Evidence of evolution
Earth is inhabited by millions of species.
A species is a group of specimens similar to each other like children to parents, related to each other, with similar environment requirements, that can breed with each other freely and have fertile offspring.
Species are different from each other but share some similarities.
to explain that living organisms are evolving;
to provide pieces of direct and indirect evidence of evolution.
EvolutionEvolution is the process by which organisms gradually change their body structure and behaviour, which results in creating new species.
Direct evidence of evolution
Evidence is provided directly by fossilsfossils and transitional forms.
Fossils are created when deceased organisms are not eaten by scavengers or decomposed, but end up in oxygen‑deprived conditions, covered up by a layer of sand or clay. Such conditions enable organic tissue, both soft and hard, to absorb mineral salts over time, such as calcium carbonate. Usually, only the hardest parts of organisms are fossilised—bones, teeth, horns, shells, carapace, eggshells and tree trunks. It is a much less common occurrence with soft tissue.
Another type of fossil are imprints of leaves, tree bark, feathers and animal tracks, which were pressed against a soft surface first, and then filled with rock that fast solidified. Based on animal track imprints, we can learn what size were the specimens of various species and how they moved.

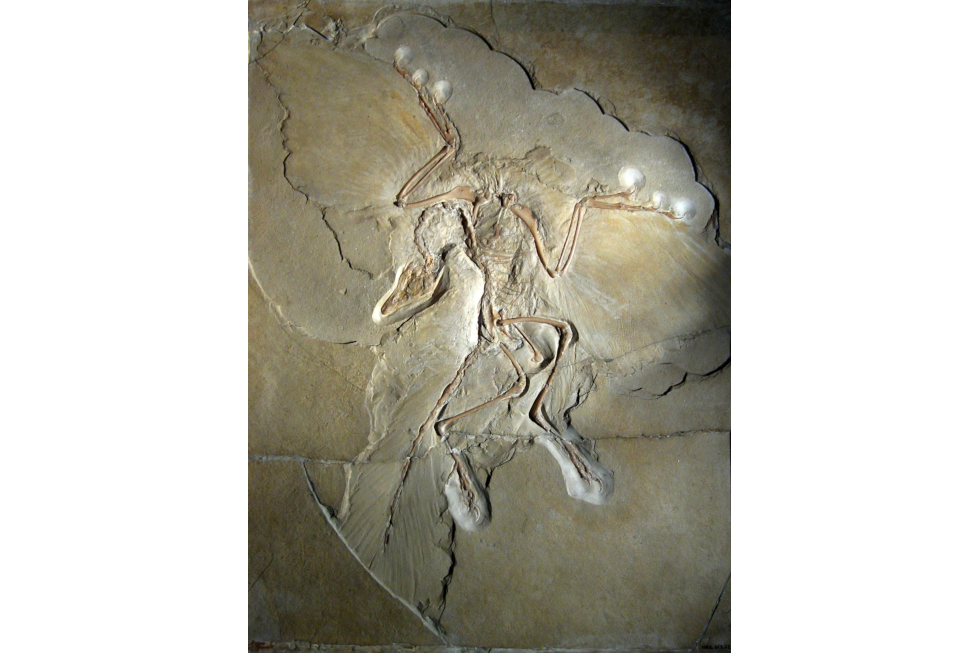
Transitional forms are fossils of species that combine traits of old and new forms. One of such fossils, which prove that reptiles were the ancestors of birds, is the Archaeopteryx. It combines reptile and bird traits.

An animal that combines traits of reptiles and mammals is the currently existing platypus, which is considered a living fossil: a contemporary organism that whose body structure is very similar to that of its long‑extinct ancestors.
