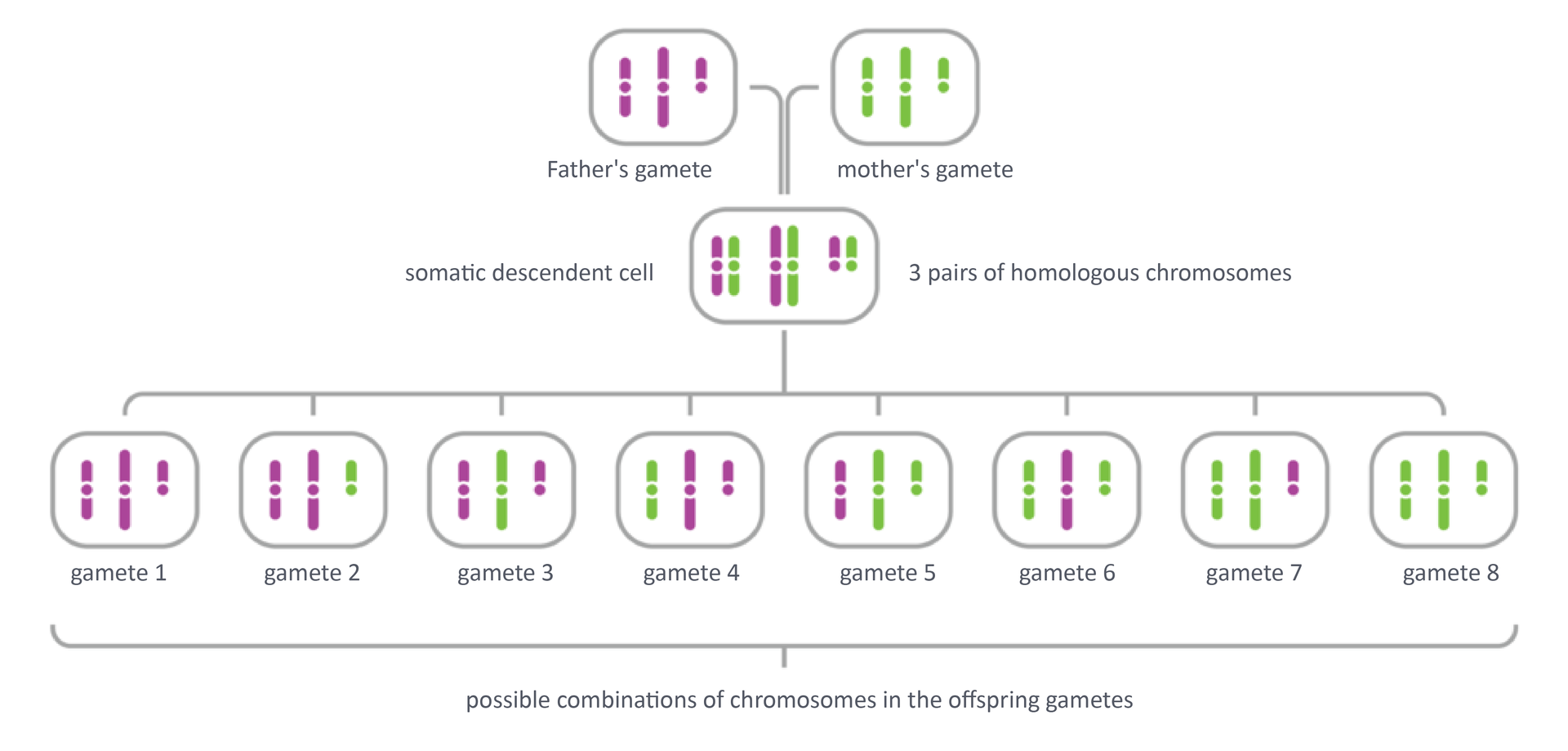
independent spread of chromosomes to gametes; take into account only three pairs of chromosomes; during the meiotic division, there are 4 gametes, but there are 8 possible combinations of allocation of only 3 chromosomes; in the case of people who have 23 pairs of chromosomes, theoretically every man and every woman can produce more than 8 million types of gametes;
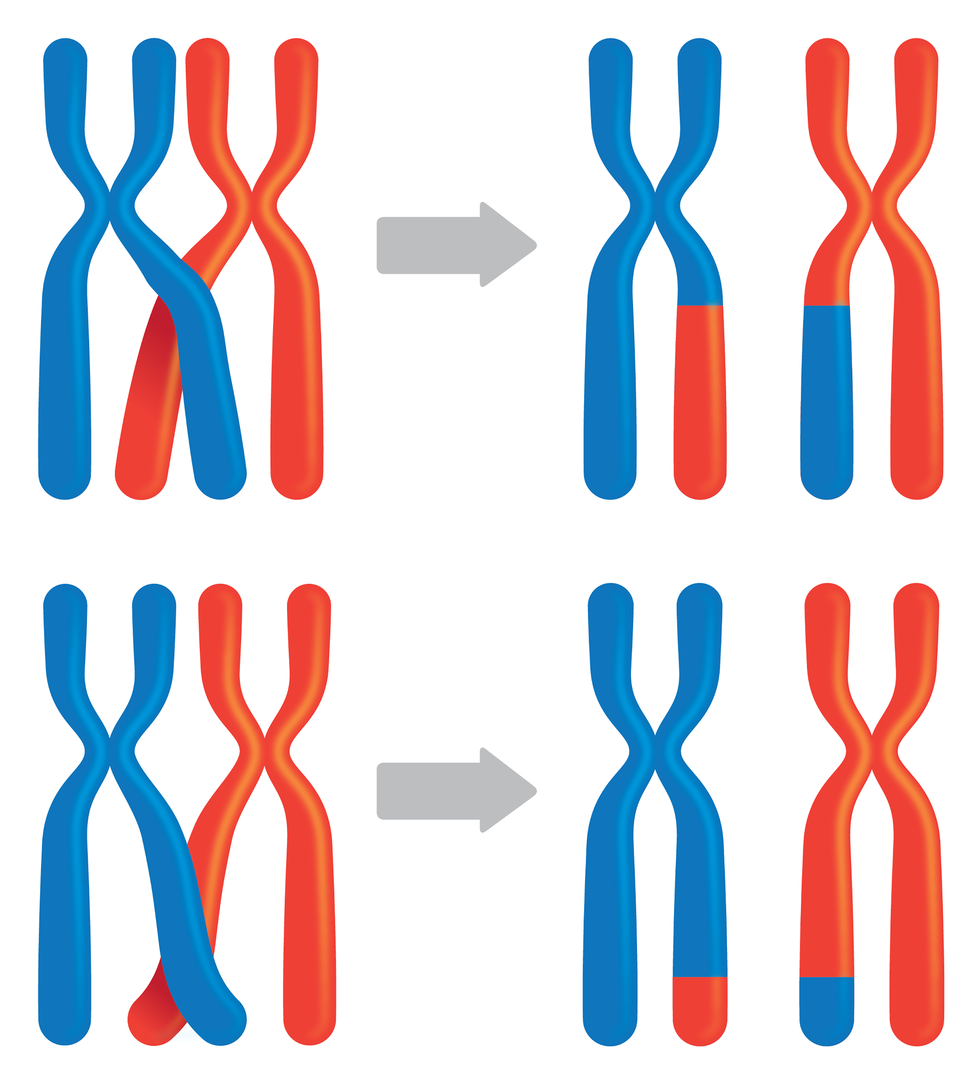
genetic recombinationgenetic recombination, taking place during the meiotic division; it is based on the fact that homologous chromosomes separeiting into the gametes, which within the pairs exchanged genetic material among themselves, so they differ from the chromosomes of the previous generation; such a process of exchanging genetic material occurs with each meiotic division;
random combination of gametes is an extra factor of genetic variability, causing that a couple of parents can have offspring with different genotypes;
mutationsmutations occurring in the sex cells.
Features subject to genetic variation are inherited. Due to variability, the individuals forming the species differ from each other. Because individuals have different characteristics, the chance that some of these individuals will survive the changing environmental conditions is greater than if all individuals were the same. Individuals better adapted to the new conditions give their offspring traits that allowed them to survive. Therefore, despite the death of individual individuals, the species still exists.
Choose two options from the ones suggested below to create a real sentence. The existence of genetic variation within one species means that:
