The origins of the Second World War
why and where the crisis of democracy had occurred;
what policy Japan pursued in the 1920s and 1930s.;
why the civil war in Spain broke out and how important it was;
the importance of the arms race for the situation in Europe;
what influence Adolf Hitler and the Nazis regime had on German politics;
what the Molotov‑Ribbentrop Pact was and why it was important for the outbreak of the war.
The 1919 Versailles Conference did not take into account all the forces in Europe. This became one of the causes of a conflict, the first signs of which date back to the early 1930s. The crisis of democracy, authoritarianauthoritarian regimes and the development of totalitarianismtotalitarianism became one of the threats to security in Europe and the entire world. The Third Reich's rejection of the Versailles arrangements turned out to be a threat to peace as well, along with the development of Japanese militarismmilitarism which sought to solve economic problems by way of conquests.
Aggressive politics in the Far East and the development of countries in Europe naturally brought Japan, Italy and Germany closer together. They formed alliances against Western countries (the Pact of Steel) and activities of communistcommunist parties (Anti‑Comintern PactAnti‑Comintern Pact).
The outbreak of the conflict in Spain (1936) was not without significance for the aggravation of the situation in Europe. The civil war between the left‑wing forces of the Popular Front and the right‑wing Falanga, led by General Francisco Franco, became a testing ground for the German army. Particularly famous for its bloodshed in this war was the Condor Legionthe Condor Legion, whose actions showed the brutality aimed not only at the forces of the opponent, but also at the civilians.
