The Constitution of the Republic of Poland
A constitution is a set of fundamental principles to which a state is governed.
The constitutional principles can be formulated in very different ways - as they were in various constitutions in the world throughout history.
The Constitution of the Republic of Poland was adopted on 2 April, 1997.
You will be able to explain the universal values that were the most important for the creators of the Polish Constitution.
You will be able to describe the process of adoption of the Constitution of the Republic of Poland.
You will know the structure of the Constitution.
You will be able to explain the most important constitutional principles and discuss, why they are important in democratic Poland.
The Constitution of the Republic of PolandPreamble
Having regard for the existence and future of our Homeland,
Which recovered, in 1989, the possibility of a sovereign and democratic determination of its fate,
We, the Polish Nation - all citizens of the Republic,
Both those who believe in God as the source of truth, justice, good and beauty,
As well as those not sharing such faith but respecting those universal values as arising from other sources,
Equal in rights and obligations towards the common good – Poland,
Beholden toBeholden to our ancestors for their labours, their strugglestruggle for independence achieved at great sacrifice, for our culture rooted inrooted in the Christian heritageheritage of the Nation and in universal human values,
RecallingRecalling the best traditions of the First and the Second Republic, Obliged to bequeathto bequeath to future generations all that is valuable from our over one thousand years' heritage,
Bound in community with our compatriotscompatriots dispersed throughout the world,
Aware ofAware of the need for cooperation with all countries for the good of the Human Family,
Mindful of the bitterbitter experiences of the times when fundamental freedoms and human rights were violated in our Homeland,
Desiring to guarantee the rights of the citizens for all time, and to ensure diligencediligence and efficiency in the work of public bodies,
Recognizing our responsibility before God or our own consciences,
Hereby establish this Constitution of the Republic of Poland as the basic law for the State, based on respect for freedom and justice, cooperation between the public powers, social dialogue as well as on the principle of subsidiaritysubsidiarity in the strengthening the powers of citizens and their communities.
We call upon all those who will apply this Constitution for the good of the Third Republic to do so paying respect to the inherent dignity of the person, his or her right to freedom, the obligation of solidarity with others, and respect for these principles as the unshakeableunshakeable foundation of the Republic of Poland.Source: The Constitution of the Republic of Poland.
Preamble – an introductory and expressionaryexpressionary statement in a document (e.g. a constitution or an international agreement) that explains the document’s purpose and underlying philosophy.
