The formation of galaxies and the evolution of stars
Powstawanie galaktyk i ewolucja gwiazd
the theory about the formation of galaxies and the evolution of stars,
to describe the theory about the formation of galaxies and the evolution of stars.
Before you start, do the following.
Remind the stages of the formation of the universe in the Big Bang theory.
The current state of knowledge does not allow for the formulation of an unambiguous theory explaining the formation of galaxies. Researchers assume that all galaxies were formed from a gas that uniformly filled the entire universe at the beginning of its existence. It consisted mainly of hydrogenhydrogen and heliumhelium, with a small admixture of light elements.
Over time, heterogeneity in the distribution of matter appeared, and its temperature decreased. In clouds with higher density of matter, so‑called protogalaxies, the first stars were created, referred to as the stars of the third population. They were large, massive stars, hundreds of times larger than our Sun. Their life time was relatively short, ended with a violent explosion, which resulted in further light elements remaining in the area of protogalaxies. The first generation of stars, according to modern hypotheses, was created around 200‑300 million years after the Big Bang.
ProtogalaxyProtogalaxy is a vast mass of gas in which the process of star formation began. It is the origin of the new galaxygalaxy.
Galaxies is large systems of stars, dustdust and gas (interstellar matter), invisible dark matter and energy.
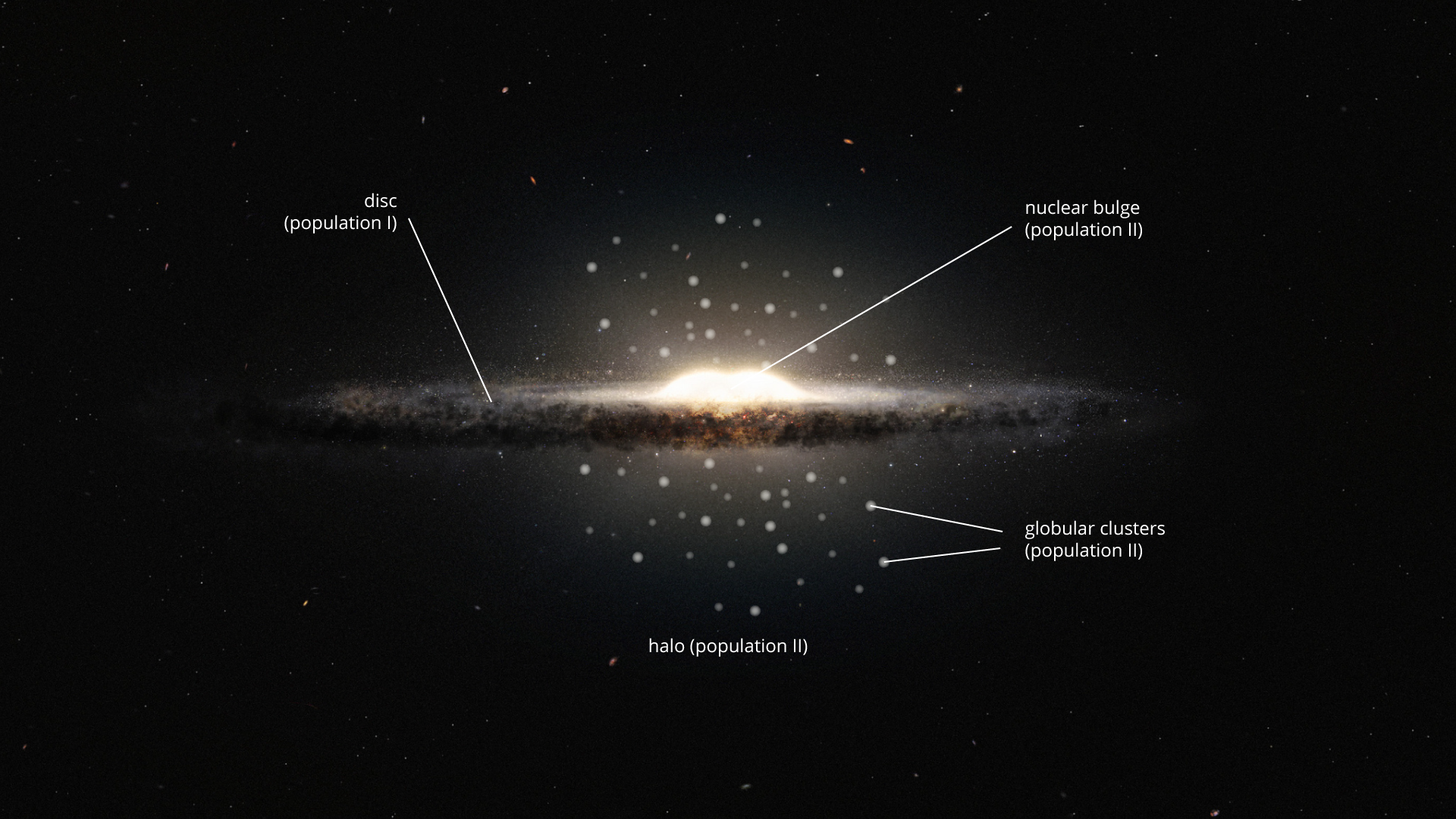
The gravitational force resulting from the enormous density of the cloud caused its collapsecollapse and temperature droptemperature drop. The movement of matter around the rotation axis caused the cloud to flatten and produce a characteristic disc and further attract gas and dustdust. Inside the disk, new stars were formed, and on the outskirts of the old cloud a halo of gas, dust and dark matter and old stars remained.