The successes of fascist Italy in Africa and the German army in Spain, as well as the conquest of China by Japan, clearly showed that the arms race that had started in the early 1930s would inevitably have to end in a European conflict.
Familiarize yourself with the timeline and learn more about the origins of the Second World War. Which of the presented events were the most important and why?
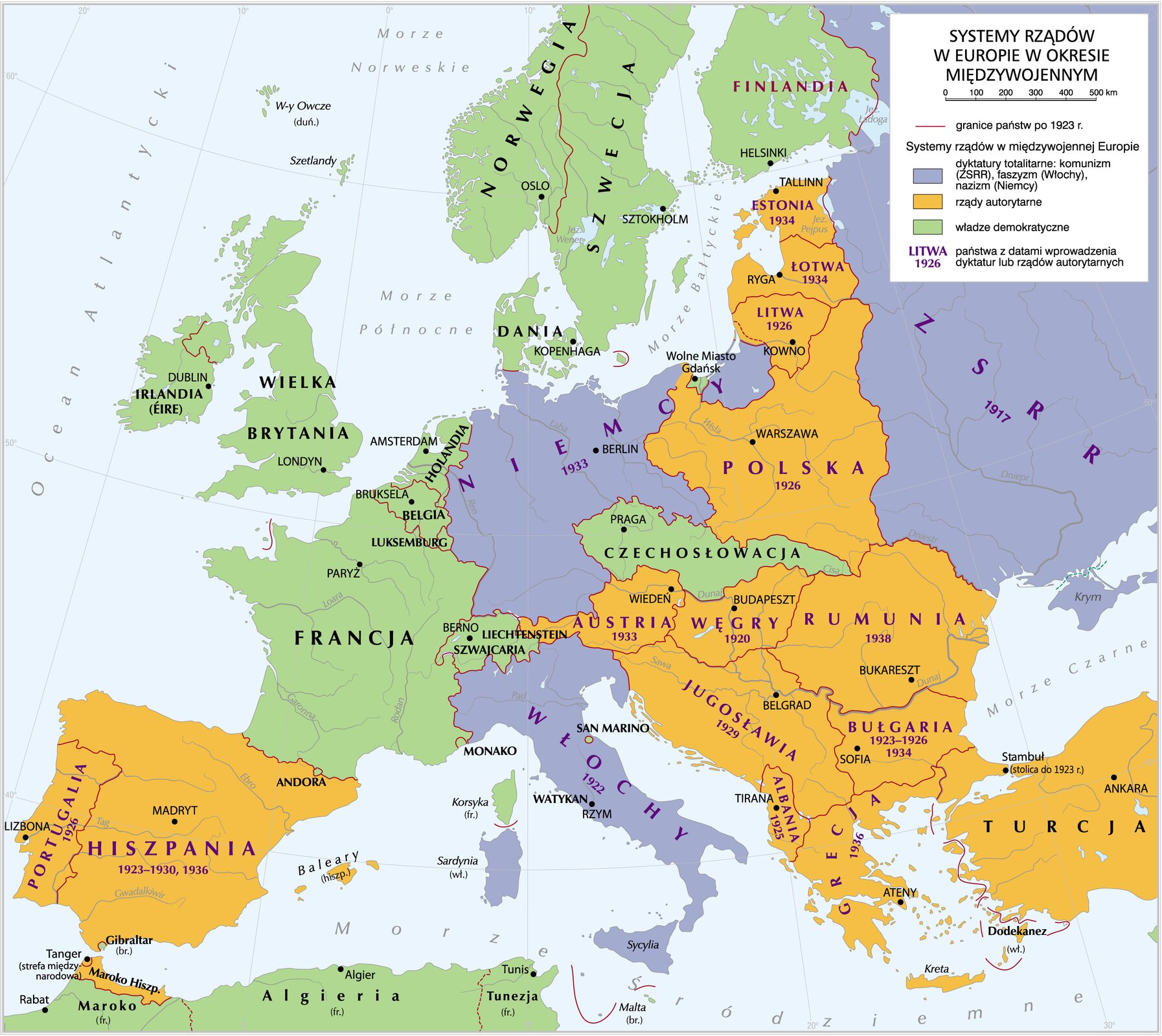
By looking at the map, match the states with their government systems.
The Soviet Union, Germany, Lithuania, Bulgaria, Albania, Latvia, Hungary, Ireland, Norway, Great Britain, France, Portugal, Romania, Switzerland, Turkey, Italy, Monaco, Denmark, Czechoslovakia, Austria, Luxembourg, Sweden, Liechtenstein, Greece, Finland, Netherlands, San Marino, Poland, Estonia, Belgium, Yugoslavia, Spain
| Democratic states | |
|---|---|
| Authoritarian states | |
| Totalitarian states |
The League of Nations' reaction to the Japanese aggression against Manchuria...
- confirmed the powerlessness of the League of Nations in resolving international conflicts.
- proved Japan's compliance with international law.
- proved the effectiveness of actions taken by the League of Nations.
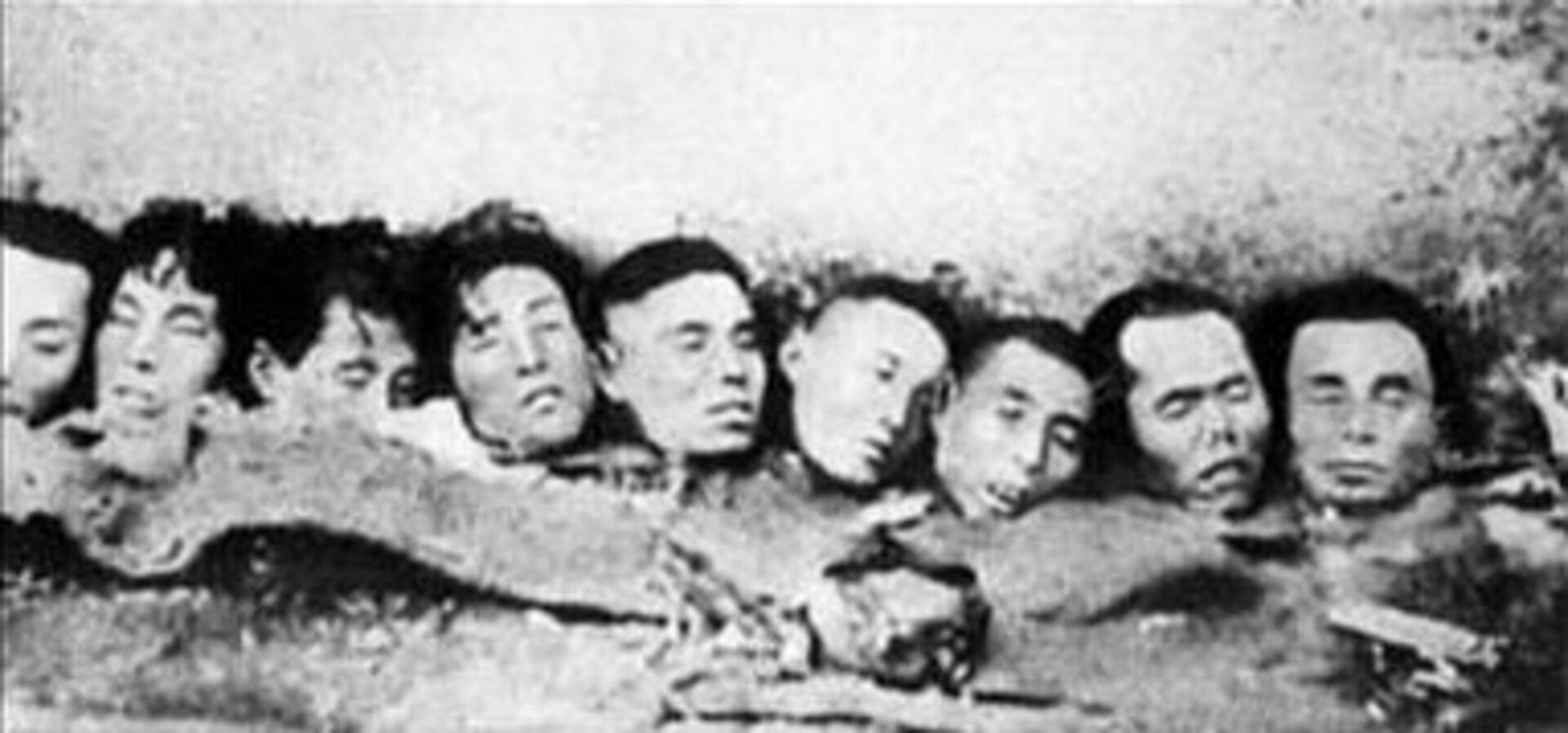

Which of the following two comments can be considered valid?
- The Japanese hoped that by acting this way, they would break the resistance of the Chinese people more quickly.
- People die in every war conflict.

The painting has become the symbol of...
