Geographic grid and cartographic grids
that the Earth has been covered with a geographic grid which enables to assign specific coordinates to each point on its surface;
that geographers developed an abundance of map types depicting the entire Earth or its sections;
that the map scale presents a degree of reduction of the image of the Earth’s surface to present it on a plane.
system of meridians and parallels on the globe and on the map;
distinguish a geographic grid from a cartographic grid;
name the types of cartographic grids and give their examples.
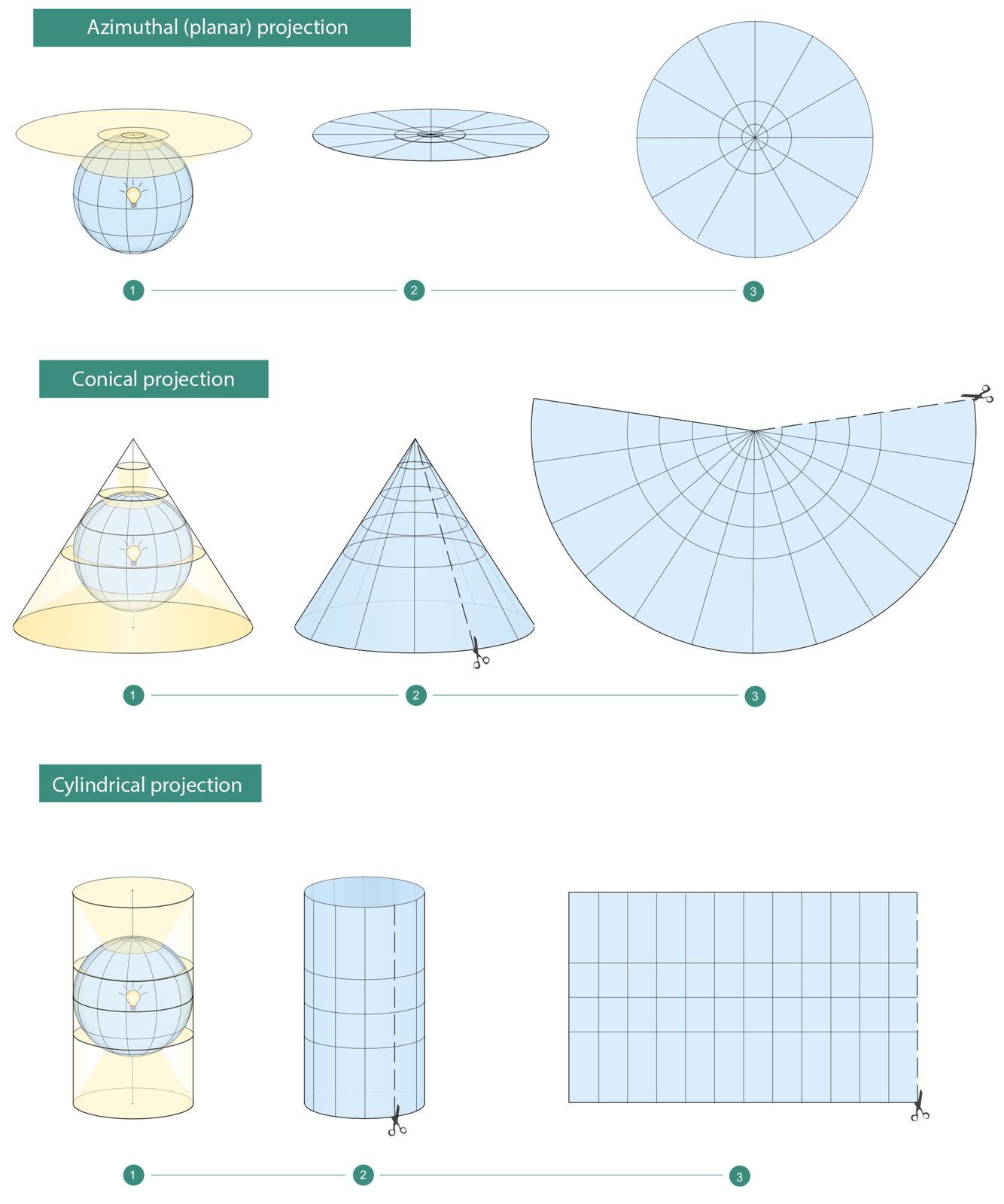
The geographic grid is a conventional system of meridians and parallels on surface of the Earth or its model, called the globe, and the cartographic grid is its equivalent on a plane. One of primary tasks of cartography, in scientific terms, was inventing a way to attain seemingly impossible – to “flatten” a spherical surface (or its section) so that it would precisely adhere to a plane. Cartographers developed mathematical and optical methods aiming to tackle this task. These methods are called map projectionsmap projections.
The easiest way to comprehend what map projection is involves imagining a glass sphere with plotted geographic grid and a glowing light bulb inside. Such arrangement would make meridians and parallels cast their shadows on a flat surface, wrapped around such sphere, thus creating a cartographic grid.
There are three basic categories of map projections, with regard to a way of application of a plane to project on:
azimuthal projection;
conic projection;
cylindrical projection;
conventional projection (a modification of the aforementioned types according to determined mathematical assumptions in order to achieve faithful projection of angles, surface or distance).
Employing knowledge gained during the lessons, do the following exercises.
Match the description to the mapping.
Azimuthal mapping, Conical mapping, Cylindrical mapping
| In these mappings, the parallels form arcs of concentric circles, while meridians are straight lines that radiate from a single point. | |
| Most often, meridians and parallels are mapped as straight lines intersecting at an angle of 90° | |
| Parallels are usually mapped as concentric circles or arcs, while meridians - as straight lines or arcs connecting at the pole. |
Show the mapping visible on the map.
- azimuthal mapping
- cylindrical mapping
- conical mapping

Fill in gaps in the following sentences.
Earth, Conic, grid, aerial, map projection, medium, cartographical, Planar
The system of meridians and parallels (circles of latitude) on a globe (i.e. model of the ............................) is called geographical ............................. When it is projected on a plane, it forms a ............................ grid. The manner the cartographical grid is presented on a plane is called ............................. ............................ grid gives the most faithful representation of polar areas. Cylindrical grid is used in marine and ............................ transport. ............................ grid gives the most faithful representation of continents and countries. It is used for areas located at ............................ latitudes.
Keywords
map projection, map, cartographic grid
Glossary
odwzorowanie kartograficzne – matematyczny sposób przedstawiania powierzchni kuli na płaszczyźnie
znaki kartograficzne – umowne znaki używane na mapach i przeznaczone do przedstawiania zjawisk, zdarzeń i obiektów; symbole mogą mieć charakter sygnatur punktowych, liniowych lub powierzchniowych
siatka azymutalna ( płaszczyznowa) – powstaje z rzutowania siatki geograficznej na płaszczyznę styczną do globusa na biegunie. Najbardziej wierne przedstawia obszary okołobiegunowe
siatka stożkowa – powstaje z rzutowania siatki geograficznej na powierzchnię boczną stożka stycznego do globusa w położeniu normalnym( oś stożka pokrywa się z osią globusa).Siatka ta przedstawia najwierniej obszary kontynentów i państw. Używana jest dla obszarów średniej szerokości geograficznej
siatka walcowa – powstaje przez rzutowanie siatki geograficznej na powierzchnię boczną walca stycznego do globusa wzdłuż równika. Siatka ma zastosowanie w komunikacji morskiej i lotniczej. Używana jest dla obszarów okołorównikowych