It is assumed that two factors decided whether spiral or elliptical galaxygalaxy was formed from the protogalaxyprotogalaxy.
Angular momentum - a protogalactic cloud with larger angular momentum moved faster and formed a spiral galaxy. In turn, the elliptical galaxy formed from a slower moving cloud.
The temperature drop - very dense protogalaxies cooled faster, and all the matter contained in them was used to create stars. Hence, there is no disk in the elliptical galaxies. On the other hand, in less dense clouds the temperature dropped slower, which allowed to create a disk with gas and dustdust.
Stars due to their age are divided into so‑called stellarstellar populations.
Population III stars - these are the oldest stars mentioned above. They are not observed, but there are hypotheses that suggest that some of them may have survived to our times. These stars should have a very poor composition with elements other than heliumhelium and hydrogenhydrogen.
Population II stars - are old stars from times when the concentration of light elements in protogalactic clouds was very low. They are found mainly in the centres of galaxies and in the surrounding halo, and form globular clusters. They move in orbits at different angles to the plane of the galaxygalaxy.
Population I stars - these are relatively young stars. In their composition there are much more metallic elements, from 2 to 4%. They are observed in the areas of galactic disks, in the arms of galaxies and in open clusters. Stars of I population usually move in regular, elliptical orbits around the centre of the galaxy and in its plane.
The universe is constantly evolving, and the process of creating stars is not over.
Some stars end their lives, and others just come into being.
It is assumed that the stars are created in the clouds of interstellar matter. The gas, consisting of hydrogenhydrogen and heliumhelium and a small admixture of other elements at the level of 1%, undergoescondensation. Such condensation may be caused by an electromagnetic wave coming from the explosion of another star. The newly created cloud begins to collapse due to gravity, and such collapsecollapse is accompanied by an increase in temperature. The gas‑dust cloud rotates around its own axis and forms a disc with a central spherical part called the protostar. The process of protostar creation can last for hundreds of thousands of years.
When the temperature inside the protostar reaches a sufficiently high value, it allows thermonuclear processes to take place. The energy released in these processes inhibits the gravitational collapsecollapse of the star, because the pressure inside the star resulting from the energy flow from the centre to the outer parts of the star is enough to prevent it from collapsing under its own weight.
The radiation emitted by it causes the star to glow.
When the nuclear reactions occur slower and slower due to the lack of elements for synthesis, the star begins to collapsecollapse. The dying star expands in a giant or supergiant phase. The star eventually explodes and becomes a planetary nebulanebula or supernova. Finally, it turns into a white dwarf, a neutron star or becomes a black hole. The final fate of the star depends on its initial mass.
Remember
The current state of knowledge does not allow for the formulation of an unambiguous theory explaining the formation of galaxies.
Exercises
Determine which sentences are true.
- The first stars formed from the condensations of the original matter at the early stage of the development of the Universe.
- The stars are mainly made of hydrogen and helium.
- The stars we currently observe belong to the population II and III.
- The stars shine, emitting energy produced in the thermonuclear fusion process.
Search in available sources, what evolutionary process astronomers predict in the case of the Sun.
Describe the process of star formation in English.
Indicate which pairs of expressions or words are translated correctly.
- protogalaktyka - protogalaxy
- galaktyka - galaxy
- zapadnięcie się - collapse
- spadek temperatury - temperature drop
- pył - hydrogen
- hel - dust
- protogalaktyka
- temperature drop
- galaktyka
- galaxy
- collapse
- nebula
- zapadnięcie się
- mgławica
- spadek temperatury
- protogalaxy
Glossary
zapadnięcie się
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: collapse
pył
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: dust
galaktyka
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: galaxy
hel
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: helium
wodór
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: hydrogen
mgławica
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: nebula
protogalaktyka
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: protogalaxy
gwiezdny
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: stellar
spadek temperatury
Nagranie dostępne na portalu epodreczniki.pl
wymowa w języku angielskim: temperature drop
Keywords
collapsecollapse
galaxygalaxy
nebulanebula
protogalaxyprotogalaxy
temperature droptemperature drop