The work on adoption of a democratic constitution in Poland lasted for many years. They started already in 1989. The lack of agreement between the main political forces on the most important constitutional principles that were to apply in democratic Poland, extendedextended the waiting time for the basic law.
Do you know the procedure of adopting the Constitution of the Republic of Poland of 1997? Arrange the stages into the correct order.
-
Constitution draft delivery:
– Constitutional Commission of the National Assembly
– A group of 56 members of the National Assembly
– The President of the Republic of Poland
– A group of 500 thousand Polish citizens - The Constitution’s entry into force
- Signing of the Constitution by the President of the Republic of Poland
- Approval of the Constitution in a nationwide referendum
- Adoption of the Constitution by a ⅔ majority vote in the National Assembly
Analyze the infographics showing the results of the constitutional referendum and solve the exercise below.
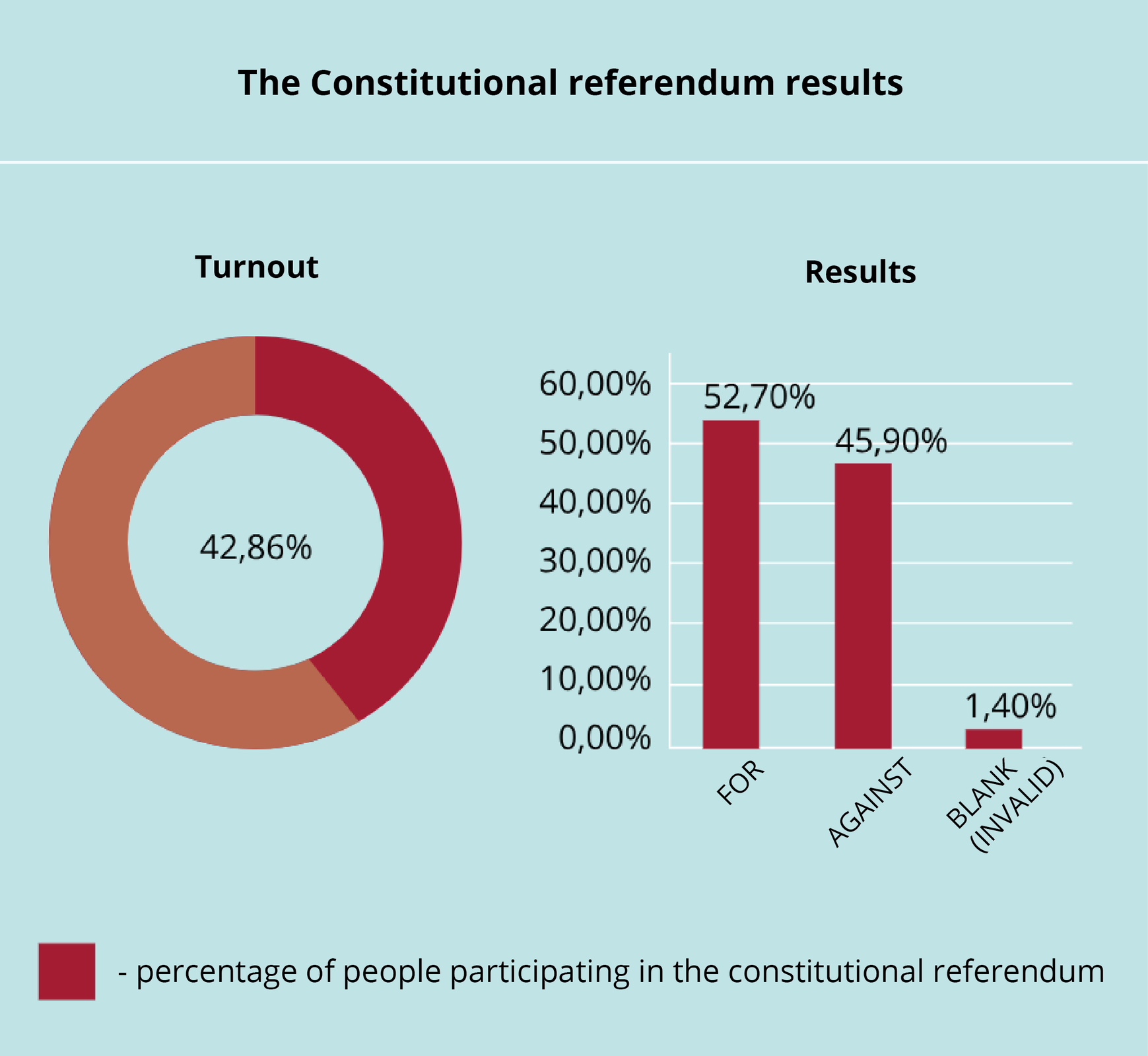
Decide whether the statements about the results of the constitutional referendum are true or false.
| Statement | True | False |
| Over half of the people entitled to vote took part in the constitutional referendum. | □ | □ |
| Over half of the people taking part in the referendum voted in favour of the new Constitution. | □ | □ |
| Over half of Polish citizens expressed their support for the new Constitution. | □ | □ |
The Constitution of the Republic of Poland, like other documents of this kind currently in force in democratic states, containscontains provisions on the basic principles of the functioning of the state, the manner of appointment, competences and responsibilities of public authorities, civil rights and freedoms and means of their protection. It consists of a preamble and 243 articles, included in XIII chapters.
Constitutional principles are legal norms of particular importance in the constitution. They express fundamental constitutional values.
Popular sovereignty
Constitution of the Republic of PolandArticle 4
Supreme power in the Republic of Poland shall be vested in the Nation.
The Nation shall exercise such power directly or through their representatives.
Source: Constitution of the Republic of Poland.
The principle of popular sovereignty indicates the entityentity to which the authority in the state belongs – according to the Constitution, it belongs to “the Nation”, to all Polish citizens.
Separation of powers
The Constitution of the Republic of PolandArticle 10
The system of government of the Republic of Poland shall be based on the separation of and balance between the legislative, executive and judicial powers.
Legislative power shall be vested in the Sejm and the Senate, executive power shall be vested in the President of the Republic of Poland and the Council of Ministers, and the judicial power shall be vested in courts and tribunals.
Source: The Constitution of the Republic of Poland.