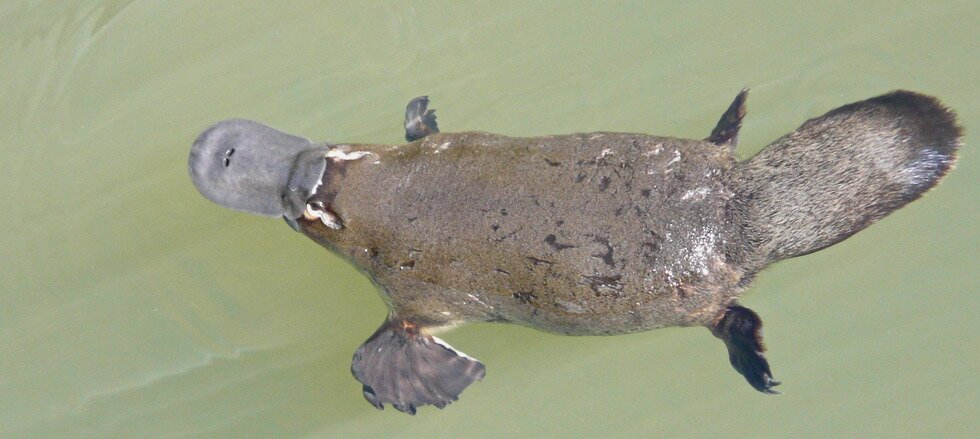

The evolution of living fossils has been a very slow process, which is why they have remained almost unchanged. Their appearance and behaviour is a great source of knowledge about similar organisms that lived in the past. Other living fossils include horsetail, scorpions, and horseshoe crabs.
Indirect evidence of evolution
The most convincing proof for a relationship and between organisms and a common ancestor is the cell structure, a similar chemical composition, and similar basic cellular processes. The building blocks of all living organisms include proteins, fats, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids. The genetic code is universal, which allows for the assumption that all species originate from common ancestors that used this code. By comparing nucleotide sequences in DNA of various species, it is highly possible to determine their relationship; the fewer differences, the closer the organisms are related.
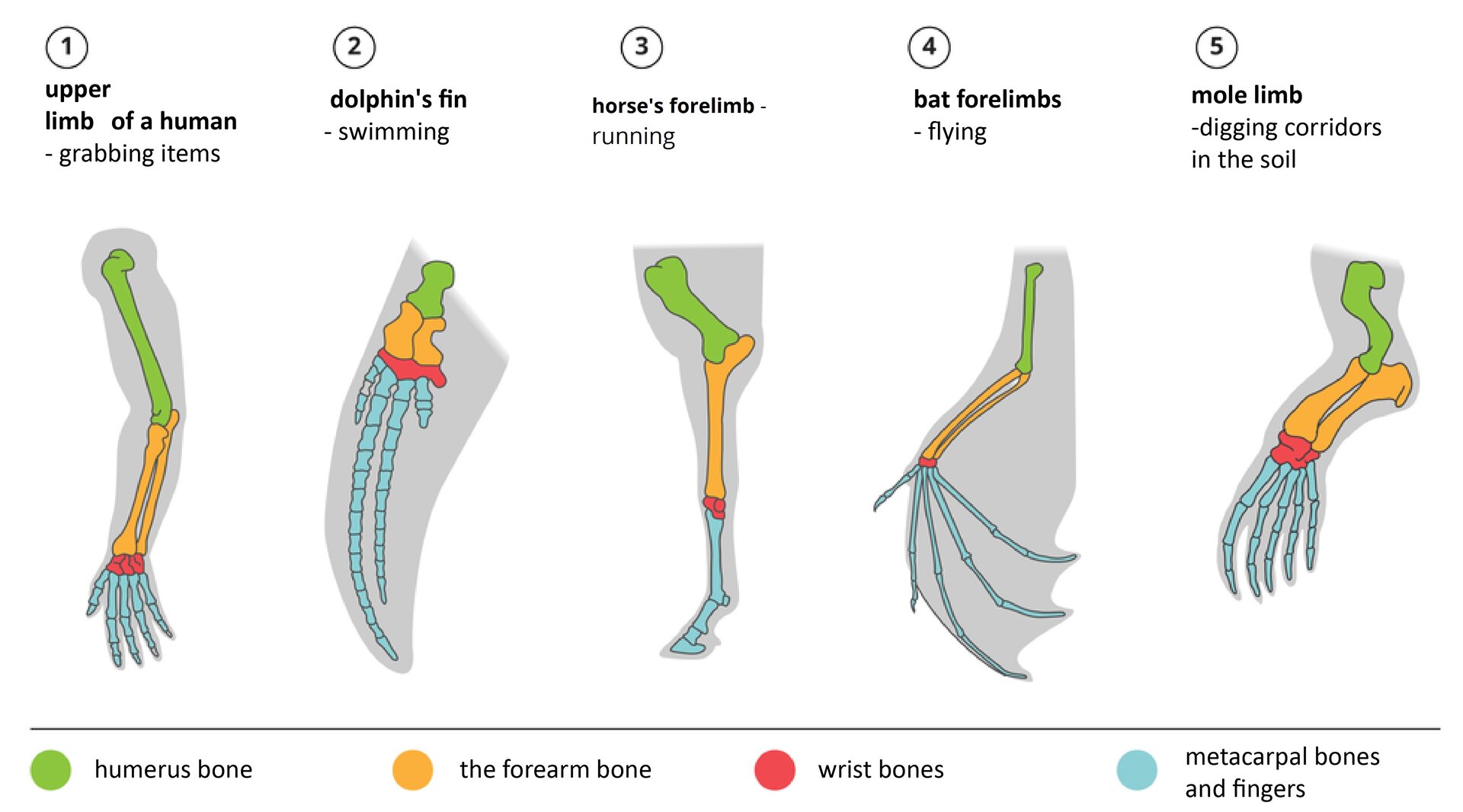
Based on Comparing of anatomical structure traits of currently living organisms, conclusions can be drawn that indirectly confirm the common descent of analysed species.
Based on the structure of a bacteria, plant and animal cell, explain the notion of a common structural plan.
Another piece of proof for interspecies relationship are vestigial organsvestigial organs, remnants of organs that used to be perform important bodily functions in ancestors, but are now nigh or entirely useless. Human vestigial organs include the appendix, coccyx, and muscles for ear wiggling.
What is biological evolution? Select the correct answer.
- a process by which environmental factors affect both the phenotype and behaviour of specimens of a given population
- a process of slow and gradual changes in living organisms whereby organisms change their forms
- a process by which offspring of the same parents differs genetically from each other