- all individuals of this species have identical genotypes
- each individual of this species has a unique genotype
- the differences between individuals, the species adapts better to changing environmental conditions.
- the similarities between individual individuals, the species adapts better to stable environmental conditions.
Why are the features of organisms living in a given environment changing as a result of environmental changes?
- Because the individuals best suited to the new conditions have the most offspring, which in turn can pass their traits.
- Because the individuals best suited to the new conditions reach many times larger body sizes than other individuals of this species.
- Because the change in environmental conditions increases the frequency of genetic recombination between chromosomes.
- Because the change in environmental conditions forces new breeding strategies on the least-favored individuals to new conditions.
Summary
The source of genetic variability is the process of gamete formation, random merging with each other and mutations.
Keywords
genetic variation, random joining of gametes, chromosomes
Glossary
mutacja – nagła, trwała zmiana w informacji genetycznej organizmu, polegająca na zmianie struktury lub ilości materiału genetycznego
mutacja chromosomowa – jeden z typów mutacji; zmiana struktury lub liczby chromosomów, wywołująca dziedziczną zmianę cech organizmu
mutacja genowa – jeden z typów mutacji; polega na zmianie sekwencji nukleotydów w DNA, co może powodować powstanie nowych alleli genów
zmienność genetyczna – naturalne różnice w sekwencji DNA, występujące u osobników danego gatunku, będące wynikiem rozmnażania płciowego i mutacji