- barbaric terror against civilians.
- the success of aviation.
- the military success of the Popular Front.
In what style was it made?
- cubism
- socialist realism
- Dadaism
With the use of what elements the painter tried to show the tragedy of war?
- colours
- the presence of animals
- a heap of people, buildings, objects, distorted bodies, open mouths (silent screams).
Which animal depicted in the painting "Guernica" symbolizes fascism?
- horse
- dove
- bull
Point out the term that can be used to characterise the Spanish system under general Franco's regime.
- authoritarian state
- monarchy
- parliamentary republic
Why couldn't the development of the army and in the field of arms take place in Germany after the First World War?
- Germans had no means for armaments.
- This was forbidden under the provisions of the Treaty of Versailles.
- The war had caused such a shock that the German government decided to liquidate the army and arms industry.
Analyze the data from the table and do the exercise.
State | National income (in billions of dollars) | Defence assigned revenue (in %) |
USA | 68 | 1,5 |
Great Britain | 22 | 5,7 |
France | 10 | 9,1 |
Germany | 17 | 23,5 |
Italy | 6 | 14,5 |
USSR | 19 | 26,4 |
Indicate the sentence that is false.
- France allocated the largest percent of national income to defence out of all countries included in the table.
- Income allocated to defence amounted to more than a quarter of national income in Japan and the USSR, and less than a quarter in Germany.
- Japan spent the least funds on armaments.
- The largest amount of national income was spent on armaments by the USA.