- a process of slow and gradual transformation of the natural environment due to human activities
Match each term with its definition.
preserved remains of an organism that lived in the past, a contemporary organism similar to its long-extinct ancestors in its body structure, a fossil of a species that combines traits of old and new forms
| fossil | |
| transitional form | |
| living fossil |
Select all statements that pertain to paleontology.
- it is a subfield of organic chemistry
- it is concerned with analysing remains preserved in rock
- helps reconstruct what a given organism might have looked like
- analyses the structure of extinct organisms
Move each element to the appropriate group.
small organisms trapped in amber, similar structure and chemical composition of cells of different organisms, similar cellular processes in different organisms, similar structure of organs of common origin, living fossils, similar embryos of different animals, transitional forms, fossilised remains of plants or animals, plant or animal imprints, existence of vestigial organs in some organisms, universal genetic code, prehistoric organisms preserved in permafrost
| direct evidence of biological evolution | |
|---|---|
| indirect evidence of biological evolution |
Summary
Direct evidence of evolution include fossils and transitional forms.
Comparative anatomical studies of currently living organisms provide indirect evidence of evolution.
Using a Polish language dictionary, define the meaning of evolution and explain what biological evolution is.
Keywords
evolution, fossils, vestigial organs
Glossary
ewolucja biologiczna – proces stopniowych i powolnych zmian świata żywego, w wyniku których jedne formy organizmów przekształcają się w inne
narządy szczątkowe – narządy o niewielkim znaczeniu dla organizmów; są ewolucyjnymi pozostałościami struktur, które były wykorzystywane przez ich przodków
skamieniałość – zachowane fragmenty organizmów, które żyły w przeszłości