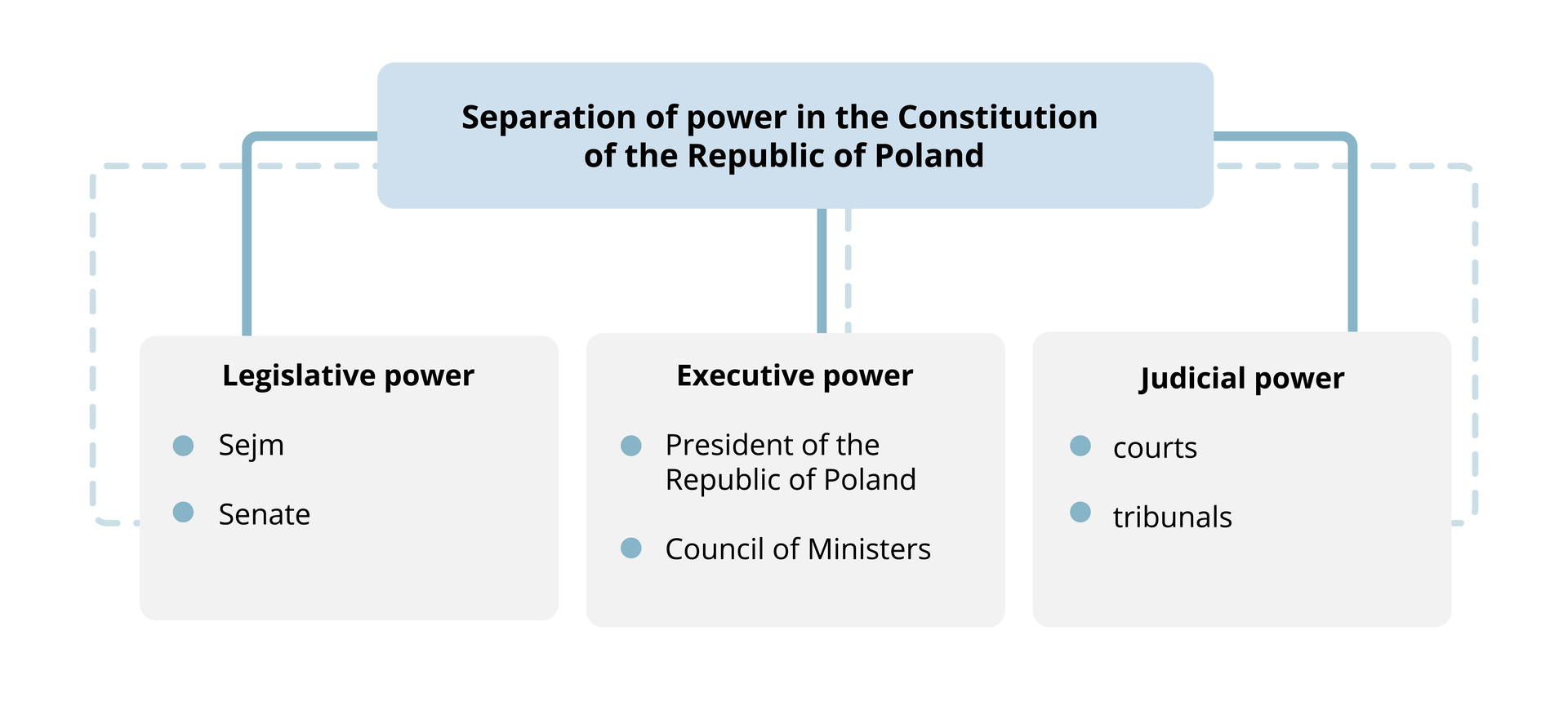
The rule of the tripartite divisiontripartite division of state power derives fromderives from the concept of EnlightenmentEnlightenment thinkers John Locke and Charles de Montesquieu. This principle indicates the need for the existence of separate, yet mutually controlling and balancing, three types of power: legislative, executive and judiciary.
Rule of law
The Constitution of the Republic of PolandArticle 7
The organs of public authority shall function on the basis of, and within the limits of, the law.Article 8
The Constitution shall be the supreme law of the Republic of Poland.
The provisionsprovisions of the Constitution shall apply directly, unless the Constitution provides otherwise.
Source: The Constitution of the Republic of Poland.
The principle of the rule of law means that all authorities in Poland and state institutions should act in accordance with the applicable law. The Constitution is the supreme legal force in the state.
Political pluralism
The Constitution of the Republic of PolandArticle 11
The Republic of Poland shall ensure freedom for the creation and functioning of political parties. Political parties shall be founded on the principle of voluntarinessvoluntariness and upon the equality of Polish citizens, and their purpose shall be to influence the formulation of the policy of the State by democratic means.
Source: The Constitution of the Republic of Poland.
The essence of this principle is the freedom of establishment and operation of political parties. A political party in Poland, in order to conduct its legal activity, must only be entered in the records of political parties kept by the regional court in Warsaw.
Listen to the abstract recording to review the material and new vocabulary. Then do the vocabulary exercise. Match the pairs: English and Polish words.
rzetelność, gorzki, oświecenie, zatwierdzenie, dziedzictwo, walka, rozsiany, rodacy
| struggle | |
| heritage | |
| compatriots | |
| dispersed | |
| bitter | |
| diligence | |
| approval | |
| enlightenment |
Keywords
constitution, preamble, Constitutional Commission of the National Assembly, popular sovereignty, rule of law, separation of powers, political pluralism
Glossary
wdzięczny
walka
zakorzeniony
dziedzictwo
nawiązać
przekazać
rodacy
rozsiany
świadomy
gorzki
rzetelność
pomocniczość
niewzruszony
o symbolicznym znaczeniu
rozciągać, wydłużać
zatwierdzenie
wejście w życie
zawierać
przepis
podmiot
trójpodział
wynikać, czerpać z
oświecenie
dobrowolność