Match concepts with their definitions in pairs.
a system of government in which power is concentrated in the hands of an authoritative leader, who most often bases his rule on the army., achieving goals through warfare in combination with the fact that the military has a decisive influence on politics, a political system of government combined with an ideology proclaiming total subordination of the individual and full control of the society by the state., ideology that proclaims the emergence of a single social class, the liquidation of private property and the need to distribute wealth evenly., national socialist, racist, anti-democratic, anti-Semitic and anti-communist ideology created and proclaimed by the NSDAP, a political and structural doctrine that emerged in Italy, proclaiming the cult of the state and social solidarity, opposing democracy, liberalism and political pluralism
| Totalitarianism | |
| Authoritarianism | |
| Militarism | |
| Fascism | |
| Nazism | |
| Communism |
Keywords
World War II, Japan, Manchuria, invasion, Far East
Glossary
Totalitaryzm – system rządów politycznych połączony z uzasadniającą jego istnienie ideologią, która głosi całkowite podporządkowanie jednostki i pełną kontrolę przez państwo społeczeństwa.
Autorytaryzm – system rządów, w którym władza skoncentrowana jest w ręku cieszącego się autorytetem przywódcy, najczęściej opierającego swoje rządy na wojsku. Decyzje są zatwierdzany przez kontrolowany przez władzę parlament. W odróżnieniu od totalitaryzmu, w państwa autorytarnych nie stosuje się terroru i kontroli na masową skalę.
Militaryzm – dążenie do realizacji celów na drodze działań wojennych, w której wojsko wywiera decydujący wpływ na politykę.
Wielki kryzys – największy kryzys gospodarczy w XX wieku. Rozpoczął się w USA w 1929 roku i trwał do 1933. Objął swym zasięgiem prawie cały świat.
Azja dla Azjatów – głoszone przez propagandę japońską hasło nieakceptowania obcokrajowców.
Pakt antykominternowski – układ z 25.11.1936 zawarty między Niemcami i Japonią, którego celem było zwalczanie działań partii komunistycznych.
Przestrzeń życiowa (Lebensraum) – nacjonalistyczna i rasistowska niemiecka koncepcja polityczna zakładająca i usprawiedliwiająca ekspansję terytorialną Niemiec dla zdobycia niezbędnej przestrzeni do życia.
Aneksja – zagarnięcie i przyłączenie, najczęściej siłą, przez jedno państwo części lub całości terytorium innego państwa. Dokonywana jest najczęściej w wyniku wygranej wojny.
Pakt Ribbentrop‑Mołotow – porozumienie zawarte między ZSRS i III Rzeszą 23 sierpnia 1939 r., jego tajny protokół przewidywał m.in. podział ziem polskich.
Faszyzm – doktryna polityczna i ustrojowa powstała na początku lat 20. XX we Włoszech. Głosiła kult państwa i solidaryzm społeczny, występując przeciwko demokracji, liberalizmowi i pluralizmowi politycznemu. Był ustrojem totalitarnym.
Nazizm – narodowy socjalizm, rasistowska, antydemokratyczna, antysemicka i antykomunistyczna ideologia stworzona i głoszona przez NSDAP – partię Adolfa Hitlera. Głosiła hasła wyższości rasy germańskiej nad innymi ludźmi.
Komunizm – ideologia głosząca powstanie jednej klasy społecznej, likwidację własności prywatnej i wspólny podział dóbr. Miała obalić istniejące ustroje polityczne i wprowadzić utopijny model państwa pozbawionego ucisku i wyzysku innych.
Ultimatum – żądanie wysunięte przez jedno państwo wobec drugiego wzywające do spełnienia określonych żądań pod groźbą wybuchu wojny lub innych sankcji. Stawiane jest przeważnie w sytuacji, gdy zawiodą inne formy dyplomatyczne.
Legion Condor – niemiecka jednostka wojskowa walcząca po stronie gen. Francisco Franco w wojnie domowej w Hiszpanii. Najbardziej znana jest z udziału w bombardowaniu Guerniki.
Caudillo – termin oznaczający przywódcę politycznego lub wojskowego używany przez dyktatora w Hiszpanii za czasów rządów gen. Francisco Franko.